The Chinese internet reaches 900 million people, most of which are mobile users, setting the foundation for success in 5G development. Forecasts show that Chinese 5G users will reach 650 million by 2023, covering around 40% of the Chinese population. Additionally, the government views 5G development in China as crucial to the country’s tech sector and economy. The government controls all three of the country’s mobile operators (China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom). It also has been “guiding” them to deploy 5G networks, which is also the reason why China is ahead in 5G.
Also, read on how China is one of the first countries to launch 6G technology.
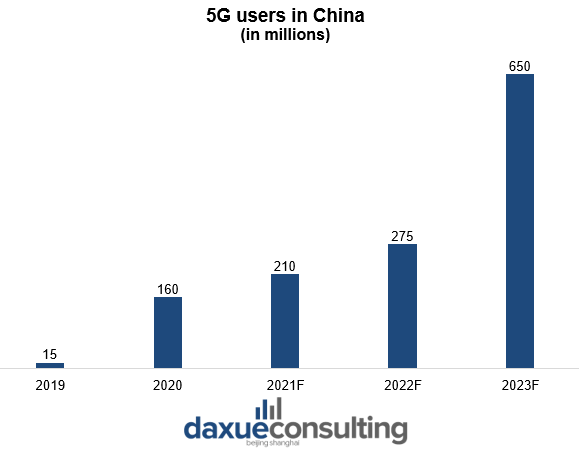
Data Source: iResearch, EY, forecast of 5G users in China
China is trying to reach one million 5G base stations by end-2020
China had already constructed over 690 thousand 5G base stations nationwide by the end of September 2020. The government said that subscribers using applications based on the 5G network already reach nearly 160 million. Moreover, China’s fixed-asset investment in the telecommunications sector increased 16.5% year-on-year in the first nine months of 2020. One third of total investment in the sector is for the 5G technology in China.
In September 2020 China Tower claimed that it had constructed a total of 345,000 5G sites in China. Meanwhile, Chinese carriers are experiencing a rapid acceleration in the number of 5G subscribers. The aim is to reach one million 5G base stations by the end of 2020.
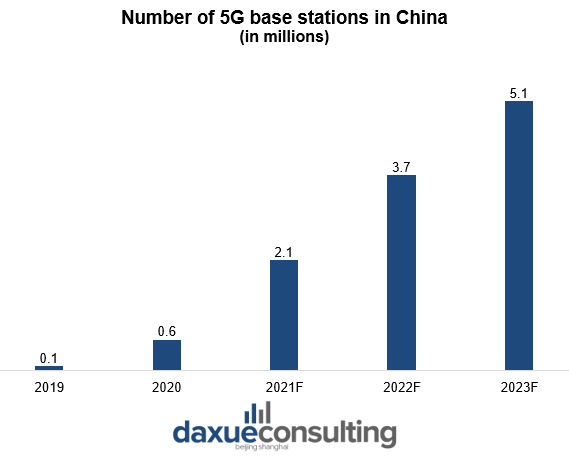
Data Source: iResearch, Forcasted number of 5G base stations in China
Competition in the world: Huawei still leads in 5G patents despite US ban
It seems nothing can stop China from leading in 5G development. Despite the U.S. cutting off the supply of crucial mobile chips, China’s Huawei remains the top filer of essential 5G patents. This telecommunications giant is the key company behind China’s 5G development.
Unlike some regions in the U.K., where there will be delays of up to three years for the rollout of 5G technology after the government decided to strip Huawei from its networks, China is leading the world in 5G. In Europe, COVID-19 will slow the 5G rollout by up to 18 months. Even the U.S. looks certain to lag far behind China in the 5G race. The 5G rivalry is threatening to further divide the world’s digital universe by accelerating the U.S.-China decoupling. However, the world does not have to suffer or break apart just because China leads in next-generation wireless technology. In the area of consumer internet innovation, China’s 5G development will strengthen its emerging role as an innovator.
