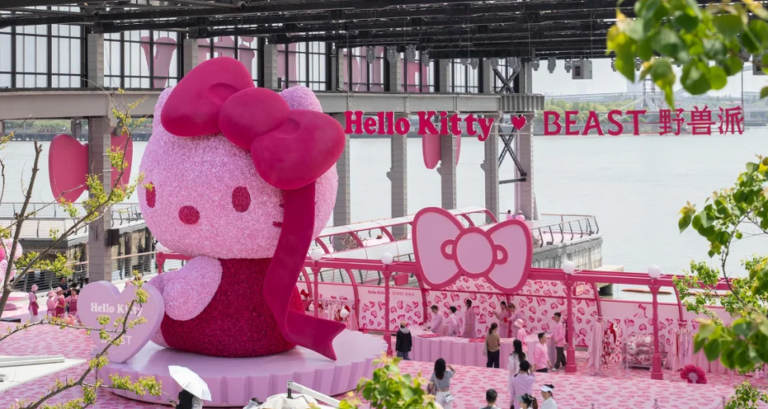
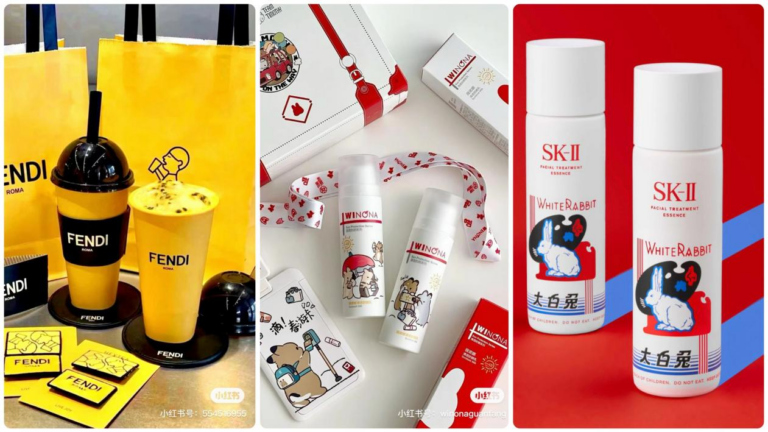
IP collaboration is a co-branding method where two or more brands mesh their brand assets (whether it be logos, colors or mascots) to create a new product or service. In the recent years, IP collaboration in China has exploded in popularity among both domestic and international brands.
Differences in IP collaboration in China and the rest of the world
Different drivers to co-brand
In China, brands often seek to build consumer trust by engaging in co-branding initiatives with reputable partners. For example, the Chinese milk brand Mengniu struggled to gain positive reputation among all the premium foreign milk competitors. Thus, they collaborated with Disney, who vaunts a strong reputation and trustworthy image among families.
In the west, co-branding is more often done to share the advantages of each brand. For example, McDonalds specializes in food and fast service, and Coca-Cola specializes in a consistent, trustworthy beverage. Coca-Cola and McDonalds collaborate to have Coca-Cola supply beverages in McDonalds, capitalizing on the advantages of both brands.
Adventurous cross-industry collaborations
Chinese consumers tend to be more welcoming of adventurous cross-industry co-branding, whereas western consumers are often more skeptical. One example is the Chinese co-branding case of KFC and LiuShan Florida Water Insect Repellent. The brands released LiuShan Florida Water flavored coffee, which was received openly among Chinese consumers. As insect repellent has a connotation of being toxic to ingest, it is counter-intuitive that a scent used in insect repellent would be welcomed in coffee.
This was not the case in South Korea, where a brand known for producing markers expanded into the beverage industry, but consumers rejected the drinks, as they did not want to associate consuming something similar to toxic markers.
Cultural and museum partnerships
Cultural heritage is often a driver of co-branding, hence partnerships with museums, cities, and old Chinese brands are common. One big player is the Beijing Palace Museum, which has collaborated with many brands such as eleme and Perfect Diary. IP collaborations in China are often goes hand in hand with Guochao marketing, a marketing tactic that aligns brands with Chinese cultural pride.
