China’s medical device market has grown significantly, reinforcing its position as a global manufacturing leader. By the end of 2023, China had more than 32,000 medical device manufacturers, generating RMB 1.16 trillion in revenue. This growth is driven by government initiatives, strong domestic demand, and rising innovation within the country’s healthcare sector.
Local giants: Powerhouses in medical device manufacturing in China
Chinese medical device companies benefit from robust government support under initiatives such as the “Made in China 2025” strategy, which aims to reduce reliance on imports and foster domestic capabilities in high-performance medical equipment. In 2023, 11 Chinese companies were ranked among the world’s top 100 medical device companies based on their annual revenues from medical devices and supply-related segments.
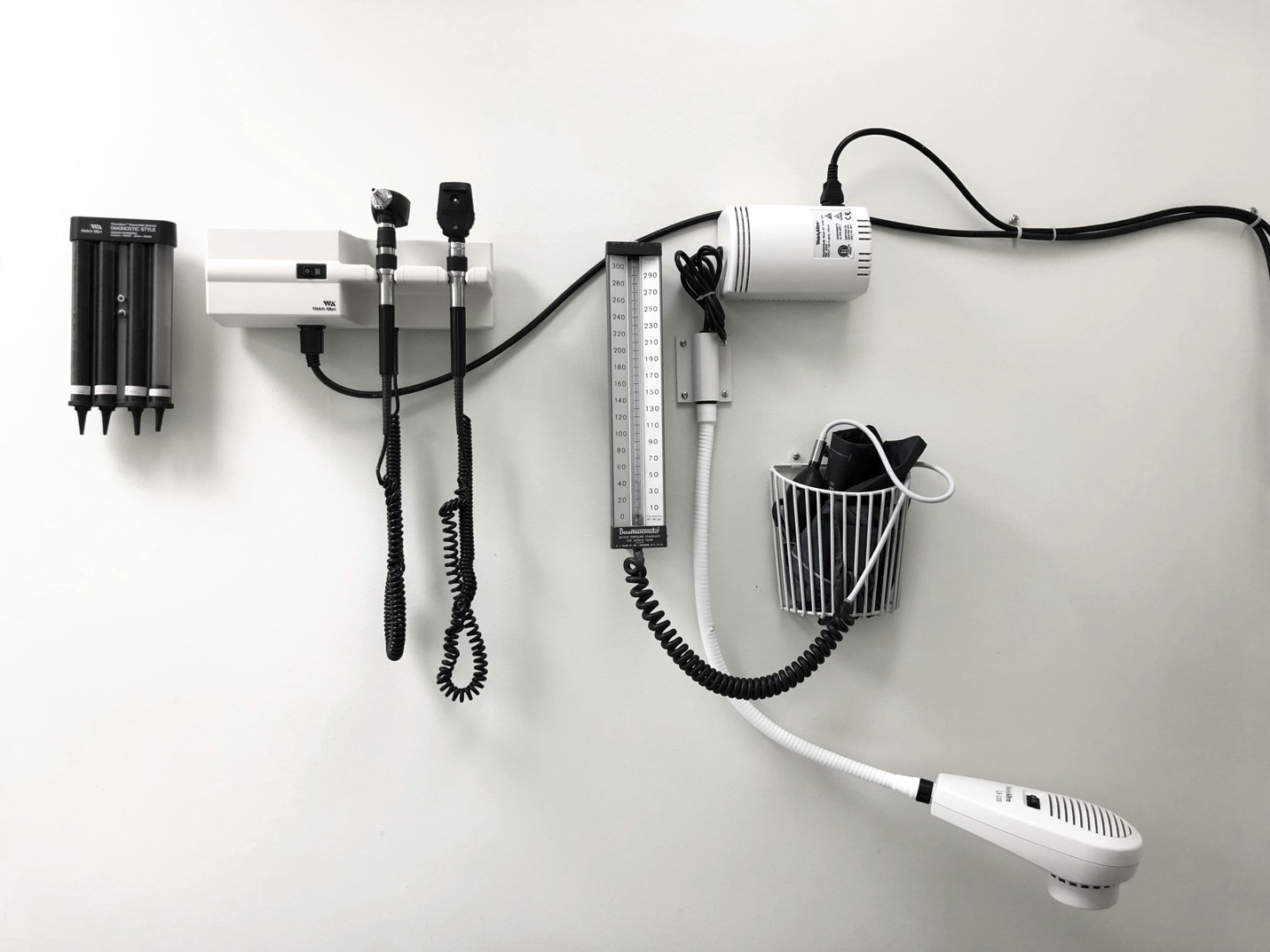
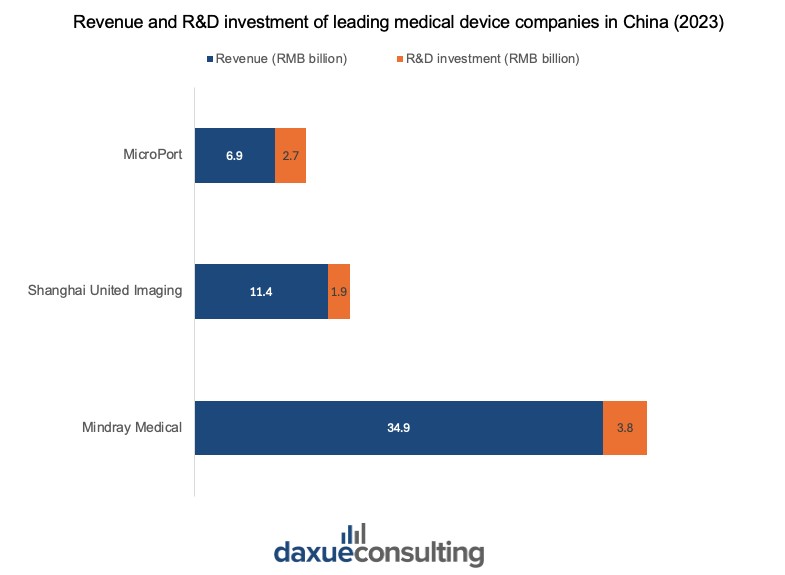
Leading companies in China have made significant investments to advance in various medical technology fields. For instance, Mindray Medical specializes in life information and support, in vitro diagnostics, and medical imaging. In 2023, Mindray generated RMB 34.93 billion in revenue, with its investment in R&D accounting for 10.82%.
Similarly, Shanghai United Imaging, known for advanced imaging devices such as MRI and CT scanners, has R&D spending that makes up 16.8% of the RMB 11.41 billion revenue in 2023. This focus on innovation led to the company securing 16th place globally and first in China on the 2023 Global Medical Device Industry Invention Patent Ranking by IPRdaily and incoPat.
MicroPort, with a global revenue of RMB 6.89 billion in 2023, has also seen significant results in its R&D projects, with RMB 2.69 billion spent. The company obtained 33 Class III medical device registration certificates from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and continues to lead with innovative devices for nine consecutive years.
Medical lab automation systems (mLAS) improve efficiency in hospital operations
