Sharing economy is an economic model where the Internet is leveraged by businesses to pair customers with service providers. It reorganizes the scattered resources and satisfies diversified economic needs. In China, the development of its sharing economy can be categorized into three stages: introduction (2000-2008), start-up (2009-2012), and growth (2013-present). Currently, China’s sharing economy is experiencing an upswing due to technological advancements and significant financial investments, despite the setbacks caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The market’s transaction size increased from 1.81 trillion RMB in 2015 to 3.83 trillion RMB in 2022. Despite the significant impact of COVID-19 on the industry and the considerable decrease in the size of direct financing, the transaction volume in 2022 still managed to achieve a 3.9% year-on-year growth.
An overview of the 7 sectors of China’s sharing economy
The State Information Center of China has identified seven sectors that form China’s sharing economy which are domestic services, production capacity, knowledge, and skills, shared transportation, shared healthcare, co-working space, and shared accommodation. The performance of domestic services, shared healthcare, knowledge and skills, and production capacity sectors showed improvement in 2022 as compared to the previous year. In contrast, the other three sectors were severely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
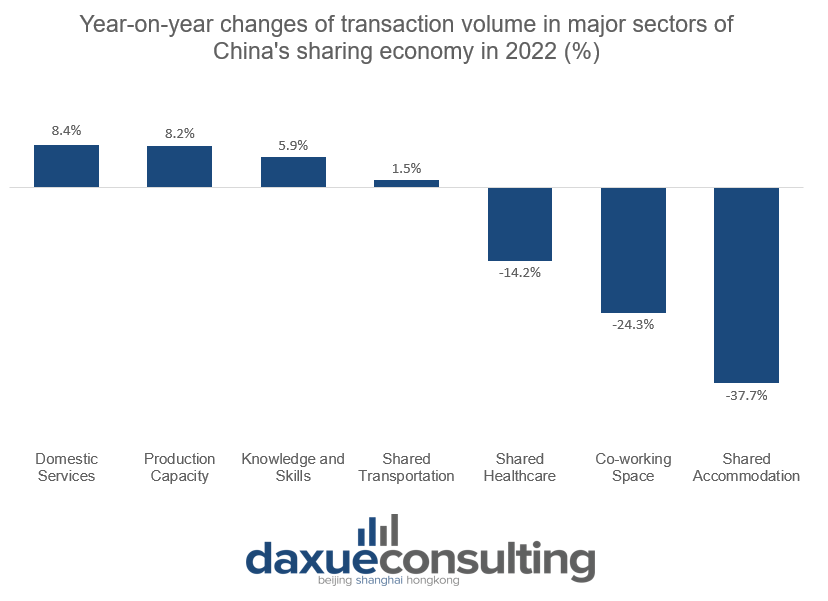
China’s sharing economy sectors that thrive despite COVID-19
In 2022, the domestic services, shared healthcare, knowledge and skills, and production capacity sectors withstood the huge pressure from COVID-19 and showed positive growth in transaction volume. The year-on-year growth rate of the transaction volume in each sector is 8.4%, 8.2%, 5.9%, and 1.5%, respectively. The COVID-19 outbreak across China and subsequent lockdowns increased public demand for services in certain sectors. As a result, these sharing economy companies expanded the variety of services that they offer.
Domestic services sector:
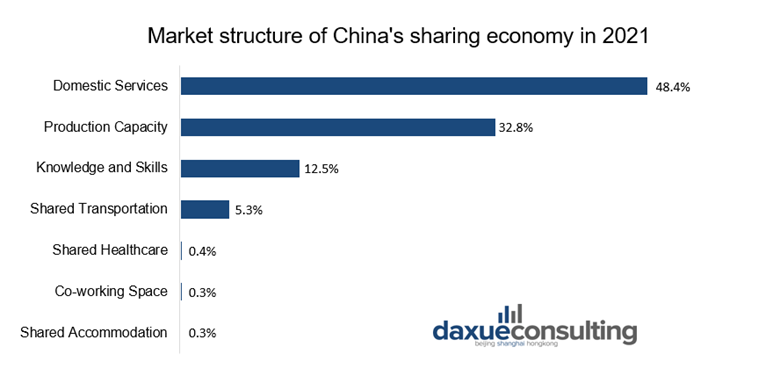
The domestic services sector has owned the largest market share of China’s sharing economy for years. In 2022, it contributed 48.4% of the transaction volume in the whole market. The State Information Center of China defined it as a type of economic activity that relies on online platforms to integrate offline dining, home care, beauty, delivery, and other life service institutions. It also reorganizes idle resources such as personal time and skills to provide consumers with more convenient ways to meet their needs for domestic services. Besides, due to the “stay-at-home economy” (宅经济) brought on by COVID-19, Chinese online consumption demand surged. Hence, companies in the domestic services sector played a crucial role in ensuring the provision of essential goods and services.
