Green buildings have established themselves as a key element in the future development of the Chinese economy. In fact, 25% of energy consumed in China is attributed to buildings. The green building industry’s expansion is occurring quickly. While the first green building was built in 2005, today there are more than 1 billion square meters rated as green. The phenomenon is estimated to reach large scale. China was one of the first countries to develop the concept of green buildings. For example, Beijing and Shanghai have even more green space than Chicago. However, those buildings are still far from being common in Chinese streets. Most buildings in China are high energy consuming meaning the industry’s potential growth is extremely high.
Sustainable buildings in China are a part of a greater development strategy
Throughout the last three decades, China has experienced unprecedented and hasty urbanization. The country developed approximately 2 billion square meters of new buildings each year. Many of the buildings have been criticized for not being energy efficient due to little insulation and insufficient heating/cooling systems. As the largest contributor of CO2 emissions worldwide, the Chinese government is making large efforts to reduce pollution and become greener. The committee of construction energy saving declared the implementation of sustainable buildings in China in now treated as a country developing strategy.
Green building development in China can save resources, reduce pollution, and create a relatively healthy living environment. According to the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, China’s green building evaluation standards divide green buildings into three levels: one star, two stars, and three stars. The evaluation of green buildings mainly focuses on the elements of “four sections and one environmental protection”, namely energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving and environmental protection.
The Ministry of Finance has issued relevant documents and other policies, urging both the government and other departments to strengthen coordination to accelerate the development of eco architecture in China. For example, national economic and social development planning outline for 2011–2015 formally proposed that the construction industry should promote green buildings and eco architecture. Local governments of first-tier cities also developed economic incentives to increase the growth rate of green buildings in China.
China’s national policy supports green buildings development
The government is planning that at least half of new buildings will follow the green standards by 2020. Following through on these commitments would grow the country’s green building sector from 5 to 28 percent by 2030, representing a $12.9 trillion investment opportunity. Besides, this will enable to enhance society production of 500 billion RMB and would create at the same time 5 million additional jobs. 13th Five Year Plan also specifies pilot programs for constructing and renovating energy efficient primary and secondary schools, community hospitals and public buildings. As the national Five Year Plan is cascaded to provincial and municipal jurisdictions, nearly 20 cities have set even more ambitious targets. For example, Changde, Zhenjiang, Zibo, Wuxi, and Suzhou, Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, and Chongqing require all new commercial buildings to be green buildings. In the pursuit of more sustainable buildings, more than 90% of China’s commercial building owners plan to have at least one net or near-zero energy building in the next ten years.
By the end of 2016, more than 20,000 green buildings were built. According to data released by the China Real Estate Association, as of the end of December 2017, a total of 10.927 green building indication projects were evaluated nationwide, an increase of more than 3,000 over the previous year.
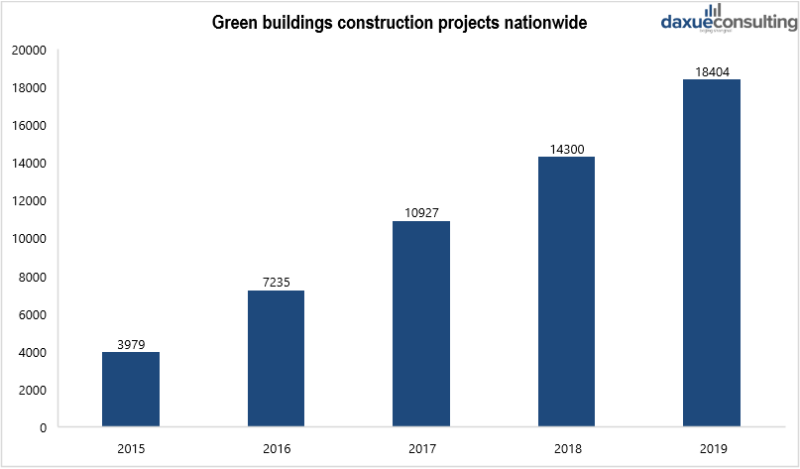
[Data source: qianzhan, ‘Construction projects of green buildings in China 2015-2019’]
Loans for green buildings in China are rising steadily
Government and banks promote green financial mechanisms such as green bonds, green credit, and green funds to develop eco architecture in China. Around 118.34 billion yuan is required to complete the 2 billion square meters green buildings target. The energy-saving upgrading of existing residential buildings is estimated to cost 350 billion yuan and the reconstruction of public buildings requires 60 billion yuan. The total demand for financing of green building in China will exceed 600 billion yuan.
Report released in December 2017 by the former China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC) showed that 21 major Chinese banks had issued green credits totaling RMB 8.22 trillion among 12 green categories in the first half of 2017. For green buildings was issued a total of RMB 730 billion in green credits from 1H 2013 to 1H 2017.
In terms of green bonds, there are two types of them: labeled (issued by diversified companies) and unlabeled (pure-play issuers). The issuance of green construction bonds in China began in 2017, with a small total number of issuances. In that year, only five were issued with a total size of 4.51 billion yuan. In 2018, the number increased to 12 green construction bonds with a total amount of 8.72 billion; in the first half of 2019, bonds for green buildings development in China totaling 2.2 billion yuan. Over the past two years, China has issued 15.43 billion yuan of bonds invested in green construction.
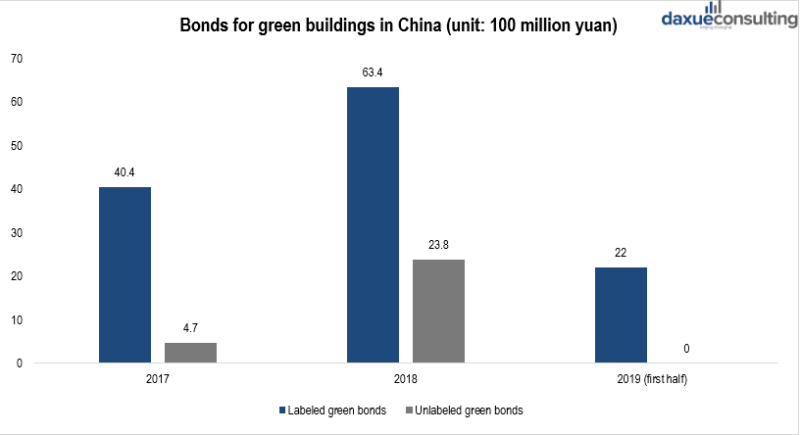
[Data source: tanpaifang, ‘Bonds for green buildings in China 2017-2019’]
SOARING DEMAND FOR GREEN BUILDINGS IN CHINA
Due to fast economic development, the urbanization rate in China will increase from 50% in 2012 to 70% in 2030, indicating a significant demand for new buildings in urban areas. Every year the total area of new buildings is up to 2 billion square meters, consuming 40% of the world’s cement and steel. Besides, buildings in China have a relatively short life expectancy of about 30 years, while in European countries it is around 80 years, and 44 years in the USA. Consequently, it is critical to initiate green building efforts so as to alleviate the potential impacts from the building sector.
Sustainable buildings in China have different degrees of improvement in indoor air quality, thermal environment, light environment, and acoustic environment. Higher rents, energy and water efficiency, better air quality, sustainability, lower operation cost, a high-quality work environment-all these factors have facilitated overall comfort and driven demand for green buildings in China.
Drivers of the green building market in China
The latest report shows that the growth of green buildings market in China is largely driven by customer demand, environmental regulations, and health-minded communities. The market achieved a five-fold increase in share from 5% to 28% by 2018. New eco homes, hospitals, and public schools are seen as the three most important areas of green building growth. Increasing consumer demand has turned the green buildings market in China into an industry with an output value of 15 trillion yuan in 2017.