Major Chinese hospitals are extending their adoption of the Medical Lab Automation System (mLAS) to improve hospital operations. MLASs automate diagnostics tests by accelerating the processing of biomedical specimen analysis and reducing the need for manual intervention. This results in quicker turnaround times for test results, enabling healthcare professionals to make faster, more informed decisions.
Furthermore, Total Laboratory Automation (TLA) takes integration further, connecting all testing systems for a fully automated lab, enhancing efficiency, and reducing human involvement. It incorporates technologies like industrial automation, specimen transport systems, and data management for streamlined operations. The automation then reduces human error, improves consistency, and optimizes resource allocation, freeing up staff to focus on higher-priority tasks.

Due to its nature, each mLAS is highly customized to fit the specific needs of individual hospitals. This localized approach ensures that the systems are tailored to the specific needs and layout of each hospital. As such, the tailored approach ensures that the system integrates seamlessly with existing hospital infrastructure, improving workflows and patient care. The custom-made solutions and deep localization of technology exclusive to Chinese medical device manufacturers position them at the forefront of innovation.
Preventive point-of-care coverage expands: Opportunities for medical device manufacturers
The “Healthy China 2030” plan placed an emphasis on early screening and intervention for chronic diseases. Thus, there is a strong focus on point-of-care testing (POCT) to improve the accessibility of healthcare services across the nation. By 2025, the goal is to achieve a 20% coverage rate for chronic disease prevention by leveraging POCT as a key enabler.
The aim is to achieve chronic disease prevention with a target coverage rate of 20% by 2025.
Key POCT-related measures include:
- Blood pressure screening in primary healthcare institutions, secondary hospitals, and even public spaces for individuals aged 35+.
- Opportunistic screening for cardiovascular diseases and cancers in hospital and community settings.
- Lung function testing for individuals aged 40+ and high-risk groups to detect respiratory diseases early.
- Hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia management with POCT tools to achieve over 65% standardized management at the primary care level.
- Expansion of cancer screening programs using accessible diagnostic tools.
“Despite tremendous advances in treatment protocols and medical technologies over the past few decades, China still faces significant challenges in screening and confirmatory diagnosis. This often results in patients beginning treatment at a late stage of disease progression, which negatively impacts their recovery prospects. To tackle this issue, China focuses not only on streamlining testing and diagnosis in large hospitals but also on facilitating early screening as close as possible to the populations, especially in rural areas. This explains the recent surge in POCT offerings across multiple therapeutic areas.”
– Irénée Robin, Managing Partner at VVR Medical
These efforts present opportunities for medical device manufacturers where there is a growing demand for portable, accurate, and user-friendly POCT devices. Moreover, the push for widespread screening and management of chronic diseases across the nation opens up new markets for scalable and cost-effective POCT devices.

Foreign players in China: Adaptation strategies by multinational companies
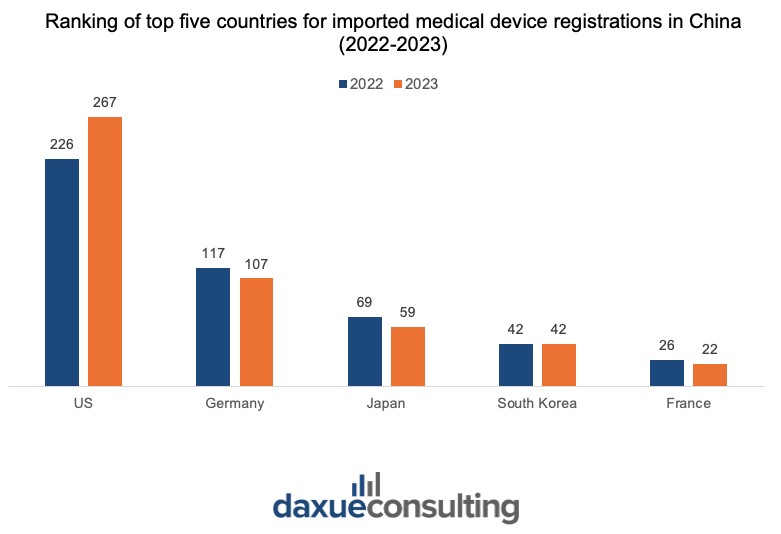
International companies remain key players in China’s medical market, contributing to the evolution of medical device manufacturing in China. In 2023, half of the approved registrations by the NMPA were for imported medical devices.
Significant changes compared to 2022 in the top five imported medical device categories included increases in the passive implantable device (by 43.3%) and dental device registrations (by 57.8%) and a decrease of 44.2% in medical imaging device registrations. Country-wise, the US, Germany, Japan, South Korea, and France together accounted for approximately 77% of the total first-time registrations for imported medical devices in 2023.
International players have adapted by establishing local manufacturing facilities and R&D centers to increase the proportion of locally manufactured products. For example, GE Healthcare, headquartered in the U.S., operates five factories in China, with a sixth under construction in Chengdu, focusing on the domestication of high-end medical equipment like CT, MRI, and PET/CT systems. Similarly, Philips runs five production bases in China, with over 90% of its China sales coming from locally manufactured products.
As one of the first multinational medical technology companies to enter China, Medtronic has introduced over 700 innovative products to the Chinese market, including cutting-edge technologies like the Micra leadless pacemaker. Medtronic’s China R&D center focuses on localized innovation to address clinical challenges, with 65 products developed, 50 launched in China, and 23 achieving global sales.
Da Vinci Xi: Locally produced robotic surgery devices breakthrough
Since its introduction in China in 2006, over 360 Da Vinci robots have been installed, benefiting 420,000 patients by the third quarter of 2023. The collaboration between Fosun Pharma and Intuitive Surgical, through Intuitive Fosun, has driven the localization of production, including an RMB 700 million investment in an industrial base in Pudong, Shanghai.
By 2023, the first Intuitive Fosun Da Vinci Xi surgical robot was successfully assembled in Shanghai. The domestically produced Da Vinci Xi received approval from the National Medical Products Administration in the same year. This represented a breakthrough in China’s medical device manufacturing technology.
Intuitive Fosun has also localized the biopsy needle production for the Ion bronchoscopy system, meeting 70% of global demand. This initiative sets a blueprint for the development of advanced “Made in China” medical devices, enhancing innovation and expanding the global footprint of Chinese medical technology.
