Artificial intelligence (AI) in recent years has been a disruptive force in reshaping various industries. Manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive are revolutionized through enhanced decision-making, task automation, and personalized experiences. Supported by state-led strategies, vast data reserves, and a dynamic tech ecosystem, China is rapidly scaling AI adoption domestically while advancing its technological ambitions on the global stage. As competition for AI dominance accelerates, understanding China’s unique approach—blending policy, innovation, and industry focus specialization—offers critical insights into the future of technology, geopolitics, and societal progress.
Download our 10 Mistakes Chinese Brands Make when Going Abroad report

State-led policies to bolster artificial intelligence in China
China’s global AI leadership is fueled by a top-down approach, with national strategies driving rapid adoption. Central to this goal are two critical initiatives: the Made in China 2025 (MIC 2025) industrial policy and the New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan (新一代人工智能发展规划 2017). Together, these frameworks aim to reduce dependence on foreign AI technologies and position China as a self-sufficient AI leader.
AI in Chinese manufacturing

Unlike Western AI development, which often prioritizes general-purpose models, China focuses on industry-tailored AI solutions, maximizing efficiency in key sectors like manufacturing. China’s rise as a global AI leader can be attributed to a distinct strategy: sector-specific AI models to drive efficiency and productivity. This approach is prevalent in manufacturing, where AI integration has driven transformative advancements. A prime example is COSMOPlat, an industrial IoT platform developed by Haier Group. It redefines production through mass customization by embedding user experience across the entire product lifecycle—from design and production to sales.
At the core of COSMOPlat lies Tianzhi, a proprietary AI platform leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning, and IoT integration. Trained on 562 industrial datasets and 3 million high-quality data entries, Tianzhi achieves 96% reasoning accuracy, enabling breakthroughs like predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization. Its AI-driven fault detection reduces equipment repair time by 75%, while intelligent maintenance solutions reduce workforce training costs dramatically. Where traditional training for technicians took a year and RMB 150,000, AI cuts this to RMB 15,000—a 90% reduction—accelerating skill development and operational agility.
Beyond manufacturing, COSMOPlat’s adaptability spans industries from automotive to agriculture, empowering companies to embrace data-driven precision. Enabling customer participation in design and production bridges factory automation with consumer-centric innovation. These advancements position artificial intelligence in China as a cornerstone of the smart manufacturing revolution, blending scalable cost savings with cutting-edge efficiency, a strategy for global AI leadership.
China’s AI-driven EV dominance

Over the past decade, China has emerged as the leader in the global electric vehicle (EV) market, reaching 13 million EV sales in 2024. This number reflects not only government support but also China’s strategic integration of artificial intelligence across its automotive ecosystem. From AI-optimized factories to self-driving systems, China’s EVs are setting new benchmarks for innovation and scalability.
AI manufacturing: Efficiency at scale
As mentioned earlier, China’s EV production dominance is rooted in AI-driven manufacturing. Smart factories leverage machine learning for precision assembly, predictive maintenance, and defect detection, enabling automakers like BYD and NIO to scale rapidly while maintaining cost competitiveness. Tesla’s Shanghai Gigafactory, regarded as the most advanced and productive manufacturing hub, relies heavily on AI-powered robots and China’s AI ecosystem to sustain its massive output. Chinese automakers like BYD and NIO, alongside Tesla’s Shanghai Gigafactory, have propelled China to 62% of global EV sales, a figure unimaginable a decade ago.
AI features in Chinese EVs
Chinese EVs are also redefining in-car experiences through AI. IM Motors (SAIC), for instance, uses cabin sensors to detect driver fatigue and stress, adjusting settings like temperature, music, or even scent diffusion to enhance alertness. These innovations align with consumer demands: 72% prioritize advanced safety and comfort features, 75% of new EVs will include AI smart cockpits by 2025, and 47% now use cars as workspaces or leisure hubs. Transforming the driving experience by integrating AI through a combination of user-centric innovation and highlighting Chinese AI’s competitive advantage.

Autonomous driving: Leading the global race
China is rapidly advancing in AI-powered autonomous driving, with brands like XPeng and Li Auto offering Level 3 self-driving capabilities. This aligns with consumer optimism; 56.9% embrace autonomous tech for safety and convenience. By 2030, 56% of new vehicles in China will feature Level 3+ autonomy. This positions China as a global leader in intelligent transportation. For businesses trying to enter the Chinese EV market, leveraging AI-driven manufacturing, integrating advanced in-car technologies, and exploring partnerships with local tech giants will be key to gaining a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving and highly dynamic industry.
AI in the everyday life of a Chinese consumer
Artificial intelligence in China has also evolved into an essential companion, seamlessly blending into daily routines, social interactions, and emotional well-being. Over 95% of consumers use AI for work or study, with 55.4% integrating it into daily life beyond productivity tasks. A majority, 55.6%, leverage AI to streamline tasks, while 39% harness it for creative usages like generating scripts or digital art. Emotionally and socially, AI’s role is just as transformative: 39% rely on it for entertainment, and 32.8% use it to navigate social platforms. Virtual influencers like Luo Tianyi exemplify this shift. Her AI-powered livestreams attracted 2.7 million viewers and nearly 2 million interactive engagements. This illustrates how AI is reshaping human social connections in the digital age.
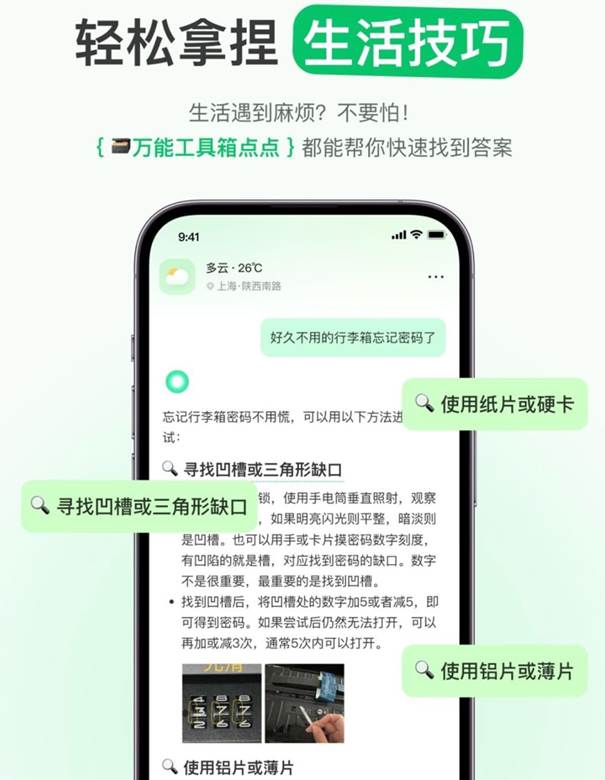
Central to this integration are innovations such as Xiaohongshu’s DianDian. It is an AI lifestyle app powered by the DeepSeek-R1 model and 300+ million user-generated posts. DianDian cuts search times by 40%, offering local recommendations for food, travel, and logistics. It was trusted by 87% of users, showcasing China consumers’ broader AI confidence. The app’s 200,000+ iOS downloads in three months underscore its demand and utility. For businesses, Xiaohongshu’s DianDian highlights the power of AI to shape consumer expectations and behavior.
Revolutionizing retail: The AI-powered transformation
Building upon social media, artificial intelligence in China has also found its place in the e-commerce and livestreaming space. With 52% of merchants adopting at least one AI tool. Half of these businesses deploy AI chatbots to handle customer inquiries. Moreover, one-third leverage AI for content generation, such as crafting product descriptions or social media posts.
Platforms like JD.com exemplify AI’s operational impact: its demand forecasting system achieves 93% prediction accuracy, covering 95% of products during the 2023 618 shopping festival. This technology enabled Nestlé to boost forecast precision from 45% to 85% while halving delivery times, illustrating AI’s capacity to optimize supply chains and enhance efficiency.

Livestreaming, meanwhile, is being transformed by digital avatars and AI hosts. China is home to 993,000 companies specializing in virtual influencers, a sector that generated RMB 333 billion in 2023 and will reach RMB 640 billion in 2025. During the 2024 618 festival, AI-powered hosts attracted over 100 million views. The virtual hosts facilitated 5 million+ interactions, demonstrating their ability to engage audiences at scale. These avatars not only host 24/7 sales streams but also personalize interactions using real-time sentiment analysis, driving higher conversion rates. An example is Alibaba’s hyperrealistic virtual host DongDong, which debuted during the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics. Hosting live streams, interacting and talking with audiences, and showcasing how AI is bridging the gap between human and machine while redefining retail entertainment. This innovation highlights China’s advancement in AI-driven commerce by positioning these avatars as brand ambassadors, salespeople, and influencers all in one.
The rising star of artificial intelligence in China: DeepSeek

DeepSeek, a rising star in China’s AI sector, embodies the speed and technical creativity driving the country’s tech ambitions. Founded in mid-2023 by Liang Wenfeng—a finance veteran with a background in AI-driven trading—the startup has quickly risen to fame by proving that cutting-edge AI doesn’t require limitless budgets or unrestricted access to advanced hardware.
At the heart of DeepSeek’s success is its ability to optimize resources. While U.S. firms pour billions into AI development, DeepSeek trained its large language models (LLMs) for just $6 million. Engineers achieved this by rethinking traditional methods. Rather than chasing the latest chips, they maximized performance on NVIDIA’s H800 GPUs. Although these chips are slower than top-tier options, they are unaffected by U.S. export bans. The result is a system that delivers advanced reasoning at a fraction of the usual cost.
Furthermore, DeepSeek’s cost-efficient AI framework has led to rapid adoption across industries. More than 20 automakers are integrating their technology for in-car assistants. Beyond automotive, gaming giant Tencent utilizes DeepSeek to enhance engagement through real-time interactions. By proving that high-impact AI can emerge from lean budgets and adaptive engineering, DeepSeek showcases artificial intelligence in China’s ability to turn limitations into opportunities and industry growth. DeepSeek’s success demonstrates how Chinese innovators are turning geopolitical constraints into competitive advantages.
Artificial intelligence in China: A success story
- Strategic, state-led policies and national initiatives such as the Made in China 2025 plan and the AI Development Plan have created a strong foundation for AI growth in China, aligning government support with private sector innovation.
- China’s position as a global AI leader is built on real-world impact. AI was deeply embedded into various sectors and backed by tangible results.
- AI in China’s success is heavily attributed to customized and sector-specific solutions, from COSMOPlat’s smart manufacturing platforms to AI-enhanced electric vehicles and intelligent retail systems that prioritize efficiency, scale, and consumer experience.
- Startups like DeepSeek exemplify China’s ability to innovate under constraint, proving that lean systems and optimization can compete globally without access to premium hardware or massive capital.
- AI is increasingly interconnected with everyday life, with tools like virtual influencers, personalized in-car assistants, and AI lifestyle apps transforming how Chinese consumers live, socialize, and make decisions.