In recent years, sustainability has become crucial in global industries, including China. Chinese consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact, driving demand for sustainable products. To meet this demand, certifications, and standards have been established to ensure authenticity and reliability in various sectors such as textiles, food and beverages, automotive, and even chemicals. Thus, sustainability certifications can enhance business success in China’s market, providing a competitive edge and solid market positioning.
Download our report on the future of the sustainable fashion in China

China’s sustainability certifications’ growing relevance: Consumer awareness and government initiatives
Sustainable development is defined as meeting current needs without compromising future generations. This term is gaining significant relevance in China due to multiple factors. First, is the heightened level of awareness concerning their consumption choices. According to a 2021 consumption report by PwC, 72% of Chinese consumers actively seek to purchase from environmentally responsible companies, compared to the global average of 54%. The findings from our 2022 Green Guilt Report revealed that consumers’ interest extends beyond the product itself; they are equally concerned about the production process.
Moreover, the Chinese government has been at the forefront of advocating and implementing measures to chart a greener and more sustainable path for the nation. In a significant commitment at the UN General Assembly in 2020, China vowed to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 and reach its peak emissions by 2030. This bold stance has positioned China as a global leader in the renewable energy sector, driving advancements in eco-friendly technologies and sustainable practices.
Given the heightened awareness of sustainability among Chinese consumers and the Chinese government’s active efforts to promote sustainable practices, sustainability certifications would be able to offer a competitive edge in the market and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Moreover, these certifications serve as a tangible way for businesses to align with the government’s sustainability policies.

Introducing China’s sustainability certifications issuers
Sustainability certifications in China are mainly given by governmental institutions, business organizations, or unaffiliated third parties. While third-party organizations carry out audits and evaluations to verify compliance, the government is vital in creating standards and norms for certifications. Several of the notable issuing authorities are:
The Certification and Accreditation Administration of the Republic of China (CNCA)
CNCA is a government agency responsible for overseeing certification, accreditation, and conformity assessments in China. Its primary role includes developing and implementing laws, guidelines, and rules related to various certifications, including those related to sustainability.
China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment (CNAS)
CNAS is China’s national agency responsible for accrediting conformity assessment bodies in China. Its role is to ensure the competence and impartiality of certification bodies, laboratories, inspection bodies, and more. CNAS operates the national accreditation system and participates in international mutual recognition programs to strengthen global cooperation.
Industry-Specific Associations
Some industries have unique sustainability certifications issued by specialized associations. For example, the China Environmental Labeling Program certification is issued by China Environmental United Certification Center (CEC), a non-profit organization that focuses on environmental certification and green products in China which is affiliated with the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China.
Sustainability and Chinese consumer priorities in F&B and fashion
Challenges in China’s green certificates market
China’s pursuit of sustainable development and a clean energy transition has led to the establishment of a green certificate market in 2017, primarily aimed at promoting renewable energy adoption and reducing the financial burden of subsidy payments. Yet, despite China’s position as a major player in renewable energy, its green certificate program has experienced slow growth. Obstacles such as low transparency, unclear compatibility with international practices, and the lack of incentive for time or geographical matching continue to hinder the green certification market’s maturity and attractiveness to buyers and sellers.
Sustainability is reshaping China’s fashion industry and F&B sector
The fashion industry in China is one of the sectors that is significantly influenced by the rising trend of sustainability. Annually, China discards 26 million tons of clothes, with less than 1% being reused or recycled. There is currently an unmet demand for second-hand clothing in China and young consumers are at the forefront of driving the sustainable fashion movement in the nation. Young consumers engaging in sustainable fashion typically make 2-4 purchases annually with the majority falling within the price range of RMB 300-500.