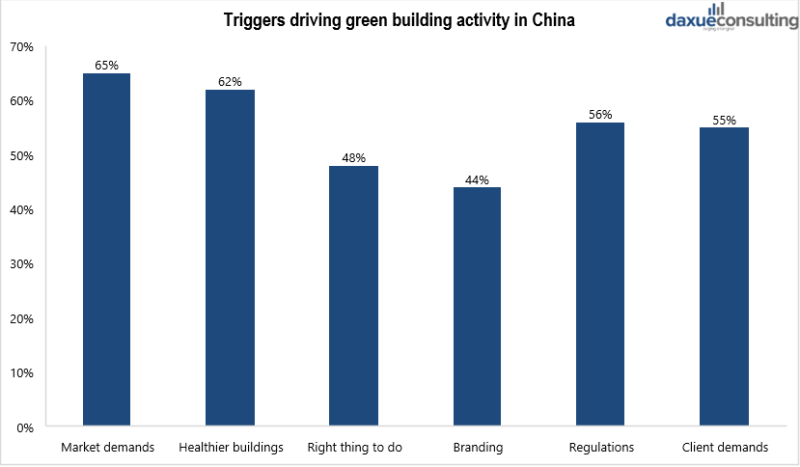
[Data source: Smart Market report, ‘Triggers driving green buildings activity in China’, 2018]
Due to soaring demand, green buildings companies increase their influence in China’s construction market. Recently, Times Media released TOP20 of China’s green housing companies in 2019. The total green building areas of Vanke, Country Garden, and China Evergrande reached 35.02 million square meters, 34.2 million square meters, and 31.31 million square meters, respectively, ranking among the top three. The green building area of the three leading real estate companies totaled 105.3 million square meters.
New building standards in major cities contribute to the growing demand
Chinese standards require a reduction of the total land used for building construction. Moreover, because of energy shortages and dependence on fossil fuels in China, standards have rigid requirements for energy saving and energy structure optimization for building sectors. Additionally, they require an increase in total green area (trees or grass), namely, total greening rate should be higher than 30% of the total project floor area. In 2019, more than 2,400 projects with an area of more than 133 million square meters were participating in LEED (Local Economic and Employment Development). According to the organization of LEED (Local Economic and Employment Development), green buildings can save 40% of water, 70% of deserting material and reduce carbon emission by around 35%. In 2019 LEED-certified space in Beijing, Shanghai, Suzhou and Shenzhen totaled 43 million square meters.
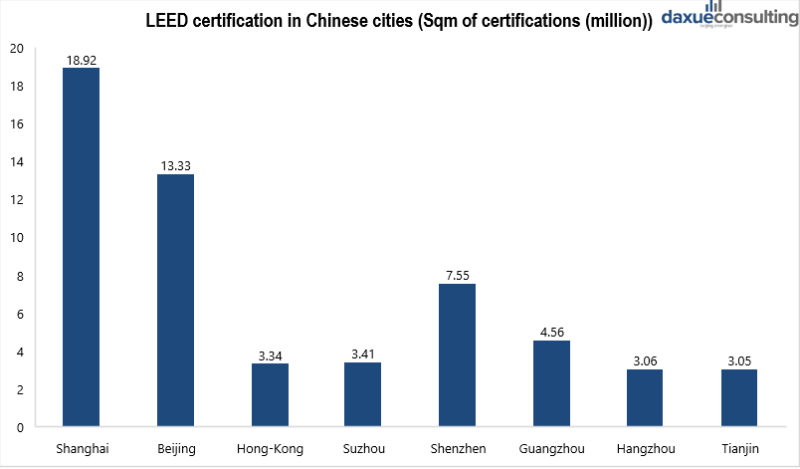
[Data source: LEED in progress, ‘LEED certification in Chinese cities (Sqm of certifications (million))’, 2019]
The implementation of green building standards is becoming more and more stringent in various places, and major cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen have proposed that land acquisition must meet the two-star domestic green building. It contributes to a demand in the green buildings market in China.
High capital value of sustainable buildings in China
In the past three years, the average capital value of green buildings is higher than non-green ones. Strong demand, good tenant allocation, and higher rents also have a positive impact on the capital value of green buildings. For example, office buildings with green certification usually have higher rents than the market rents of traditional office buildings. From the perspective of energy conservation and environmental protection, green buildings have an advantage in attracting high-quality tenants. At the same time, high-quality tenants and the green premium of rents have a positive impact on the capital value of the property and the return on investment.
Building owners point out that green buildings, whether newly built or remodeled, result in a 7% increase in asset value over traditional buildings. For example, from 2012 to 2018, the stocks of green office buildings in Shanghai increased by 9.1 times. Moreover, most of future construction projects plan to apply for green building certification and enter green buildings market in China. In the past three years, the average capital value of green office buildings in Shanghai has been higher than that of non-green office buildings. In the third quarter of 2018, the average capital value of non-green office buildings in the city was 69,680 yuan per square meter, while the capital value of green-certified office buildings reached 76,411 yuan per square meter, with a premium rate of 9.7%.
China is a global leader in green buildings
Eco architecture in China is based on the constant stimulation of government policy, the constant innovation of scientific research, continuous improvement in the standard system, and continuous technological innovation. Green buildings are moving seeing new dynamics. Today, 80% of domestic green projects are located in the top 10 Chinese provinces showing the potential growth expected by less developed cities of China. Green building growth will also be accompanied by the development of larger amount of green commercial buildings since today only 30% of total green buildings are commercial. At the end of 2016, China had selected more than 4,500 green building assessment identification projects, accounting for more than 500 million square meters of green buildings. According to 2017 China Green Building Report, the green buildings development in China has been accepted by more and more property developers and local governments.
This has already made China the world’s second-largest market for LEED-certified projects, trailing only the United States. Major developers including Soho China, Excellence Group, Sino Ocean Group and Ping An actively engage in green buildings market in China.
Best green buildings practices: Changning, Wuxi, Suzhou
Changning
Shanghai’s Changning District put in place an energy monitoring platform that tracks 160 of the district’s 165 public buildings. Thanks to the project, 32 buildings have been retrofitted to achieve an average 20 percent energy savings. To encourage the remaining 133 public buildings to renovate, the district is considering using a third-party ranking system to rate buildings on their energy performance. The district also provided $3.34 million in subsidies to help building managers make their buildings more efficient. This lowered the payback period for the private sector, which in turn encouraged them to invest an additional $20.33 million.
Wuxi
City High-Tech Industrial Development Zone is the engine of the Wuxi economy. With 560,000 residents, the zone contributes 17 percent of Wuxi’s economic activity. To drive the construction of energy-efficient buildings, Wuxi issued an innovative investment guidance policy in February 2016: incentives for buildings that meet criteria for green buildings in China: LEED and China’s national three-star rating system.
Suzhou
As China continues to urbanize, entire new cities are being built from scratch. Suzhou Taihu New City in Jiangsu province is one example. Currently in the planning and design stages, Suzhou Taihu New City will house 200,000 residents and focus on high-end service industries such as education and training, research and development, tourism and finance. All of Suzhou Taihu New City’s buildings designed to receive at least a two-star rating for green buildings in China. The city also will boast a green building demonstration area, constructing several projects such as zero-energy schools and monitoring their energy performance.
Liuzhou: The world’s first forest city

[Source: Stefano Boeri Architetti, ‘Liuzhou forest city. Masterplan’]
In 2020, China plans to begin the construction of the world’s first Forest City in Liuzhou, Guangxi Province, China. The Liuzhou forest city is planned to house more than 40,000 trees and 1 million plants of more than 100 species, for its 30,000 residents which will absorb almost 10,000 tons of carbon dioxide and 57 tons of pollutants, and produce approximately 900 tons of life-giving oxygen annually.
The forest city will also be self-sufficient and will help to decrease the average air temperature, improve local air quality, create noise barriers, generate habitats, and improve local biodiversity in the region. The whole city will run on renewable energy especially solar and geothermal, according to its planners.
The Liuzhou authorities want to build about 70 buildings cascading with foliage which will have homes, hospitals, hotels, schools and offices. It is the country’s first attempt to control notorious pollution. The Liuzhou forest city is a pilot in a series of mini sustainable cities that could become a template for future green buildings development in China.