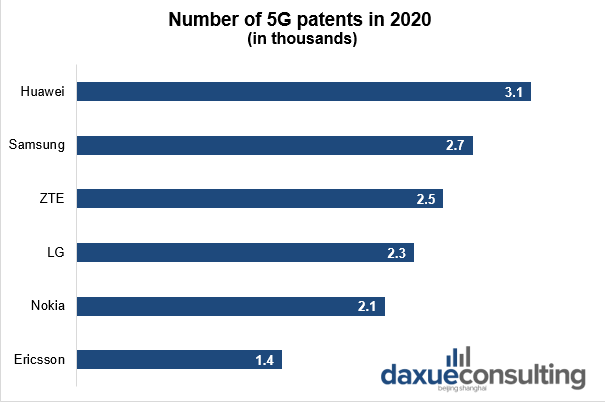
Data Source: TechWireAsia, Number of 5G patents in 2020
In 2020, 5G in China still has latency problems
5G development in China includes not only public usage, but also private usage by enterprises. Among 800 enterprises, which already deployed 5G, most connect machinery and harvest data to identify ways for productivity improvement. 5G features like ultra-reliable and low latency communication and enhanced mobile broadband have yet to be exploited by most industries.
One exception is augmented reality (AR), where low latency is crucial for a better user experience. Allen Wu, co-founder of AR glasses company HiAR said that 5G still has latency problems at the moment although it’s a big improvement from 4G. While 5G reduces latency to less than 10 milliseconds, it does not refer to end-to-end computational latency. And it is more meaningful barometer because it reflects the latency felt by end users. Wu said current 5G networks are not fast enough to complete end-to-end computations in less than 30 milliseconds.
Currently the frequency of 5G technology in China is between 24 GHz and 86 GHz. It provides the necessary capacities for the most applications, however there is still a room for improvement.
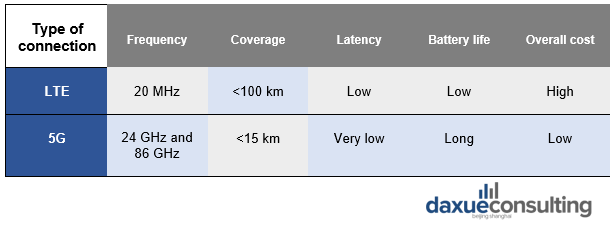
Data Source: EY, LTE vs 5G capability comparison
Huawei is the key player of the 5G development in China
5G has been available in China since November 2019, when Chinese carriers officially launched 5G services. Huawei stands at the origins of the 5G development in China.
Huawei launches successful simplified 5G solution
In February at the 2019 Mobile World Congress (MWC), Huawei released a full-scenario 5G commercial system that provides what the company calls a “simplified 5G solution” along with 5G phones and a line of cloud core network products. The Simplified 5G Solution is designed to help operators build 5G networks with ultimate experience and usability.
Throughout 2018, Huawei has partnered up with worldwide operators such as Vodafone (Spain), Sunrise (Switzerland), LG (South Korea), and NTT DOCOMO (Japan) for testing and verification of many 5G products and technology. At MWC 2019, Huawei also demonstrated the world’s first multi-operator 5G call, 8K high-definition (8K HD) live streaming, and new applications such as Cloud VR and AI gaming in China.
Can Huawei’s Simplified 5G Solution give consumers what they want after 4G networks?
After the release of 4G networks, users still wanted faster connectivity, faster browsing, better quality video calls and ultra-high-definition. Huawei’s simplified 5G solution will be able to give them some of the things in which they want. The solution provides faster speeds, faster connectivity, and quicker access to the cloud. Traveling over super-high-frequency airwaves provides faster speeds and more broadband width. Faster connectivity is possible because of zero latency, which reduces lag time between devices and services. For faster access to the cloud, the simplified 5G solution acts as a cloud server. It also performs computing and data storage bringing data closer to the devices for quick and easy access.
The technology behind 5G products and solutions
Key factors to the simplified 5G solution are the end-to-end core chip, Huawei TIANGANG, and a base station. Huawei TIANGANG is an e2e chip that is highly integrated. It can support large-scale combining of an active power amplifier (PAs) and passive antenna arrays into tiny antennas. It also holds super high computing capacity such that up to 64 channels. Other features of the chip include active antenna units (AAUs) being smaller and lighter and being able to support simplified China’s 5G development. The base station with antenna units and different modules can combine as needed, allowing installation to be simple and easy. The installation time is much shorter than it takes to install a 4G base station.