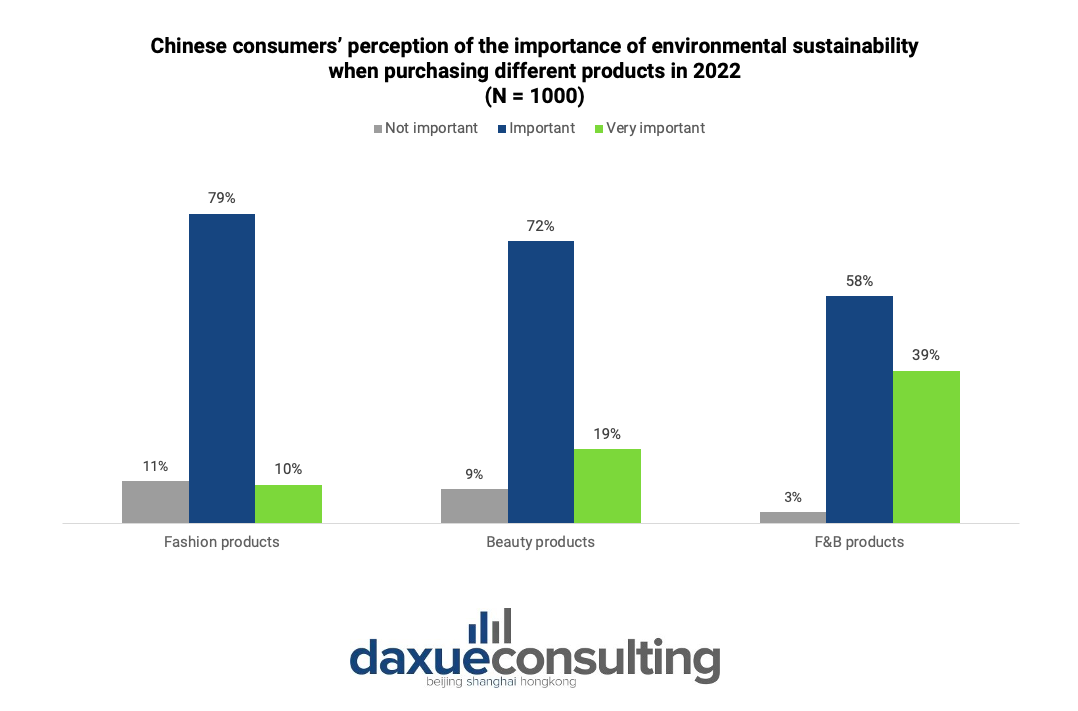
The sustainability trend’s influence extends significantly to another critical sector – the F&B industry. According to our 2022 survey, Chinese consumers express the highest level of concern for the sustainability of their food and beverage products. COVID-19 has played a pivotal role in driving this awareness of sustainability and health in the F&B sector. According to Accenture’s 2021 China Consumer Insight, the pandemic has led to dietary changes for 44% of Chinese respondents, with an increased preference for organic products, compared to 18% in the US. This preference is rooted in the perception that “green” equals safer supported by the findings of McKinsey’s 2023 China Consumer Report, which reveals that Chinese consumers prioritize safe and natural ingredients within their top 3 considerations when making F&B purchases.
China is nurturing its agricultural excellence by implementing “Three Products One Standard”
“Three Products One Standard” (三品一标) is a pivotal strategy guiding China’s agricultural advancement. It underscores the need to elevate the quality, safety, and standards of agricultural goods. This initiative responds to changing consumer preferences, guarantees food security, and bolsters the competitiveness of Chinese agricultural products in global and local markets. This concept encompasses three categories of agricultural products and the establishment of one set of standards for each category. The three categories are:
- Green Food (绿色食品): agricultural products that are produced using environmentally friendly practices, with minimized use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers. They are also subject to strict quality and safety standards, positioning these products as healthier choices for environmentally conscious consumers.
- Organic Food (有机食品): Produced through organic farming methods without synthetic chemicals, GMOs, or artificial inputs. Focuses on soil health, ecological balance, and animal welfare. Known for natural qualities and a lower environmental impact.
- Geographical Indication Products (地理标志产品): Originating from specific regions, possessing unique qualities tied to that origin. These products showcase cultural and environmental attributes due to traditional methods and local expertise.
Each category adheres to specific production, processing, and labeling standards. These guidelines guarantee product quality, safety, and authenticity, while also offering consumers trustworthy information about origin, production methods, and overall product quality.
Deeper dive: China Environmental Labeling (CEL) Program
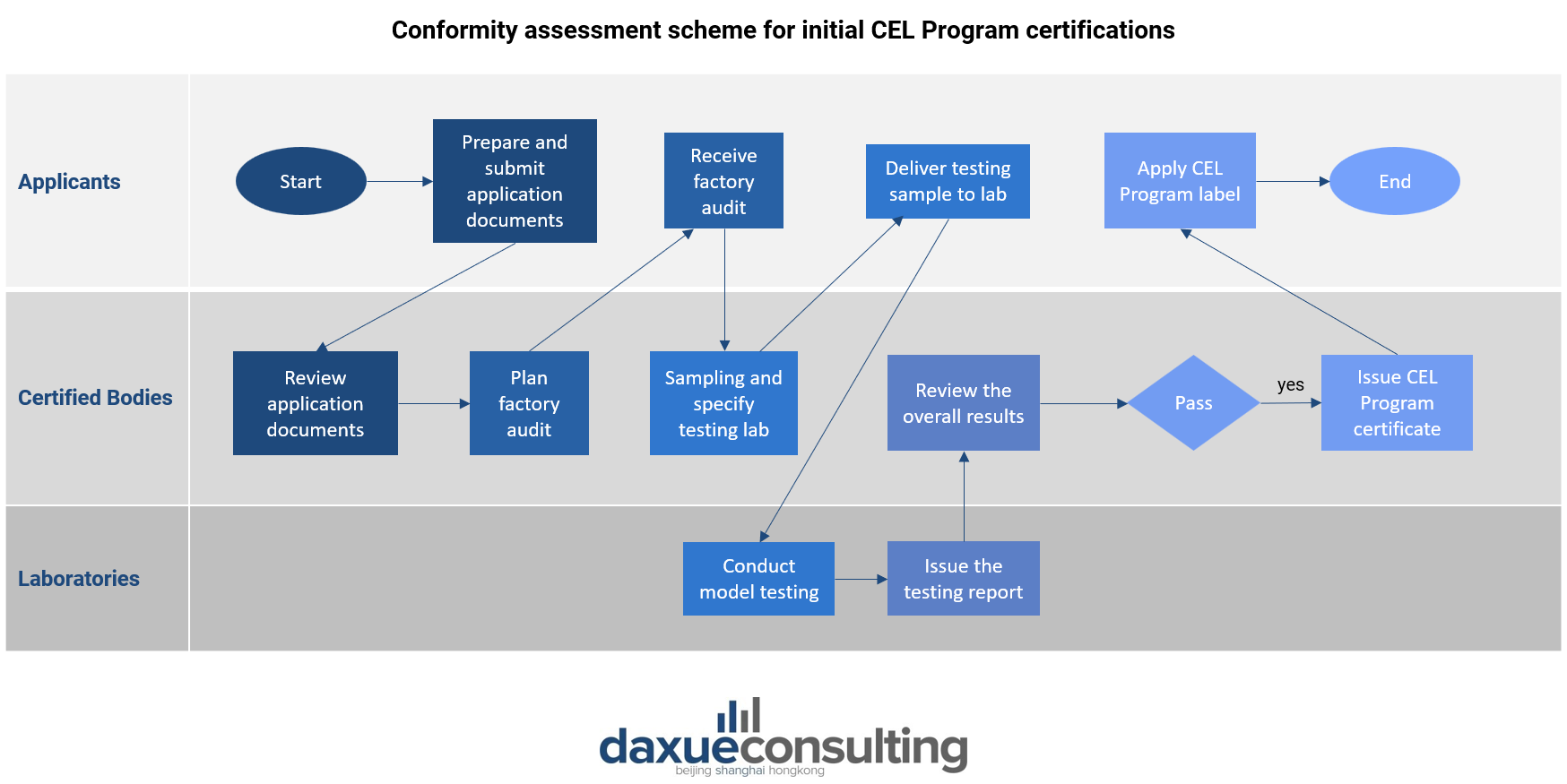
