Recently, Chinese government initiated several crackdowns on different industries. One of them was China’s gaming crackdown. Strict regulations regarding this sphere started as early as 2019 and continued in 2021, they included rules for video game characters and limited time to play games for minors. The number of underage Internet users in China in 2019 was 175 million, and the internet penetration rate was as high as 93.1%. Compared with 2015, the number of young users increased by 41 million, an increase of approximately 31%. Therefore, the new restrictions on gaming for minors might have an impact on key platforms in this industry.
This article aims to analyze how gaming companies obey new restrictions and how new rules influence their operation.
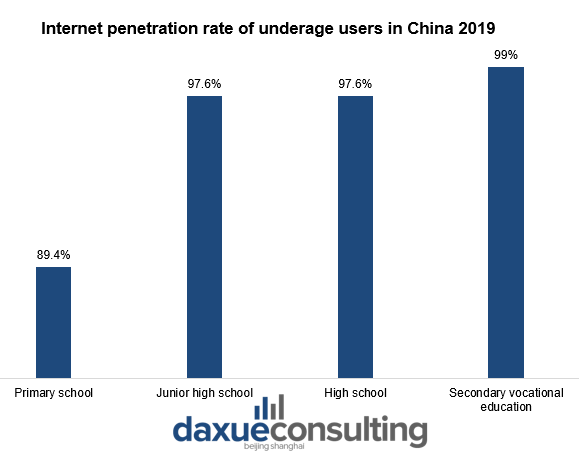
Data Source: CHIIC, Internet penetration rate of underage users in China
Regulations on violence and erotic characters in video games
According to the current Chinese laws and regulations even 18+ games must not contain elements such as violence, sexual elements, blood, terror, and bad statements.
The “2021 China Game Industry Potential Analysis Report” by Gamma Data in December 2020 pointed out that two-dimensional games have become the main growth force of the Chinese game market. More than 90% users around the age of 20 to 25 are interested in two-dimensional games. The surge of two-dimensional players has strengthened the market, but it has also brought about some problems. In order to attract attention, some two-dimensional games deliberately expose the image of female characters in an erotic way. In particular, the design of clothing can easily cause violations of laws and regulations. More violations may hinder the development of two-dimensional games, especially at the time of increasingly strict supervision.
Regulations minor’s gaming habits
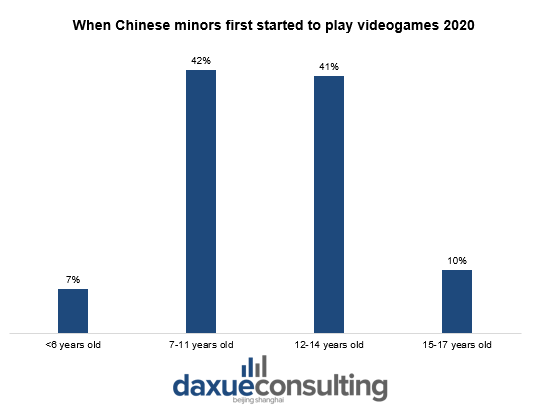
Gaming has become a major leisure activity for Chinese teenagers. Research data collected in 2020 shows that 42% of Chinese minors first started playing videogames between the ages of 7-11, and 41% started between 12-14 years old. At present, the penetration rate of electronic devices among Chinese minors is relatively high. The proportion of 7-11 years old having an electronic device is 61%. Additionally, according to the “Research Report on the Internet Usage of Minors in China in 2020”, 62.5% of minors are currently using the Internet to play videogames, while the proportion of playing mobile games is 56.4%.
China’s gaming crackdown started in 2019
In addition to stricter censorship of game content, China has gradually stricter control over youth gaming. Starting from the “Notice on Preventing Minors from Indulging in Online Games” released in 2019, the anti-addiction regulations for minors officially kicked off. The “Notice” pointed out that the real-name system for online games should be established and the time for minors to play should be further reduced and controlled. Based on this, each game in China has set up anti-addiction systems for minors in accordance with national regulations.