Meituan (美团), China’s leading e-commerce platform for services, upgraded its intra-city logistics system to ensure its ability to fulfill orders and maintain service quality. In addition to expanding the storage and sorting facilities, it also increased its frontline sorting personnel nationwide by 70%. At locations which are severely impacted by the pandemic, Meituan increased the number of delivery personnel by 1.5 times compared to locations that were less affected. The utilization of idle human resources through these strategies during the pandemic effectively met the pressing consumer needs for food, groceries, and medicine.
Shared healthcare:
The sharing economy applies to healthcare by utilizing online platforms to bring together a diverse and widespread collection of specialized healthcare resources. Healthcare resources can be fully utilized since the healthcare providers match their healthcare resources, such as medical knowledge and nursing services, with the demand side. In 2022, this sector had the second-highest increase in transaction volume compared to the six other sectors. This was due to the rising demand for online healthcare services from the public, which was caused by both the COVID-19 outbreak and prolonged nationwide lockdowns in China.
By June 2022, there were 300 million people who used shared healthcare services in China, accounting for 28.5% of the total number of internet users in the country. Correspondingly, the companies in this sector increased the scope and variety of their services to meet the high level of demand. As of the end of 2021, 85% of cities, and 69% of counties in China had set up regional health information platforms. Meanwhile, over 7,000 public hospitals joined the shared healthcare platforms.
Knowledge and skills sector:
Knowledge and skills sharing is sharing the individual or institutional dispersed and intellectual resources with individuals or organizations through online platforms. The use of intellectual resources in society is then maximized. Meanwhile the production and service needs are met with higher efficiency and lower costs. In recent years, the combination of the internet with traditional sectors like education, professional advancement, and business development. This resulted in the emergence of several specialized sharing platforms across a variety of fields in China. Meanwhile, people in China also had a surging dependence on online platforms for education due to the “Suspending Classes Without Stopping Learning” policy published by the government. For instance, video conferencing platforms like VooV Meeting (腾讯会议) that helps teachers to teach online. Besides, online education platforms like Zuoyebang (作业帮) support students’ studies and enhance their self-discipline by providing online tutoring services.

Production capacity sector:
Sharing economy in the production capacity sector refers to a new production model where the idle production capacities in different companies are integrated through online platforms. Production capacity sharing can be categorized into crowdsourced production and business collaboration, based on the distinct business scopes of the companies seeking additional production capacity. Crowdsourced production is commonly carried out by sales-focused companies. These companies outsource the entirety of their production processes to suppliers who possess idle production capabilities. While these companies can achieve personalized customization, innovative production, and cost savings, the suppliers can attain operational efficiency and cost reduction. On the other hand, a business collaboration model is normally practiced by manufacturing-focused companies by outsourcing some of their business operations such as assembling and packaging to the suppliers. As a result, operational efficiency, time management, and cost reduction on both sides can be achieved.
Shared transportation, shared accommodation, and co-working space sectors experienced a market downturn
From 2021 to 2022, the transaction volume of shared transportation, shared accommodation, and co-working space sectors decreased by 14.2%, 24.3%, and 37.7% respectively. Such a market downturn in these three sectors is attributable to the impact of COVID-19 on consumer behavior. Due to the nationwide lockdown in 2022, consumers were unable to go out to engage in social activities, travel, and work. Thus, their need for transportation, accommodation, and workplace, in general, were minimized during the lockdowns.
Shared transportation:
Shared transportation refers to integrating idle vehicles, carpooling space, driving skills, and other transportation-related resources through online platforms. With the support of big data, the supply and demand for traveling can be efficiently matched. Over the past few years, the whole sector experienced a fluctuating growth rate in transaction volume. After having a 3.0% year-on-year growth rate in 2021, the number dropped to -14.2% in 2022. And the reason behind such a decrease in the market size is the nationwide lockdown in China that lasted for months. The public’s demand for shared transportation, including shared options, decreased as a consequence. The volume of orders made on ride-hailing platforms such as DIDI Chuxing (滴滴出行) in 2022 experienced a 16.8% decline compared to the previous year.

Shared accommodation:
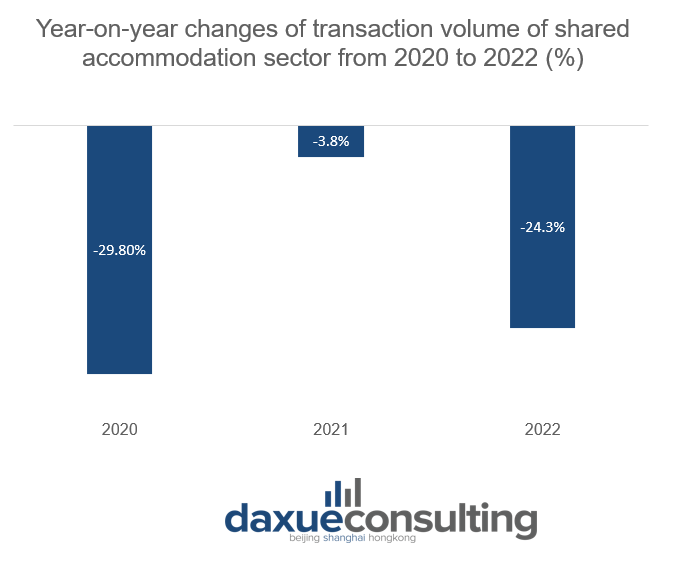
Shared accommodation is defined as utilizing online platforms to offer short-term lodging to tenants by consolidating details of unoccupied residential properties that are either owned or rented. Some of the major platforms in China are Tujia (途家网), Xiaozhu (小猪), Mayi (蚂蚁短租), Meituan (美团民宿), Muniao (木鸟民宿). The sector’s market size has been decreasing for three consecutive years due to the nationwide lockdowns in China in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Besides, the volume of transactions in this sector decreased in 2020 by 29.8%. It was then followed by a 3.8% decline in 2021, and a further 24.3% decrease in 2022. The further reduction in the number of transactions in 2022 is due to the decreased demand for travel, as indicated by the 22.1% year-on-year decrease in the number of domestic tourists in China in 2022. As a result, the need for short-term accommodation has also declined.
Co-working space:
Co-working space refers to a workplace model where companies share an environment that is specifically designed and arranged for individuals to work independently on their projects. Three major reasons why companies choose to join the co-working space are the ease of entry, cost savings on office rentals, and a conducive working environment. However, the co-working space sector faced significant challenges in 2022, with a noticeable 37.7% year-on-year decrease in transaction volume. The exit of many companies during the pandemic has created a substantial strain on the remaining companies in this sector. Ucommune, one of the few remaining co-working companies, posted a net loss of 2.163 billion RMB in 2021, which represents a significant year-on-year decline of 325.8%.
How businesses can turn challenges into opportunities:
Companies in China’s sharing economy industry are confronted with challenges. However, with the right mindset, they can turn these challenges into opportunities.
COVID-19 has caused a significant economic downturn in the past three years. However, it has also led to increasing demand for the sharing economy as consumers look for ways to save money. This presents an opportunity for companies to capitalize on this growing trend and adapt their business models to meet this demand.
Due to the sharing economy’s relatively short history in China, there is concern that the market can be disorganized, and the current system may not be operating effectively. However, on the other hand, the short industry history indicates the huge room left in the market for innovation and new applications.
Trust issues have been a major concern for consumers when it comes to the sharing economy. To address this, companies can improve the credit guarantee schemes on platforms and partner with credit reporting agencies to enhance the credit identification and management of users. This can lead to increased trustworthiness among users and enhance their overall satisfaction with the service.
China’s sharing economy amidst COVID-19 pandemic
- Despite setbacks caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the sharing economy in China had a 3.9% year-on-year growth in transaction volume in 2022.
- Domestic services, production capacity, knowledge and skills, shared transportation, shared healthcare, co-working space, and shared accommodation are the 7 sectors of China’s sharing economy.
- Although COVID-19 presented challenges, the domestic services, shared healthcare, knowledge and skills, and production capacity sectors in China sharing economy still showed positive growth in transaction volume.
- The shared transportation, shared accommodation, and co-working space sectors in China’s sharing economy saw a significant decline in market size in 2022, which is mainly due to changes in consumer behavior caused by COVID-19.
- By adopting a proactive approach, companies in the sharing economy industry can overcome the challenges posed by COVID-19, short industry history, and trust issues among the users.
Author: Sandra Chen