In the west, partnerships with museums are often one-off events and have more focus on a modern take on art, but not for the sake of cultural pride.
Looser trademark laws
China’s looser trademark and IP protection laws leave more space for quicker and more frequent co-branding. In countries like the US where IP laws are stricter, collaborations are less frequent and slower as often times a new logo has to be created that interferes on neither side’s existing brand assets.
The four key decisions we take into account for clients IP collaborations in China
- Risk management. Daxue Consulting audits for potential risks of co-branding partners and methods. Risks range from PR crisis to low return on investment.
- Goals. Decided by the client, impact which partner and co-branding method. Goals range from building brand reputation to reaching new consumer bases and expanding product services.
- Partner. Based on client’s goals, and other factors like risk and level of investment, Daxue Consulting will shortlist potential partners for co-branding.
- Acceptable investment. Co-branding methods each require different levels of investment, and different partners are willing to accept varied levels of investment. Simple promotional activities take a low investment, while co-creating a product line takes a high investment of money and time.
Defining goals for co-branding in China
Co-branding and IP collaboration can bring brands a variety of benefits in their brand image, consumer acquisition, and product development.
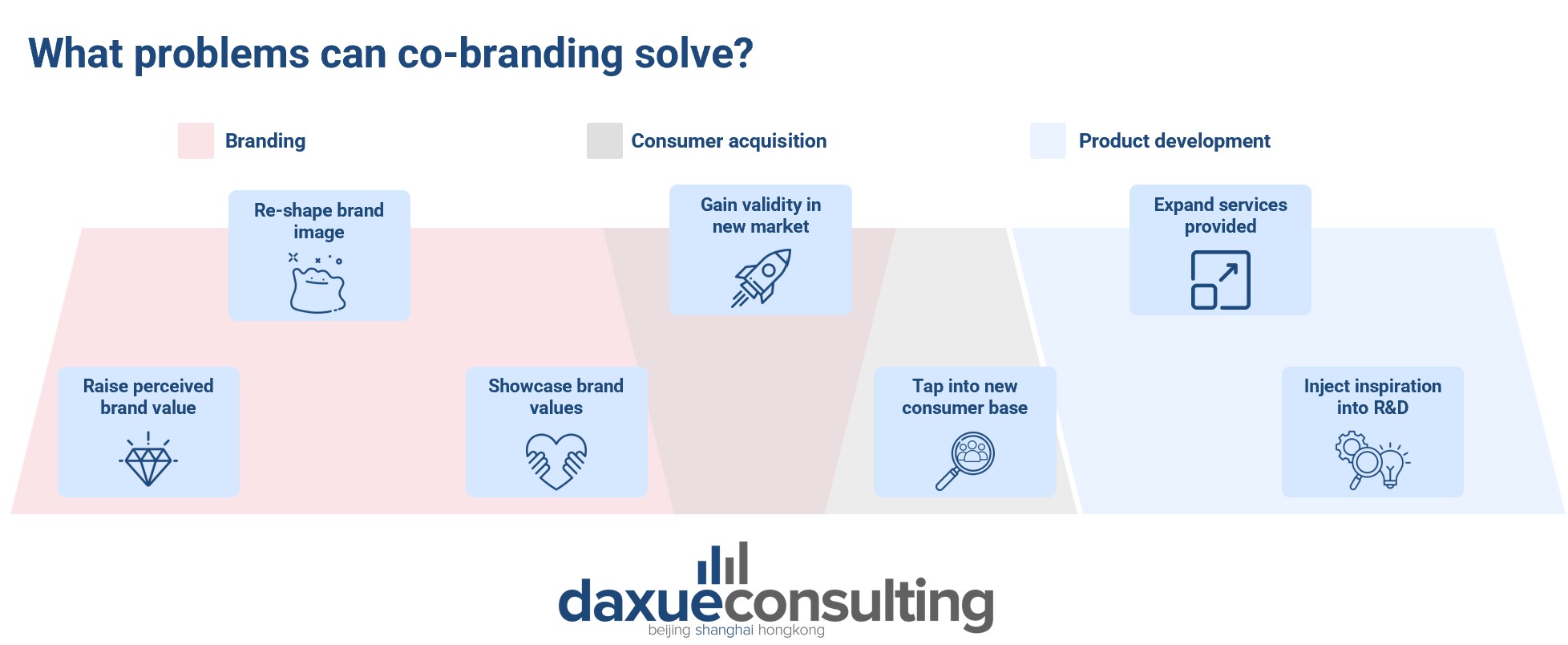
Co-branding for brand image
- Raise perceived brand value. Limited edition items and collaborating with high-value brands can raise the perceived value of a brand.