How key videogame platforms obey new regulations
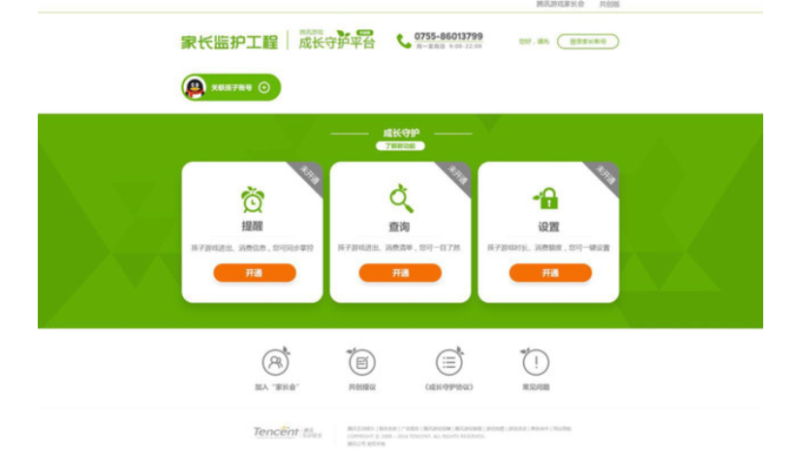
Already in 2019 mainstream game manufacturers have introduced self-discipline protection measures for minors. For example, Tencent’s “Growth Guardian Platform” not only allows parents to supervise their children, but also allows teachers to supervise students. Users under the age of 13 are limited to 1 hour of play per day, the users from 13 to 18 years old are limited to 2 hours of play per day. NetEase Games has also launched a “Parent Care Platform” that allows parents to inquire about their children’s game information and manage their gaming time. The larger the game company, the more important it is for them to adapt to regulatory trends in advance and avoid illegal operations; small and medium game companies are using large companies as the benchmark to achieving full compliance as soon as possible.
Large-scale mobile games generally require identity verification and restrict the login of players under a certain age. However, history has proven that this did not have a significant negative impact on the game’s revenue growth. The biggest change in the proposed amendment to the Law on the Protection of Minors is to extend the existing regulatory system to the mobile game market. In March 2020, Tencent stated that in the fourth quarter, minors under the age of 18 accounted for 6% of their online game turnover in China, of which minors under the age of 16 accounted for 3.2%.
The results of China’s gaming crackdown in 2019
On average, 17.8 million accounts of minors were kicked offline every day for “exceeding the standard” login time in 2019. In addition, Tencent started exploring facial recognition applications. In February 2019, an average of 7.24 million accounts were logged in every day, and 60,000 accounts triggered facial recognition verification during payment. Among them, about 90.5% of the accounts faced anti-addiction supervision due to rejection or failure to verify age.
China’s 2021 gaming crackdown
In 2021 the Chinese government accused video games of being addictive to minors, after that, Tencent’s shares fell 10%, losing 60 billion dollars in market capitalization. Moreover, media organizations’ share also fell shaprly such as NetEase falling by more than 7%, and Bilibili by more than 4%. After that, major game manufacturers had to follow the “Notice on Further Strict Management and Effective Prevention of Minors from Playing Online Games” issued by the National Press and Publication Administration. The platforms now can allow minors play games only one hour from 20 to 21:00 on Fridays, Saturdays, and Sundays.
From the perspective of the effectiveness of the anti-addiction system, more than half of the minors think that compulsory measures have worked”; only 14% of the minors think that the anti-addiction system is “less useful” or “not useful”.
How will it influence game companies?
First of all, mainstream game companies will definitely have to re-examine and improve their product’s content, which requires a certain amount of time and considerable investment.
Popular games in China like Hearthstone and Genshin Impact are free to play, attracting huge audiences, and then generating income from the fact that users have to buy certain items in order to progress in the game. But at the same time, many games are manipulative. There are multiple daily and weekly use-or-lose quests. Users receive rewards for logging in and for continuous streaks of games. The goal is for the player to spend enough time playing the game over a couple of months to unlock all features. It is such games that can especially feel the effect of the new regulations of the Chinese government regarding games.
In addition, minors still are important to game companies: although they have insufficient spending power and limited turnover contribution, they have more leisure time, which is an important part of the game market ecology. For games with high DAU of all ages, underage players can enliven the game atmosphere and help a game to achieve a diversified distribution of players. Therefore, if the gaming behavior of minors is further restricted, the gaming industry will still be affected to a certain extent.
The impact of China’s gaming crackdown on e-games industry
China has been actively developing its e-sports industry in recent years. E-sports talents are becoming younger and younger: the peak period of the average professional players is 16-22 years old. In the short term, the introduction of this policy will bring some resistance to the training process of e-sports players.
Key takeaways for brands in the midst of China’s gaming crackdown
- Although minors don’t have big purchasing power, China’s gaming crackdown might change the landscape of DAU for some games, leading to them losing some revenue.
- The Chinese E-sports industry, which focuses on underage players, also might experience difficulties due to new gaming regulations.
- In terms of stricter control on games in general, two-dimensional games might face problems, as they trying to expand their users base by using attractive female characters and violent scenes.