Competitive edge: How companies leverage their strengths in the Chinese market
China’s medical device market is shaped by domestic firms’ cost-effective solutions in lower-tier cities and rural areas, while international brands dominate premium segments. However, tendering mechanisms and quality-based evaluations create opportunities for multinationals to compete on innovation and service rather than price. For instance, Beijing’s scoring system assigns 70 points to quality—considering clinical efficacy, innovation, brand, and after-sales service—and 30 points to price, favoring differentiated international products.
To further enhance brand reputation and trust, foreign medical device companies also invest in localization and sustainability initiatives. For example, Philips focuses on supporting equipment upgrades and lifecycle service solutions, while GE Healthcare engages in health awareness programs such as the Pink Ribbon Campaign for breast cancer awareness. These efforts help strengthen their market positioning and long-term competitiveness in China’s evolving medical landscape.
Engine of growth: Regional manufacturing hubs contributing to growth and export
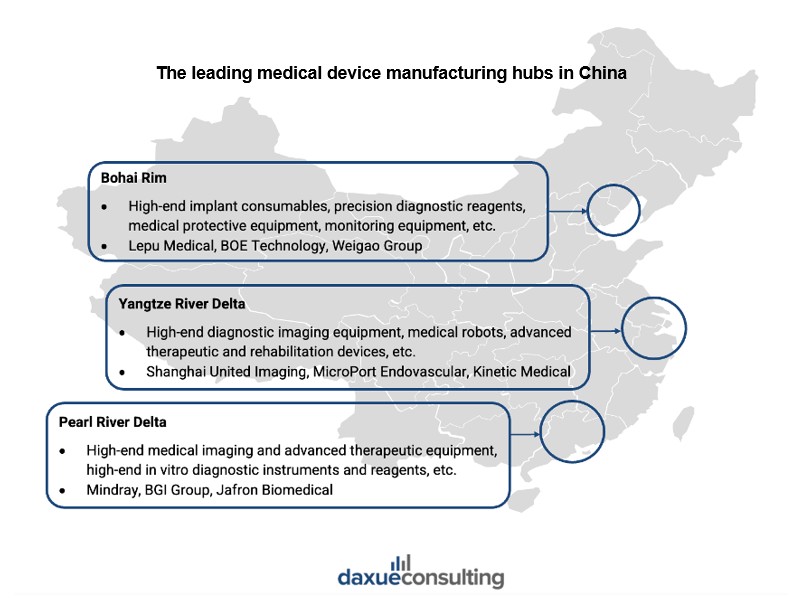
The Yangtze River Delta, Bohai Rim, and Pearl River Delta are the main bases of medical device manufacturing in China, each offering unique strengths. While these hubs produce a wide range of devices, they are increasingly focusing on high-end diagnostic imaging, precision diagnostics, and in vitro devices.
The Yangtze River Delta, centered around Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Nanjing, is a major hub with more than 120 higher education institutions offering medical device-related programs and around 280 clinical trial centers, representing 20% of the national total. Shanghai leads in the registration of first-time imported medical devices, accounting for 64% of the national total in 2024.
The Bohai Rim, with Beijing as its core, is a center for technological innovation and research, supported by institutions like Tsinghua University and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Beijing accelerates innovative medical device approval through fast-track approval programs, including a green channel for urgent imports and tailored support for domestic breakthroughs in registration and licensing.
The Pearl River Delta, centered around Shenzhen and Guangzhou, is a key manufacturing base. Shenzhen pioneered China’s first 3.0T high-field MRI equipment, making China the third country to master such technology. Furthermore, the region plays a crucial role in exports. Guangdong province accounted for 23.9% of medical device exports in the first half of 2024, valued at RMB 40.42 billion.
Medical device manufacturing in China at a glance
- The medical device market is growing rapidly with strong government support and rising domestic innovation in medical device manufacturing in China.
- Local players like Mindray, United Imaging, and MicroPort are key drivers of growth, though they face challenges in global expansion.
- Foreign companies such as GE Healthcare, Philips, and Medtronic are adapting to China’s market by localizing production and R&D.
- Competitive factors such as pricing, quality, after-sales service, and brand reputation play a crucial role in defining success.
- Regional hubs such as the Yangtze River Delta, Bohai Rim, and Pearl River Delta are critical to China’s medical device manufacturing success, each offering unique strengths and opportunities for innovation and export.






