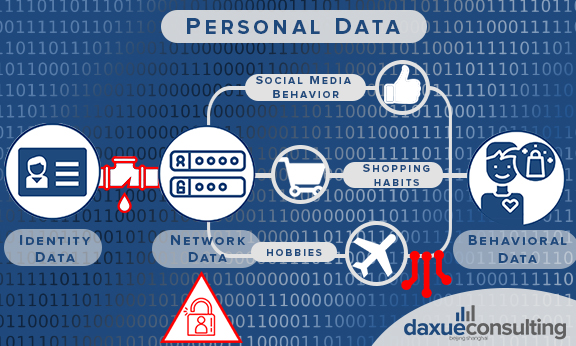
Personal data is becoming a new valuable resource in the 21st century that touches all aspects of society. Personal data can be divided into three categories: identity data, network data, and behavioral data.

Identity data includes basic information of a person, such as a name, gender, mobile phone number, and identity card number, which are mainly applied to authenticate users’ identities. For example, when logging in WeChat for the first time, users are required to register with a phone number as phone number can be traced to national ID in China.
Network data contains location data, log data, and device information, supporting fraud detection and account security.

When users browse websites or Apps, those behaviors are recorded to extract user behavioral habits, which generate behavioral data. Taking food orders as an example, when one customer orders spicy food at high frequency, the system will know his flavor preference and then recommend similar spicy food the next time he opens the menu.
These three types of personal data help companies create substantial business value, such as increasing sales through precision marketing, which is based on the analysis of user behavior data. However, some challenges in personal data usage and collection exist. The main ones are personal data leakage, people’s concern of privacy infringement, and data dispersion.
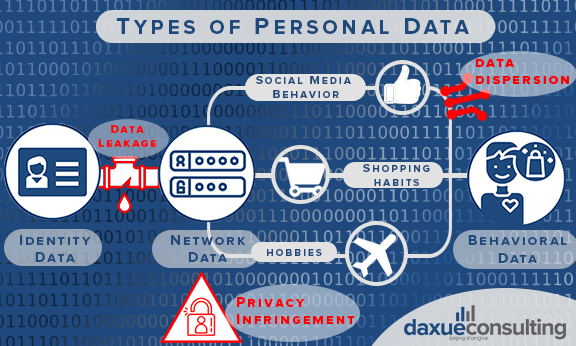
Personal data leakage has brought a great deal of damage
As online shopping has become prevalent in China, its consumers have boosted their online purchases. E-commerce and mobile payment involved a large amount of personal data, thus, they became the gathering place for personal data leakage. The typical case happened in JD, in 2016, where a data package counted 12G was revealed from JD to the black market, and those data came from a system security. The revealed data package included usernames, passwords, mobile phone numbers, identity card numbers, and other important personal data. What’s even worse is that hackers attempted to log into other websites with the personal data obtained from the black market, and some hackers even broke into financial accounts, stealing capital from these accounts. Numbers of personal data leakage incidents have also occurred in Alipay, Dangdang and yhd.com, as well as some online ordering platforms, such as Ctrip and 12306 (a Chinese railway ticket ordering platform), and those problems were caused by system security bugs or internal employees’ betrayal.
Personal data leakage can occur when people perform a transaction at the bank, purchase a pair of shoes on Taobao, register on a mobile phone app, or other trivial things in daily life. It has triggered attention among customers and caused massive damage. Based on the results of Chinese Internet Users’ Rights and Interests Protection Survey Report, 2016, published by Internet Society of China, 54 percent of Chinese internet users thought personal data leakage was a severe issue in China, among which 21 percent thought it was significantly serious in China. It was estimated that 91.5 billion RMB ($14.5 billion) cost by internet information leaks and fraud in 2016, and the average amount of capital loss per internet user was 133 RMB, indicating the serious damage caused by personal data leakage.
Privacy infringement was the No.1 concern among online shopping consumers and also the focus of the Chinese government’s legislative work
Increasingly prominent problems of personal data leakage have given rise to public concerns. “Online Shopping Integrity and Consumer Recognition” questionnaire designed by the China Consumer Association has shown that leaking personal data was the No.1 concern among online shopping consumers. 25.1% of respondents thought online shopping services had problems of revealing personal data, which topped total problems listed on the questionnaire. Increasingly severe situations of personal data leakage and the concern of personal privacy from Chinese people call for the action of the Chinese government on data protection. The Chinese government has introduced 2 regulations and laws to standardize personal data collection and protection, Cybersecurity Law and “Information security technology—Personal information security specification”, which indicate China’s increasingly reinforced legislative work on data protection.
Cybersecurity Law, which took into effect in June 2017, clearly states that user consent must be obtained before data collection have the consent from users, and individuals have the right to request network operators to delete personal information if they violent the provisions of laws. Information security technology—Personal information security specification sets a requirement on data storage, regulating de-identified process must be implemented after data collection, as well as separately store of data. It also poses a limitation of minimal amount and frequency of data collection, and data collected from users must be directly related to providing products and services. It is said by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (Samm, 2018) that the law of new national standard on personal information protection coupled with Cybersecurity Law contains more burdensome requirements than the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and GDPR is one of the largest-scale and the most punitive privacy laws in the world.
High-quality, large-scale, and integrated user data is currently under-supplied
According to the insight Daxue Consulting drew from interviews, high-quality, large-scale, and integrated user data is currently under-supplied. Generally, giant internet companies, such as Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba, have their own data ecosystems, and they gain large-scale and aggregated data from their auxiliary products and services. However, other companies only possess a small amount of data, and data sharing hardly happens across different companies, making it hard for some companies to advertise or improve their products and services. For example, when doing precision marketing, users’ behavioral data are analyzed to draw user portrait. Specifically, their preferences are analyzed and based on that, they are given different data labels (e.g. “keen to travel”; “makeup lover”). Then, companies with advertising needs show specific ads to potential customers based on the matching of labels. Apart from precision marketing, data analysis permeates to various industries, driving companies place a higher value on personal data. Companies tend to keep their own data confidentiality, thus, large-scale and integrated user data cannot be easily accessed by most of the companies.
Although the challenge of personal data leakage, people’s concern of privacy infringement, and data dispersion have brought some setbacks and negative effects on Chinese society, it can not stop the advent of the era of data. Facing those challenges, Chicness government, enterprises, and civics are determined to pool efforts together to greet the prosperous future of big data industry.
The extra article can be interesting to the international companies, presented in the Chinese market, is about the abilities of companies to predict future using Big Data in China.
Daxue Consulting can help with the analysis of any market in China, including the personal data industry
Daxue Consulting, as a market research company, provides the adapted data in one of the most challenging markets in the world, China. We have a wide range of services to deliver a competitive market research. To know more about the personal data market in China, do not hesitate to contact our project managers at dx@daxueconsulting.com.