- Re-shape brand image. When co-branding, brands often adopt aspects of the other brand’s image, such as a youthful appeal or high-value.
- Showcase brand values. Co-branding is one way to showcase values like sustainability, charity, and cultural heritage (which is especially relevant in China)
Co-branding for consumer acquisition
- Gain validity in a new market. Co-branding with a reputable brand can help a newer brand jump-start their reputation in the Chinese market.
- Tap into new consumer bases. Co-branding allows brands to increase brand awareness in each-others’ consumer bases.
Co-branding for product development
- Expand service offerings. Rather than investing in adding more services, a brand can collaborate with entities that already provide those services.
- Inject inspiration into research and development. Co-creating a product can bring fresh perspectives to R&D.
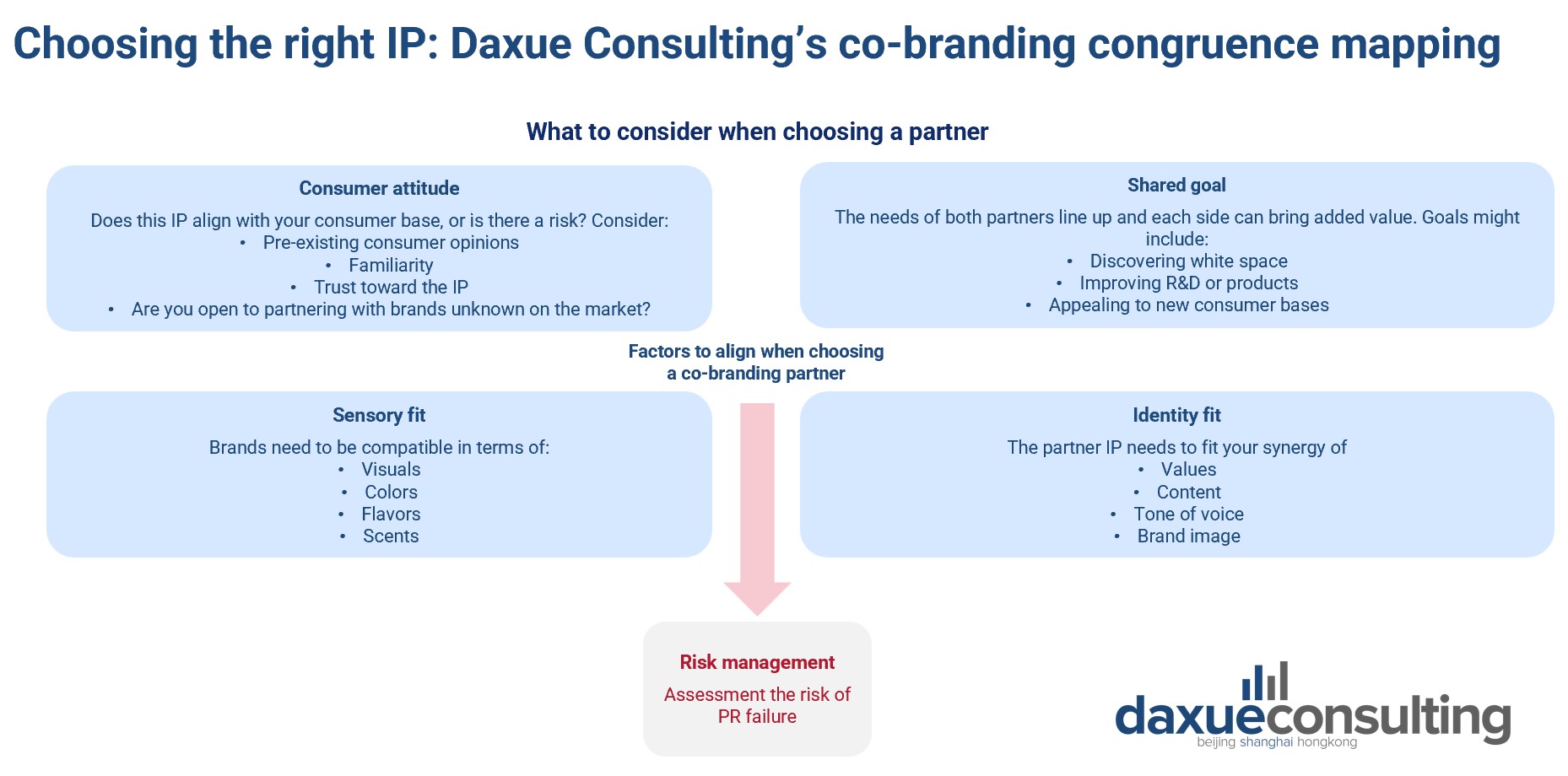
Choosing the right IP collaboration partner in China
There are many aspects to align when choosing an IP collaboration partner in China. Elements to align include consumer attitude fit, shared goal, sensory fit, and identity fit. All of this must also be balanced with risk management, is the