CEL Program was established by the Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) and has been a key part of China’s efforts to address environmental issues and promote green consumption since its launch in 1993. The CEL Program aims to promote green development, reduce pollution, and drive the green transition in various sectors. The program covers a wide range of industries, including furniture, building materials, textiles, electronic products, automobiles, daily chemical products, and packaging. With over 5,100 licensees and nearly 1.5 million certified products, it has become one of China’s most successful and influential ecolabelling programs. The program’s adoption has been further accelerated by the China Green Public Procurement process, with government procurement reaching RMB81.35 billion in 2020, accounting for 85.5% of similar product procurement. The program’s impact extends to education, with over 1.3 billion certified Green Printing textbooks used in schools.
Driving business success: How sustainability certificates benefit companies in China
There are various benefits earned by a company that obtained a sustainability certificate. For example, a sustainability certificate can significantly boost a company’s reputation and brand image by demonstrating its commitment to environmental responsibility and social consciousness. Additionally, in China, sustainability-certified companies can benefit from various government incentives and subsidies designed to promote sustainable business practices. These incentives may include tax benefits, grants, and access to favorable financing options, providing additional motivation for businesses to embrace sustainability. Moreover, implementing sustainable practices can lead to long-term cost savings, as adopting energy-efficient technologies and waste reduction measures can result in lower utility bills and waste disposal expenses, further enhancing a company’s financial sustainability.
Rising trends: Navigating sustainability certifications in China
- Sustainability certifications are gaining relevance in China due to heightened consumer awareness and government initiatives.
- China’s sustainability certifications are issued by various authorities, including governmental institutions like CNCA and CNAS, as well as industry-specific associations.
- The green certificate market in China aims to promote renewable energy adoption but has faced challenges, including low transparency and limited incentives for time and geographical matching of renewable supply.
- Chinese consumers are increasingly paying attention to sustainability in the fashion and F&B industries, driving demand for eco-conscious choices and sustainable practices.
- “Three Products One Standard” is a strategic cornerstone of China’s agricultural progress, aiming to enhance the quality, safety, and standards of agricultural products.
- The CEL Program, established is a significant part of China’s green consumption efforts and has seen notable success with numerous certified products and government procurement support.
- Obtaining sustainability certifications in China provides companies with improved reputations, consumer appeal, government incentives, and potential cost savings through sustainable practices.





