The Chinese market keeps booming through 2021 Q2 fueled by vaccine rollouts and improved macroeconomic indicators. The target GDP growth rate in 2021 was set to be at least 6% at the National People’s Congress held in March. Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q2 will continue to prove resilient to challenging global economic conditions.
Brief Review of Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q1
According to PWC’s Global IPO Watch Q1 2021, there were 116 IPO deals in Mainland China with total proceeds of US$12.6 billion, 27 IPO deals in Hongkong with total proceeds of US$10.8 billion, and 20 Chinese IPO deals in the US with total proceeds of US$4.37 billion. The largest global IPO in 2021 Q1 in terms of proceeds raised was Kuaishou Technology listed on Hongkong Exchange, which raised US$6.2 billion. For more info, see our article on Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q1.
Overall Outlook of Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q2
Global economy is recovering from the coronavirus pandemic and the stock markets are showing positive momentum. According to Black Rock’s stock market outlook for Q2, the second quarter is expected to bring greater economic re-awakening, underpinning the constructive outlook for the stock markets. April PMI in Mainland China exhibited significant improvement compared to prior months, indicating an expansion of business activity and overall confidence. Despite the trend that the US government will put more stringent oversight over foreign company listings and the tensions between the US and China, the sentiment over the outlook of the improved US economy will drive more Chinese companies go public in the US in 2021 Q2.
Six Chinese companies which will have IPOs in 2021 Q2
Energy Monster
Energy Monster, founded in 2017, is a power bank rental startup. It went public on the NASDAQ stock exchange on April 1st. Energy Monster is expected to be one of the youngest Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q2.
Energy Monster provides table-mounted and portable power banks placed in Points of Interest (POIs) operated by their location partners, such as entertainment venues, restaurants, shopping centers, hotels, transportation hubs, and public spaces. According to Energy Monster’s prospectus, it’s the largest mobile device charging service provider in China in terms of gross revenues in 2020, which accounts for 34.4% of the total market share. Through their mini-programs, users can rent portable power banks which can be returned after use at any location partner. As of December 31st, 2020, Energy Monster had a network of over 664,000 POIs covering more than 1,500 out of the 2,846 counties and county-level districts in China. It had approximately 149.1 million and 219.4 million cumulative registered users as of December 31st, 2019 and 2020, respectively.

Source: Energy Monster, the company’s position is clear as a mobile device charging company
Hello Chuxing
Hello Chuxing was founded in 2016 and started as a bike-sharing firm called Hello Bike. It is backed by fintech giant Ant Group and has filed for NASDAQ IPO on April 24th, making it one of the most anticipated Chinese IPOs in 2021 Q2. In addition to shared two-wheeler services, Hello Chuxing also added car-pooling and ride-hailing services in 2019 and 2020 respectively. It announced to sell intelligent electric bikes at a product launch held two weeks before submitting its prospectus, in which Hello Chuxing also released some other services that they are pilot testing, such as an in-store services marketplace, hotel reservations, mobile grocery stores, and online advertising services.
Hello Chuxing’s prospectus said it was the No. 1 shared two-wheeler provider in China in 2020 by the number of total rides and as of December 31st, 2020, Hello app was China’s third-largest local services platform by transaction volume and China’s most active local services platform by average transaction volume. However, the company has been unprofitable for the past three years.
See our report on the Ride Hailing Market in China.
Waterdrop Inc.
Waterdrop, founded in 2016, is an online insurance and medical crowdfunding platform backed by Tencent. Waterdrop debuted on the New York Stock Exchange on May 7th with the ticker code WDH. The company has established a huge social network that offers crowdfunded financial assistance to patients who cannot afford their medical expenses. So far, Waterdrop has served nearly 80 million users, 70% of whom are from smaller cities and towns.
Waterdrop said in its prospectus that it’s the largest independent third-party insurance platform in China in terms of life and health insurance first-year premiums, or FYP, distributed in 2020. Waterdrop has built a massive social network for raising awareness of insurance and ultimately providing insurance and healthcare service to consumers in China through its mutual aid platforms and insurance marketplace.
Soulgate Inc.
Soulgate Inc., founded in 2016, is well known for its online dating app, Soul. It filed for NASDAQ IPO on May 10th. Soul’s mission is to build a ‘soul’cial metaverse for young generations.
According to Soulgate’s prospectus, Soul App is a virtual social playground, where people can live in the moment, express themselves and draw inspiration from each other’s creativity. The features of Soul App are appearance-agnostic, interest-driven, decentralized, and gamified. In March 2021, Soul App was said to have 33.2 million MAUs and an average DAU of 9.1 million, representing a growth of 109.0% and 94.4% over the same period in 2020. It’s worth noting that 73.9% of the average DAUs were born in or after 1990, who are native to mobile internet and more sensitive to the loneliness technologies bring.
Soul App has experienced strong growth in revenues from value-added services such as virtual items and membership subscriptions but it also recorded net losses in the past three years.

Source: Soulgate Inc., Social platform for Chinese young generations
Eastroc Beverage (Group) Co., Ltd.
Eastroc Beverage (Group) Co., Ltd. founded in 1994, is a beverage company producing functional drinks, citrus lemon tea, citrus drinks, packaged drinking water, and other products. Eastroc Beverage (Group) Co., Ltd. issued the IPO Prospectus on April 16th and planned to be listed with RMB 1.49 billion fundraising on the Shanghai Stock Exchange.
Eastroc Beverage (Group) markets its products throughout China which occupies the second largest market share (15%) in China after Red Bull (57%). Energy drinks were the biggest contributor to Eastroc’s revenue, accounting for around 95% of the total revenue. Energy drinks are not traditional Chinese drink, but they are gaining popularity among youngsters. Eastroc Beverage still has hug growth potential in energy drinks market in China.
Ximalaya Inc.
Ximalaya, founded in 2012, is China’s largest online audio platform in terms of average MAUs, total mobile listening time, and total revenues in 2020, according to China Insights Consultancy. It filed with the SEC in May targeting to list on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker name of “XIMA”.
In the first quarter of 2021, its average monthly active users reached 250 million through mobile, IoT devices, and other platforms. Throughout 2020, users on Ximalaya spent a total of 26 billion hours listening to its audio offerings, including podcasts, audiobooks, audio drama shows, livestreaming, education programs, and audio comics.
Today, Ximalaya works together with well-known car manufacturers in the development of car entertainment systems for the Chinese market. And there are also cooperation agreements with manufacturers of intelligent household appliances, smart speakers, and smart wearables.
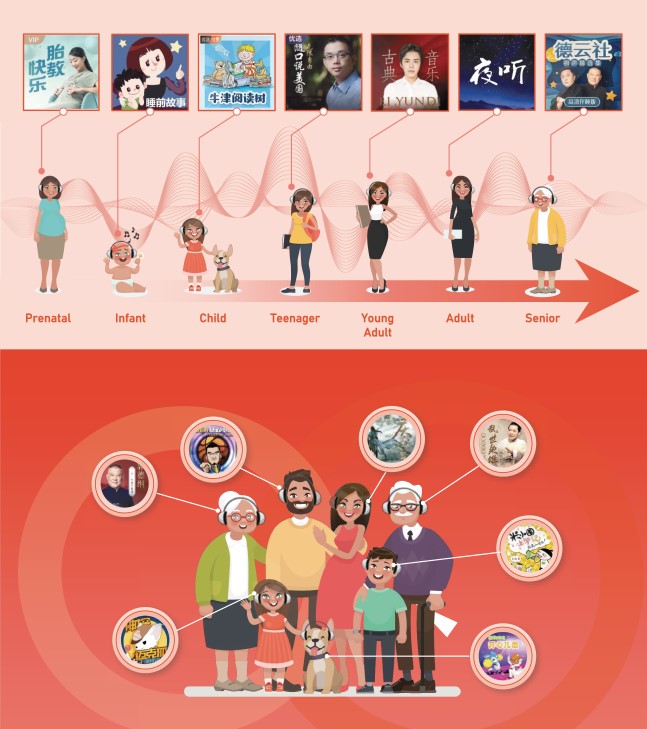
Source: Ximalaya Inc., Lifelong Nourishment to every generation within the family through audio entertainment
Why many Chinese companies listed in the U.S.
Chinese companies are listing in the U.S. at the fastest pace ever. According to U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission, as of May 5th, 2021, there were 248 Chinese companies listed on the U.S. exchanges (NASDAQ, New York Stock Exchange, and NYSE American) with a total market capitalization of $2.1 trillion.
According to FACSET, China is now the top 1 foreign IPO in the US. IPOs by China-based companies have shown greater interest in having a U.S. IPO starting in 2017.
Here are 5 reasons why Chinese companies go public in the U.S.
- Lower time cost. It is more lengthy and opaque to be listed in China than in the US as the entry permission in China is through torturous examinations while in the US is by speedy registration. The companies will save a mass of time cost especially in the period of rapid development that most needs financial support.
- More open policy. Listing in China’s domestic stock markets requires continuous profitability in the last three years, but in the United States, there is no such requirement, as long as it can be profitable in the future. China is also known for having incredibly strict listing requirements once companies are public, which has led some of China’s largest companies to list in the US.
- Higher valuations. The US has the two largest stock exchanges in the world by market cap. Listing in the US gives Chinese companies access to a larger number of investors, which can bring a higher valuation.
- More Liquidity. Listing in the world’s largest, most active, and deepest capital market helps Chinese companies increase their liquidity and raise more money if their shares are traded on US markets.
- Better credibility. Getting listed on NYSE and NASDAQ will make companies receive more media attention and create stronger brand awareness, bringing an increase in credibility and recognition.
Author: Nana Sun
Learn something new? Stay updated on the Chinese market by following our WeChat, scan the QR code below, or subscribe to our newsletter

See our 2021 report on China’s M&A market
Listen to over 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast