The Chinese tech industry’s global prominence has surged, driven by factors such as government support, a vast domestic market, and a culture of entrepreneurship. Companies like Huawei, Tencent, Alibaba, and Xiaomi have risen to international prominence in sectors such as telecommunications, e-commerce, gaming, and artificial intelligence. Foreign tech investments in China have played a crucial role, allowing these giants to expand their reach, acquire cutting-edge technologies, and foster global innovation. It is estimated that Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) in China’s high-tech manufacturing and high-tech service sectors increased by 48.6% and 27.9% respectively, from 2021 to 2022. These investments have not only fueled growth but also solidified China’s position as one of the major players in shaping global tech trends and standards.
Download our report on Gen Z consumers

Driving forces behind foreign tech investments in China
The driving forces behind technology FDIs in China are multifaceted. The increasing interest of global investors in China’s tech sector can be attributed to China’s expansive consumer market and the emergence of innovative business models. Furthermore, China’s comprehensive manufacturing ecosystem facilitates the process of multinational corporations translating their state-of-the-art technologies into market-competitive products.
What does China gain from foreign tech investments?
China’s heavy dependence on foreign technology has been a pivotal driver of its economic growth. First, foreign investment has spurred technological progress in China’s tech sector. An example is the partnership between Tesla and the Shanghai government to build the Gigafactory in China. This investment contributed to the economic growth of the country, by creating more than 19,000 jobs. Moreover, through the training provided by Tesla, the Chinese workforce can develop their skills. The presence of foreign tech firms can also stimulate the technology ecosystem in China, attracting talent and encouraging local innovation to compete.

Secondly, these overseas investments facilitate the expansion of Chinese tech firms into international markets, enabling them to establish a global presence and diversify their revenue streams.
Lastly, FDIs can also contribute to enhanced competitiveness and innovation. The competitive nature of China’s tech sector is exemplified by the rivalry between Tencent and Alibaba. Both companies have received investments and support from various foreign entities. This competition has driven innovation in areas like e-commerce, mobile payments, and cloud computing, benefitting not only the companies themselves but also consumers and businesses through improved services and products.
China’s tech crackdown’s impact on Chinese firms and foreign investors
In 2020, the Chinese government wished to relinquish control over private technology companies after witnessing that their rapid growth was detrimental to the Chinese Communist Party’s power. The regulatory tightening and increased scrutiny of tech companies in China have created an environment of uncertainty and caution among foreign investors. As a result, big tech companies lost over RMB 7.3 trillion in market capitalization of Hong Kong-listed stocks in the past two years. Alibaba Group, Tencent, Meituan, and Baidu are prime examples of this crackdown, with their stock value plummeting towards the end of 2020 or the beginning of 2021. It is estimated that the beginning of this massive crackdown was marked by the shelving of Alibaba affiliate Ant Group’s RMB 270 billion IPO in late 2020.
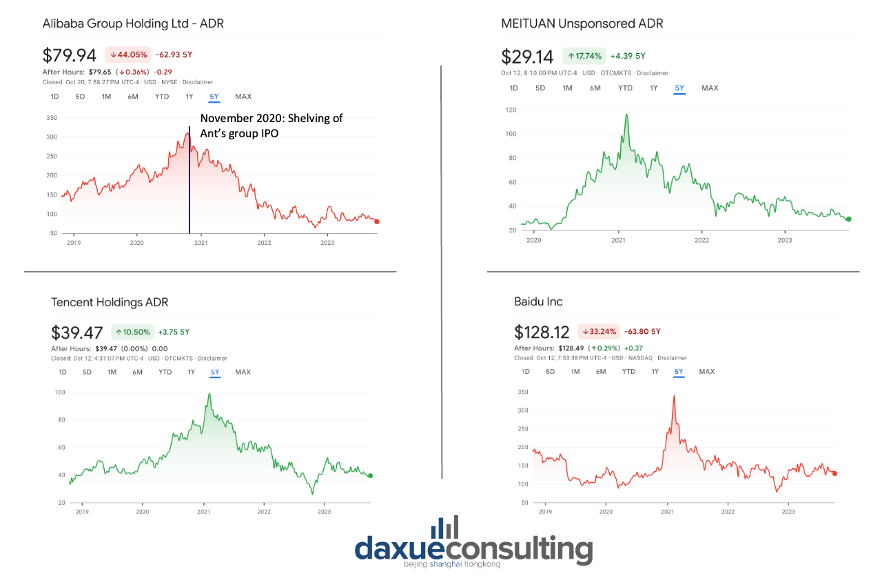
At the beginning of 2023, Chinese officials promised greater access to foreign investors. Moreover, China’s state planner acknowledged the contributions that Tencent and Alibaba made in terms of tech innovation. This appears to be a sign that the Chinese government is becoming more favorable to the technology sector again.
Recent regulations to limit foreign tech investments in China
US curbs investments in certain Chinese tech sectors
The US government’s restrictions on investments in sensitive areas, such as technology and national security-related industries, have made it more challenging for Chinese firms to access crucial funding and resources in the United States. The US is aiming to limit China’s access to advanced technologies, that could potentially be used in wars and threaten the US’ national security. The restriction includes an interdiction or restriction of new US investments in certain technologies, including semiconductors and microelectronics, quantum information systems, and some AI systems, in mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao. The measure focuses on private equity, venture capital, joint ventures, and greenfield investments.
Chinese tech companies and startups face challenges
US investments in Chinese companies were already in decline due to the strained relationship between the two countries, declining from RMB 10.1 billion in 2021 to RMB 3.2 billion in 2022. In August 2023, US investments reached RMB 2.8 billion. Recent US regulations restricting investments in specific sectors have placed Chinese tech companies and start-ups in an even more challenging position.
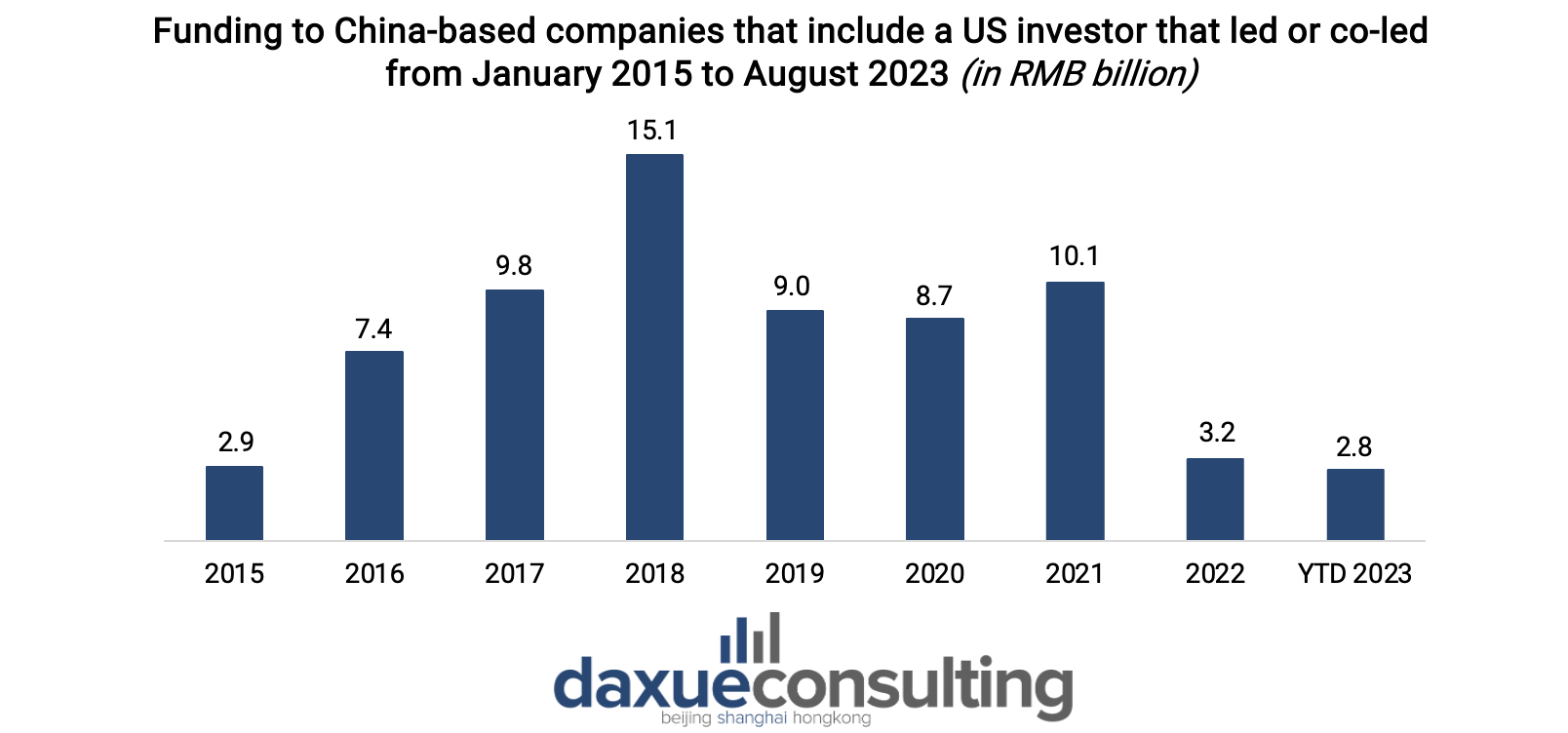
This new measure could prompt some Chinese tech companies to go public in mainland China rather than in the US, negatively affecting US venture capitalists. Moreover, Chinese companies could be forced to seek alternative sources of investment and partnerships, both domestically and in other countries, to sustain their growth and innovation efforts.
China’s response to the US measures
China’s foreign ministry was unhappy with this measure taken by Biden’s administration and reserves the right to retaliate. This measure is seen by China as a way of “hindering global economic and trade exchanges”, and a massive obstacle to the world’s economic recovery. The impact of this measure on diplomatic relations between the US and China appears significant as it has contributed to heightened tensions in an already strained relationship.
The UK is following the US’s lead
The British government is contemplating stricter regulations on investments in China following the announcement of new measures by the US president. The UK Foreign Secretary, James Cleverly, outlined the country’s revised strategy, emphasizing the need to safeguard national security by mitigating potential threats from China while actively participating in domains like trade, investment, and climate crisis initiatives. However, this stance has encountered resistance from businesses. A senior executive at HSBC characterized the UK government as “weak” for yielding to U.S. government pressure to adopt a more adversarial approach to conducting business with China.
Chinese tech companies stay strong without foreign investments
Chinese tech companies have demonstrated remarkable resilience and continued to thrive despite US sanctions. In September 2023, Huawei launched its latest smartphone, the Mate 60 Pro, equipped with a Kirin 9000S chip with advanced capabilities like an integrated 5G modem. The chip was made locally, by China’s largest semiconductor manufacturer SMIC. This has drawn the attention of US policymakers. They question how, despite restricting China’s access to advanced chips, the country has not slowed down its chip design capabilities but has continued advancing.
In 2019, the Trump administration imposed several sanctions that severed Huawei’s access to critical technologies, encompassing 5G chips, Google software, and its state-of-the-art mobile processor. These technologies have played a pivotal role in propelling Huawei to its status as the world’s largest smartphone manufacturer. As a result, Huawei suffered a 41% year-on-year decline in sales in Q4 2020.
Huawei’s ability to withstand foreign sanctions underscores the resilience and innovative capabilities of China’s tech industry.
What we can learn from foreign tech investments in China:
- Foreign tech investments have played a vital role in propelling China’s tech industry to global prominence. Companies like Huawei, Tencent, Alibaba, and Xiaomi have benefited from overseas investments, expanding their reach and acquiring advanced technologies. This has contributed to China’s rapid growth in sectors such as telecommunications, e-commerce, gaming, and artificial intelligence.
- Recent regulatory tightening and scrutiny in China have created uncertainty among investors. Big tech companies, including Alibaba, Tencent, Meituan, and Baidu, have seen significant losses in market capitalization. This crackdown, paired with US restrictions on investments, has forced Chinese tech companies to seek alternative sources of funding and consider going public in China.
- Nevertheless, Chinese tech firms, like Huawei, have displayed remarkable resilience, maintaining innovation and self-sufficiency despite foreign sanctions and restrictions. This evolving landscape emphasizes China’s determination to become a global tech powerhouse.