Challenges in the green building market in China
Over the last few years, the Chinese have been developing a real interest in “green buildings” but they are meeting some obstacles and challenges. Sustainable buildings in China are finding it more difficult to attract clients due to misunderstandings of the green building concept. In 2014, the newest version of green buildings standards was published by the government to clarify the meaning of green building. The Chinese tend to believe green buildings are only high-end buildings with better facilities. Some consider green buildings as a long-term investment with immediate rewards. They are not aware of the more natural and more comfortable living environment of green buildings. This is why in the coming years green building developers will need to accompany their campaign with strong marketing but those are still demand for higher governmental subsidies. In 2016 China’s green building investment gap was nearly 2 trillion yuan.
Lack of environmental awareness hinders the development of green buildings
Despite the using of LEED certification system, the green building concept does not always make it to the Chinese market. Under the new environmental requirements people are debating on the costs and rewards of green buildings. Lack of understanding of green buildings and misaligned incentives are the prime reasons why the adoption of green buildings slowed down in China.
The environmental awareness of different stakeholders has a significant impact on the development of green buildings in China. Builders often base their construction decisions on short-term costs, such as material and labor cost, instead on energy efficiency or green building techniques which offer long term savings. The significant energy saving is tied to an increase in costs, the global leader in real estate service CBRE estimated additional costs for green buildings below 4% however the LEED says those vary between 0.4% and 12.5%. Experts claim the 2% additional cost is enough to reach standards. Constructors are relieved by the CBRE latest report stating that in big cities of China, green buildings are sold at a price 1.5 to 25.7% compared to other buildings. Some developers in China may not see immediate cost savings and often overlook the green features—such as better insulation and sealed windows—that could help the government meet its energy targets. This is especially true in the multi-family residential buildings that most people in urban China live in.
The popularity of green buildings is growing, but the percentage in the construction market is still small
At the 5th China Green Smart Real Estate Forum (2019) many experts said that green buildings market in China has great potential, and its value can reach US $17.5 trillion. Green buildings are undoubtedly an important approach for the Chinese building industry in terms of environmental responsibilities and market benefits, but green buildings market in China still has a small scale and eco architecture in China is not so popular. Still, sustainable buildings make up a small percentage in China’s construction market that is more interested in maximizing profits and lowering building costs, compromising sustainable design and energy efficiency considerations.
However, green buildings market in China has a great potential. More and more construction companies turn to a green development. According to professor at the University of Sheffield Kangjian, “The real green building is building have a balance of nature, human and expenditure. Is something that can benefit people right now.”
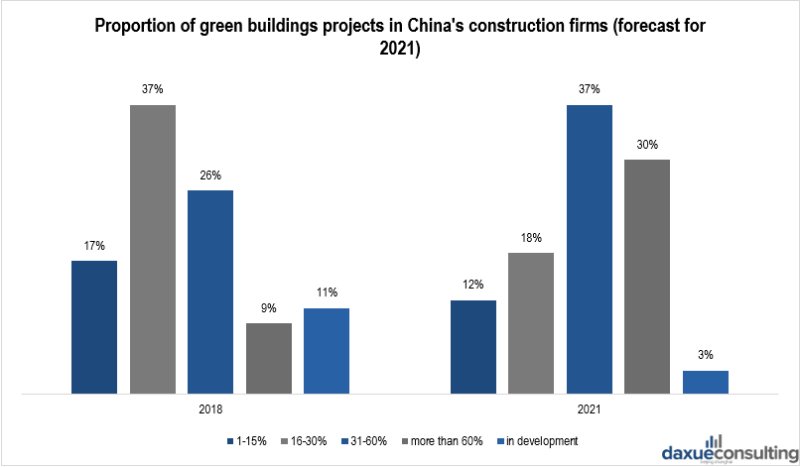
[Data source: qianzhan, ‘Proportion of green buildings projects in China’s construction firms (forecast for 2021)’]
Daxue Consulting can offer a wide range of services to create your competitive marketing strategy. To know more about the green buildings market in China, do not hesitate to contact our dedicated project managers by email at dx@daxueconsulting.com.
Author: Valeriia Mikhailova
Let China Paradigm have a positive impact on your business!
Listen to China Paradigm on iTunes