Mobile Banking in China
[More market research in China]
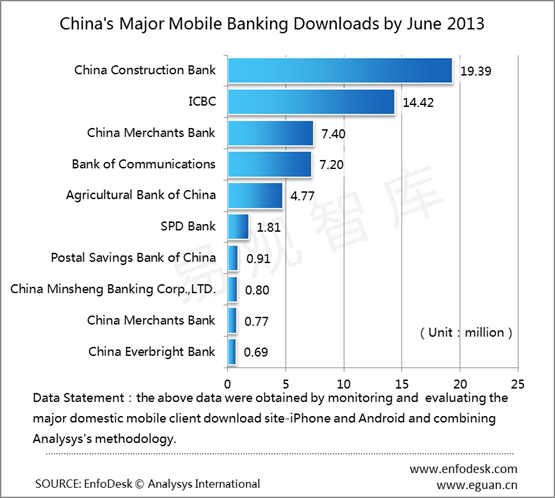
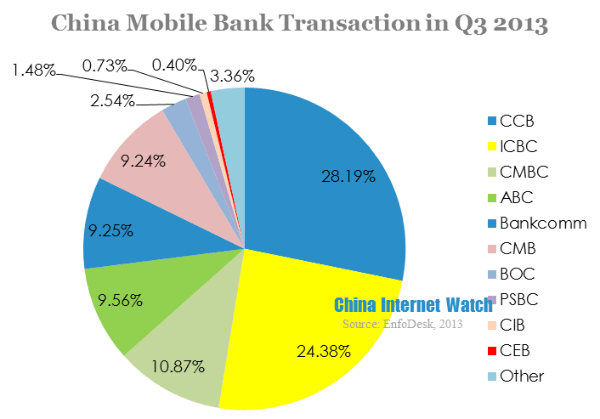
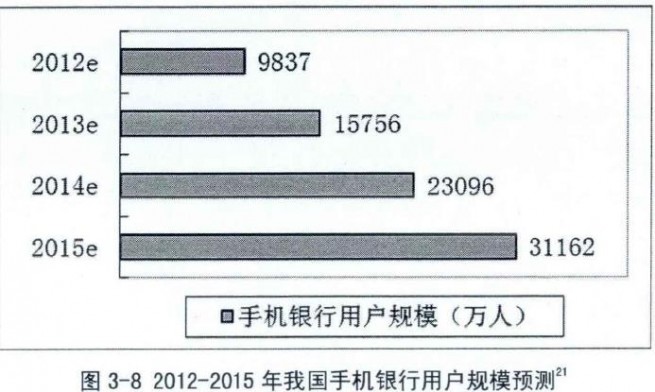
In 2012, the number of mobile banking usage reaches 150 million in China. This is 40% of world’s total. And the number is still rising. In 2012 users had grown by 100%, and transaction value had grown by 300%.
Chinese Banks’ Strategy in Mobile Banking:
CMBC focused on developing mobile bank business, and it opened Sina Weibo enterprise account and first launched financial service platform for micro and small customers. Although its mobile app was not launched till July 2012, its transaction kept growing due to micro and small customers.
Inspired by CMB, banks all improved their service on Wechat platform in Q3. The goal of Wechat banks at present was to increase user loyalty, by sending out coupons and offer other services.
What customers Want from Mobile Banking:
Market research in China showed that the most requested functionality is the ability to check account balances (75%). More than half of respondents want to receive notifications of potential fraudulent activity (59%) through mobile banking, make payments from their account (53%) and transfer money between their accounts (50%) using their smartphone.
Mobile banking still need development of its coverage in China
Chinese customers claimed that there are many bank branches or ATM in not far distance. Many stores have credit devices. But only 29% of purchase can be done through mobile banking for the moments. And cell-phone cannot substitute bank and computer for all service yet.
Mobile Banking in China’s rural Areas
There is an urgent need for mobile banking in China’s rural areas:
In 2012, there are only 65 Rural Merchant banks in China, and the problem of loans is severe, as many provide much more loans than credits. The amount of loans per capita decreases from 50.8 thousand to 31.2 thousand.
There are several reasons why mobile banking development is crucial in such areas. For instance, poorer families, particularly those in remote areas, have trouble accessing accounts and use them mainly for encashment, which can often require costly travel to bank branches or ATM in distant cities and towns. There is a lack in ATM and other paying devices available in rural areas.
Therefore, rural area is a huge potential market for Mobile Banking. Nowadays, 64 percent of China’s rural and migrant population does not have access to formal banking services.
The trading and finance managing demand in the rural area is high. Still, there are not so many bank branches. Market research data shows that we have totally 175 thousand branches in China, but only more than 30 thousand in rural areas. In 2010, the number of bank outlets and cooperatives banks in rural areas was 1,238 nationwide, rural commercial banks had 1,164 outlets nationwide and rural credit cooperatives had 28,886 outlets. That’s too few compared with a population of over 720 million.
While the equipment in term of withdraw and banking system in rural area is that low, 82% of rural people have cell phone, but only 54% of them can access to computers. Market research data also shows that 45% of rural people get online exclusively from mobile devices. It means that rural areas have a higher mobile Internet penetration than urban internet users.
On the other hand, agriculture related loans made by financial institutions have been on the increase during recent years with the government’s increasing attention paid to agriculture. At the same time, the demand of rural residents for basic financial services, such as deposites and withdrawals, remittances and settlements and insurance, has been increasing; as a consequence, the rural financial service capacity has been further strained.
See also China Internet Watch