partner prone to scandal and therefore risky for your brand? Is there a high or low risk associated with missing the mark in a new consumer base? Below is Daxue Consulting’s congruence mapping for choosing a co-branding partner in China.
In China, it is more common to collaborate with entities that are not simply consumer brands. Like mentioned above, it is very common for brands to partner with institutions like museums. In China, it is also more common than in the west to collaborate with cartoon character IP, especially while targeting adult consumers.

The most common industries for co-branding in China are the anime, comics and games market, followed by fashion and food and beverage. The size of the sections in the below visualization are relative to the prevalence and online buzz created by co-branding cases in the industry, based on our social listening research.

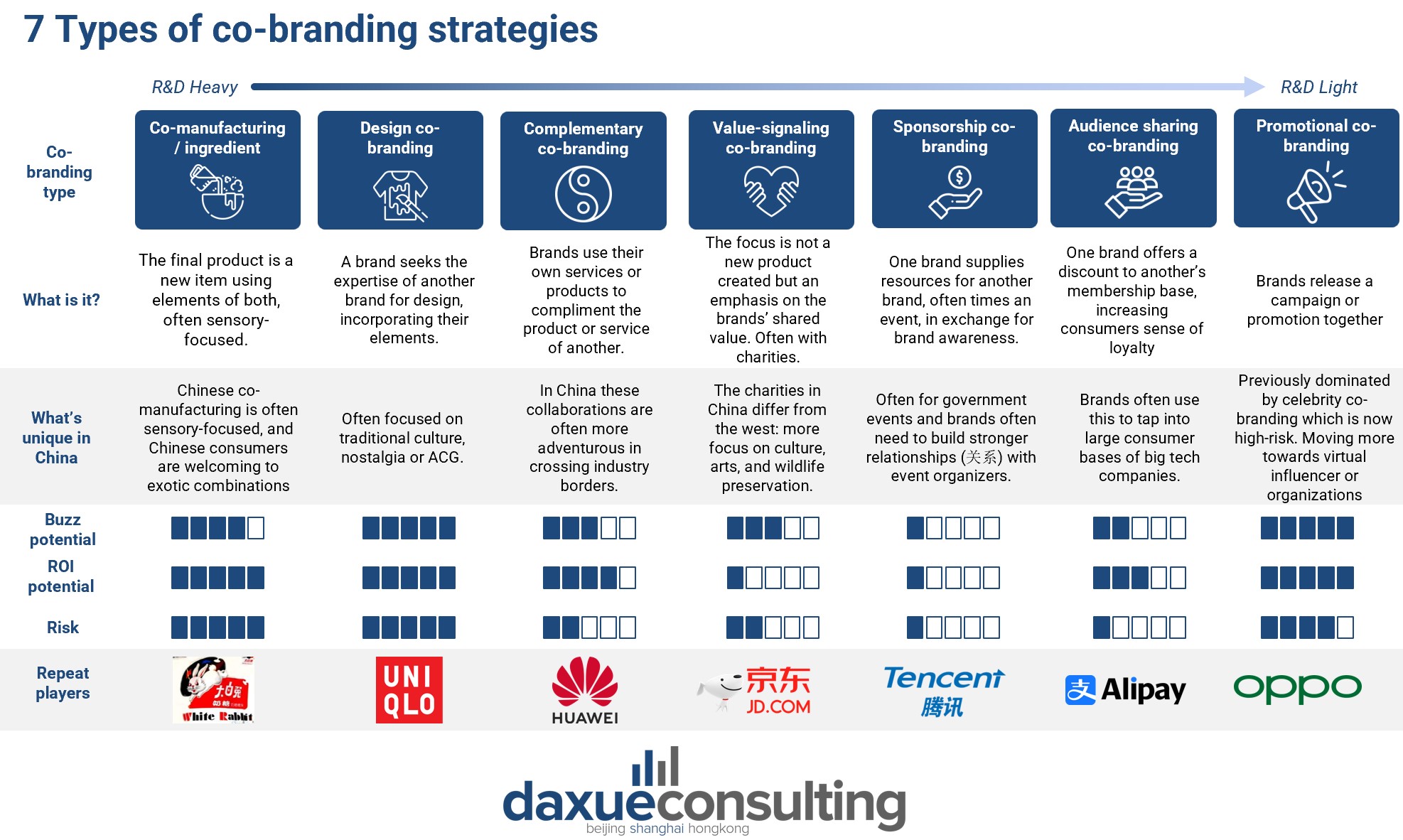
7 types of co-branding strategies
We identified the following kinds of co-branding types which are not mutually exclusive. These are listed in order on expected level of investment in research and development.
- Co-manufacturing or ingredient co-branding: The final product is a new item using elements of both, often sensory-focused. Chinese co-manufacturing is often sensory-focused, and Chinese consumers are welcoming to exotic combinations.
- Design co-branding: A brand seeks the expertise of another brand for design, incorporating their elements. In China, it is often focused on traditional culture, nostalgia or ACG.
- Complementary co-branding: Brands use their own services or products to compliment the product or service of another. In China these collaborations are often more adventurous in crossing industry borders.
- Value signaling co-branding: The focus is not a new product created but an emphasis on the brands’ shared value. Often with charities. The charities in China differ from the west: more focus on culture, arts, and wildlife preservation.
- Sponsorship co-branding: One brand supplies resources for another brand, often times an event, in exchange for brand awareness. Often for government events and brands often need to build stronger relationships (关系) with event organizers.
- Audience sharing co-branding: One brand offers a discount to another’s membership base, increasing consumers sense of loyalty. In China, brands often use this to tap into large consumer bases of big tech companies.
- Promotional co-branding: Brands release a campaign or promotion together. Previously dominated by celebrity co-branding which is now high-risk in China. Moving more towards virtual influencers or organizations

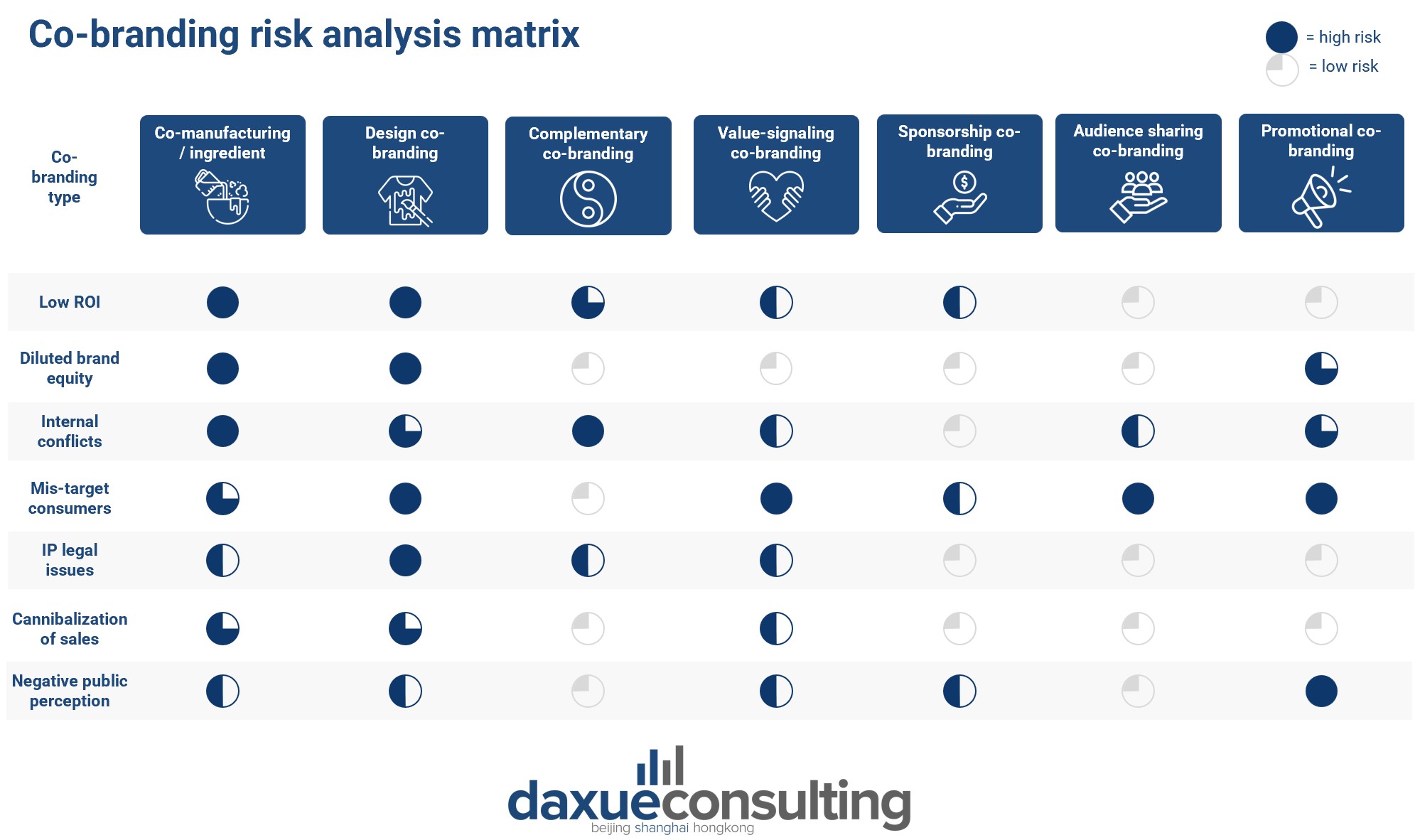
How to know what kind of co-branding strategy to choose?
Based on the client’s goals in co-branding or IP collaboration, we map out what potential avenues they can choose for strategy.

Of course, goals are not the only thing to align. There is also a different amount of risk with each co-branding strategy, below is our analyst’s map on the associated level of risk with each co-branding method.
Where to start your co-branding or IP collaboration campaign in China?
Daxue Consulting is experienced in IP collaboration projects and can help your brand find the ideal partner and strategy. Learn more about our co-branding method here and contact our consultants to get started on your China co-branding or IP collaboration campaign by emailing dx@daxueconsulting.com.