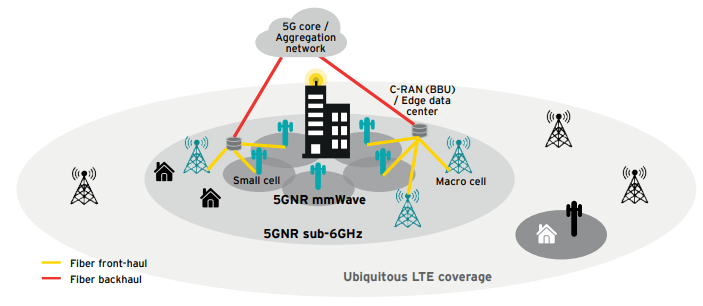
Data Source: EY, Qualcomm, 5G architecture
5G development in China is reaching more cities
In 2020 Shenzhen has become the first Chinese city with the full 5G coverage with a total of 46,480 stations. Now more and more cities install 5G base stations promoting the 5G development in China.
Pilot 5G-based smart transport system in Changsha
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology said it will support the city of Changsha in Hunan province in establishing a pilot zone for a 5G-based smart transport system.
The initial goal will be to deploy a cellular-based vehicle-to-everything network (C-V2X) along highways and public roads in Changsha. Using high speed 5G technology in China, C-V2X enables the exchange of information among vehicles, pedestrians and roadside communications infrastructure. It aims to improve road safety and the efficiency of traffic flow.
Beijing reaches full 5G coverage
Beijing has become the second city to achieve full coverage of 5G technology in China. As of the end of July 2020, Chinese operators had installed a total of 44,000 5G base stations across the city. Moreover, the figure will reach 50,000 by the end of 2020, according to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
Currently, there are about 5.06 million 5G users in Beijing. The city will also boost the development of 5G applications, such as unmanned vehicles, and promote 5G construction at the Beijing Daxing International Airport and the 5G transformation of venues for the 2022 Winter Olympics.
Prospects of the 5G development in China
5G Connectivity: more industries are using 5G
Along with the simplified 5G solution, Huawei released the ‘Cloud X’ business model of smart terminals and cloud appliances. The ‘X’ can stand for three forms of technology: pc, gaming, and AR/VR. Cloud PC is a cloud hosting service that can work as a mobile base station or gaming host, all based on 5G. Cloud Gaming replaces local gaming hosts with cloud-based gaming hosts. Cloud AR/VR applies rendering and computing on the cloud with 5G being required after rendering for user experience.
As China’s 5G development is going further, companies and industries are preparing to utilize the commercialization of 5G. Sunrise (Switzerland) plans to release their 5G network using Huawei’s simplified 5G solution. South African mobile network operator Rain, in partnership with Huawei, has released the first 5G commercial network in Africa. In the China’s car industry, automaker Zhejiang Geely Holding Group plans to mass-produce a line of intelligent-connected vehicles using 5G networks and C-V2X technology readied for release into the automobile market as early as 2021.
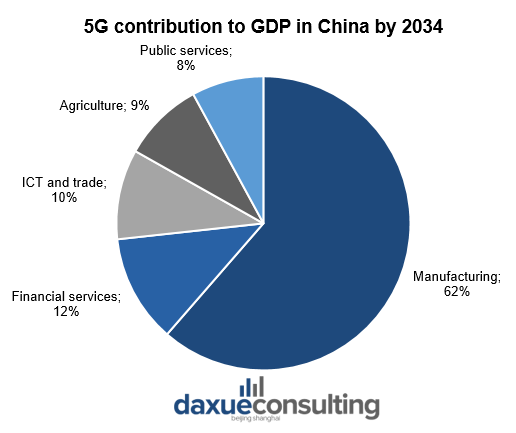
Data Source: GSMA, 5G contribution to GDP in China by 2034
COVID-19 pushes the commercial usage of 5G
The COVID-19 outbreak in China has driven a major chunk of the workforce online. It made inevitable the huge market prospects for 5G network investments and enabled 5G technology in China. Since the beginning of the epidemic, China has witnessed the faster and more extensive use of 5G in various fields. According to a report from China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, 5G applications are used heavily in the medical care, public security, education, manufacturing, and logistics sectors.
Statistics shows that 22 Chinese provinces and cities implemented 5G applications to combat COVID-19. Among them, the provinces of Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Jiangsu as well as Beijing, Shanghai, and Wuhan, the former epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak. They are now the main hubs for 5G application trials. Therefore, coronavirus epidemic has become one of the key drivers of China’s 5G development.
See our report on China’s AI ecosystem
Listen to over 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast