Cloud computing has become a fundamental element of modern computing and mobile devices. It involves the integration of services, such as storage, databases, networks, and software which are not in a specific electronic device, but over the internet, or the “cloud”. The term gained prominence in 2006, when Amazon introduced AWS (Amazon Web Service) in collaboration with the business web-based service EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud).
The range of services in the cloud computing can be divided into three main groups: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Plus, it can be both private and public, depending on who owns that particular space on the internet.
Download our 10 Mistakes Chinese Brands Make when Going Abroad report

China is almost ready to challenge the US in the cloud computing market
China’s cloud computing market reached a revenue of more than USD 30 billion in 2022, marking a 10% increase from the previous year. However, China wants to push further its cloud services, expecting to increment the annual revenue to USD 90 billion by 2025. The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) dominates as the biggest cloud service, accounting for more than 75% of the overall market in Q1 2023.
Despite China boasts the second largest cloud computing market after the United States, American cloud computing companies still dominate the top 10 worldwide cloud services providers in 2023. At the top of the ranking, Amazon’s cloud service AWS is the biggest cloud computing service, with almost 32% of global market share, followed by Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. Alibaba Cloud is the first Chinese cloud provider in the list, ranking 4th, with around 4% of market share.
The Chinese government made huge investments to launch Chinese cloud computing services worldwide
The cloud market has particularly strong growth potential, underpinned by government initiatives and major investment by leading players in infrastructure and human capital. As an example, in 2020, the government announced an infrastructure plan to boost digital transformation, signalling China’s ambition to emerge as a strong global competitor in the cloud computing market, particularly against the United States. As part of a larger development strategy for advancing Chinese software and information technology services, the government plans to continue to make large investments over the next few years to drive development of cloud computing in China. As an example, in October 2023, it announced their main objective of boosting the Chinese cloud computing market by 50% by 2025.
Furthermore, China cloud computing companies are also targeting the South-East Asian market to compete with US for the dominance on this part of the world. Expected to reach a revenue of almost USD 13 billion by the end of 2023, the South-East Asian cloud computing market represents a huge opportunity for companies. Therefore, many Chinese cloud services providers, such as Alibaba Cloud and Huawei Cloud, have started investing for a hundreds of million USD in this sector to overcome US companies such as AWS. Placing low prices is the main strategy which Chinese providers are using in the South-East Asia market. Their services, indeed, are generally 20%-40% cheaper than the US companies.
Public cloud soars ahead of private In China there is a huge gap between public and private cloud computing. Indeed, the public cloud computing market is almost twice as large as the private cloud computing, and it’s growing faster too. In 2022, the public sector increased by 70% compared to the previous year, whereas the private one struggled to reach 30%. However, the private sector’s popularity is also growing year-on-year, reaching a revenue of more than USD 14 billion in 2021.
The biggest players in Chinese cloud computing market are domestic companies
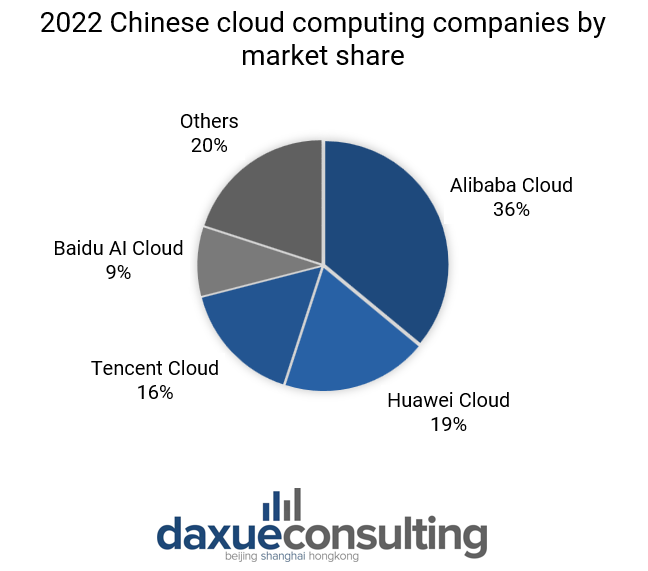
As of 2023, the biggest services for cloud computing in China are Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Baidu AI Cloud, which overall hold almost 80% of the total Chinese cloud market share. As of 2022, Alibaba Cloud detained took up 36% of the total Chinese cloud computing market share. Furthermore, the Chinese cloud company boasted a year-on-year growth of 4% in Q2 2023 and accounted for 8% of the total Alibaba Group revenue in 2022.
Huawei Cloud and Tencent Cloud are the other two biggest cloud providers in China, owning respectively 19% and 16% of the total cloud computing market share in 2022. Nevertheless, the substantial gap between them and Alibaba underscores the enduring popularity of the latter.
Strict laws and regulations to manage cloud technologies are the reason why most of the biggest competitors in this market are domestic companies. Foreign cloud services firstly need a license released by the government for entering the market, and their users’ data can only be stored in China. Foreign cloud companies which entered China such as AWS cannot be seen as a single unit, but the provider is divided in regions and operated independently due to the Chinese requirements and laws for data safety. For example, the Beijing region is operated by the internet data center Sinnet, whereas in the Ningxia region, AWS is linked to another Chinese cloud data center called NWCD (Ningxia Western Cloud Data).
Alibaba Cloud is the biggest cloud computing provider in China
With a worldwide revenue of more than USD 11.7 billion in 2022, Alibaba Cloud is the biggest cloud computing service in China. It opened to third-party customers in 2009 and offers a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including web hosting, elastic computing, data migration, database, storage and content delivery networks, large-scale computing, security, and management and application serves.
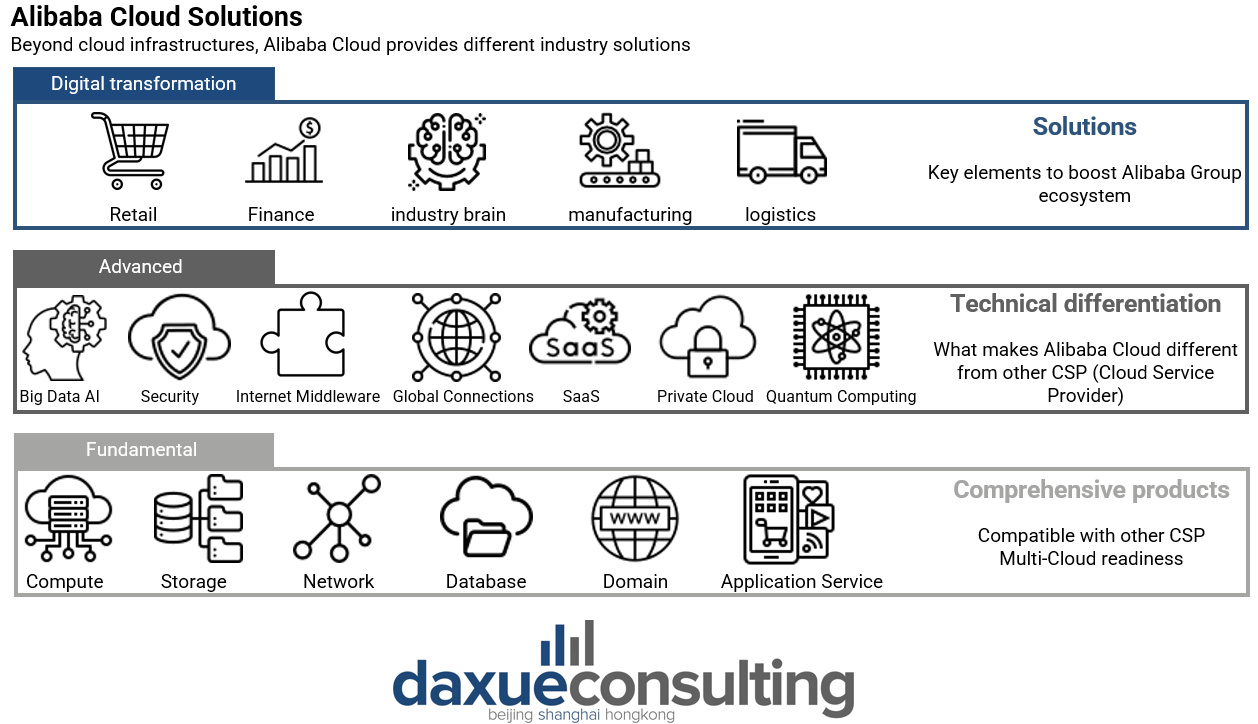
One of Alibaba Cloud’s biggest strengths lies in its wide network. Indeed, as of 2023, the company can operate in 89 data centres situated in 30 locations across the world and half of them are only in China. Other than previously mentioned domestic competitor, AWS represents the biggest foreign player to challenge Alibaba Cloud. However, the latter outperforms the American cloud provider both for its interconnections and price. Indeed, Alibaba Cloud can count on a wide network consisting in approximately 2,500 data distribution centres spread across 31 Chinese regions as of September 2023. Therefore, the service provided by the company is quicker and cheaper than any other foreign cloud.
Cloud computing in China: public vs private and Alibaba’s dominance in the market
- China’s cloud computing market reached over USD 30 billion in 2022, with a 10% YoY increase, targeting USD 90 billion by 2025, primarily driven by Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Despite being the second-largest market, Chinese cloud companies, including Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Baidu AI Cloud, face strong competition from dominant American players like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- China aims to challenge the U.S. in the global cloud computing market, with substantial government investments and initiatives to boost digital transformation, planning to increase the Chinese cloud computing market by 50% by 2025.
- Chinese cloud services providers are targeting the Southeast Asian market with significant investments, particularly Alibaba Cloud and Huawei Cloud, offering lower prices (20%-40% cheaper) compared to U.S. competitors.
- In China, the public cloud computing market is nearly twice as large as the private cloud computing market, growing faster. In 2022, the public sector increased by 70%, while the private sector struggled to reach 30%.
- The biggest players in the Chinese cloud computing market are domestic companies, with Alibaba Cloud leading with a 36% market share, followed by Huawei Cloud (19%) and Tencent Cloud (16%). Strict laws and regulations make it challenging for foreign companies to compete.





