The ride hailing market in China is increasingly competitive and price-driven. Although DiDi has long held the largest share, lesser known ride hailing platforms in China are emerging to challenge the company’s dominance. With Geely’s Caocao Chuxing (曹操出行), Tencent and Alibaba-backed T3 Chuxing (T3出行), JD.com-backed Dida Chuxing(嘀嗒出行)entering the local ride hailing market with lower prices, DiDi launched the stand-alone ride hailing service “Huaxiaozhu”(花小猪), hoping to lure more customers with affordable rides than its main DiDi app. Unlike other ride hailing services, Huaxiaozhu focuses in third- and fourth-tier cities, offering low-cost rides, further sinking the market to leverage the larger proportion of population.
Unfortunately for DiDi, the news reported that numerous local city regulators in China have asked DiDi to suspend its new service Huaxiaozhu for a lack of operating licenses for the platform in their regions. However, at the Huaxiaozhu launch event, the CEO of DiDi Chuxing, Liu Qing has pointed out that many companies release cheaper alternatives to their main products, “Alibaba launched Juhuasuan (聚划算)besides Taobao and Tmall; Volkswagen has Porsche, Audi in addition to Skoda. We noticed that we haven’t met the needs of many young customers and the customers longing for low prices in the past”.
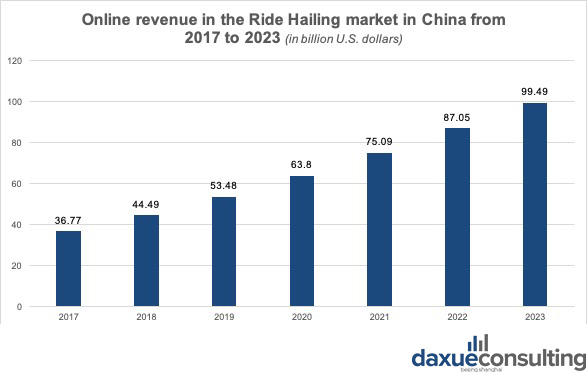
Data source: Statista, Ride hailing is trending in China. Although it is not a profitable business yet, the revenue of the ride hailing market in China is expected to grow at a double-digit rate.
Emerging rideshare services share similar marketing strategies lead to high market competitiveness
The marketing strategies these ride hailing apps share are price subsidies and social fission marketing. Social fission marketing involves leveraging existing customers as brand ambassadors, and rewards them when they share the product with friends. Such a marketing approach is familiar to the Chinese customers, for many Internet-based businesses such as the online retailer Pinduoduo (拼多多), bike-sharing services, Luckin Coffee managed to attain a vast customer base through aggressive subsidies and fission marketing.
These apps lure price-sensitive customers by offering massive discounts; this group becomes the app’s early adaptors. Then, the rideshare services encourage their existing customers to share links to friends on social media, mainly WeChat, to invite their friends to try the apps or collect “boosts” from friends in return for ride vouchers.
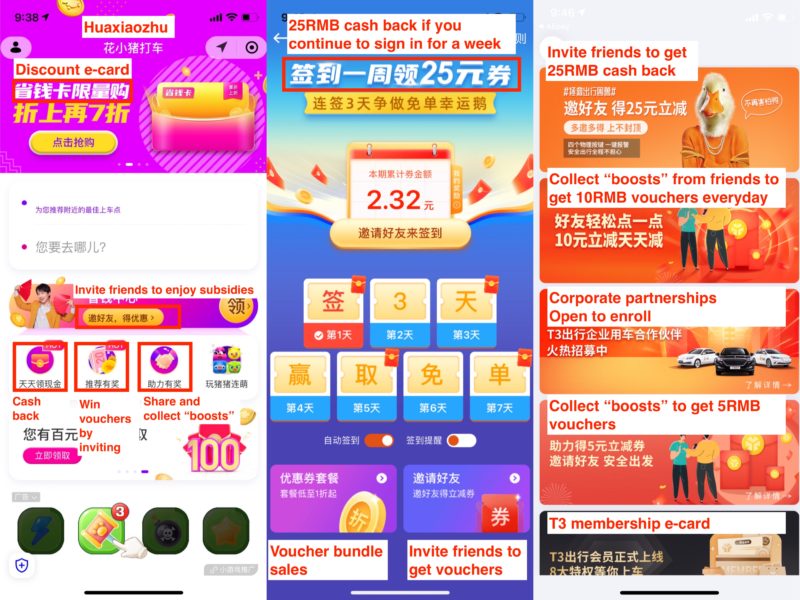
Image Source: Huaxiaozhu (left), Caocao (middle), and T3 (right) Chuxing apps, New rideshare services have rolled out various subsidies to attract users with the focus being luring their existing users to invite friends to use the app in return for vouchers.
Aggressive discounting and social fission marketing create a price-driven market
While effective in hitting a higher volume of orders and daily active users, these marketing strategies are not without problems. With these emerging ride-hailing apps competing aggressively on prices, their customers are most likely to prioritize cheaper prices over the quality of service. Hence, customers tend to make decisions based on the lowest prices and are not loyal to any of these brands.
The customers are prone to download several apps and switch between apps since customers’ switching costs are fairly low, leading to a highly competitive, price-driven market. In addition to high switching rates, these market players might soon have to address high abandon rates if they stop subsidizing users for profiting reasons.
Tech and automobile companies synergize to take on DiDi in the ride hailing market in China
DiDi currently claims more than 80% share in the ride hailing market in China. Unchallenged though it might be, many emerging players are taking on DiDi in the Chinese ride-hailing market. One of the reasons is that numerous PR crises involving DiDi drivers misconduct have tainted the company’s reputation in the ride hailing market in China. Besides, in 2018, since car sales in China fell for the first time since 1990, and Chinese automakers are getting into the rideshare scenes.
“If the (car) manufacturers do not participate in the ride-hailing business, they will eventually be eliminated by the market, just like Nokia and Motorola.”
Liu Jinliang, Head of Caocao Chuxing
Introducing the lesser known ride-hailing platforms in China
Caocao Chuxing, the first NEV-hailing platform in China to get a license
Caocao Chuxing (曹操出行) is a strategic investment of Geely Technology Group to deploy “new energy vehicle (NEV) sharing ecology”. It is the first licensed NEV-hailing platform in China’s ride hailing market. Caocao Chuxing targets passengers who value quality services. Hence, Caocao’s customers are asked specifically to assess the cleanliness of the car’s interior after every ride.
Caocao uses electric vehicles produced by its parent company, Geely, and hires drivers directly, so the company has more control over both the cars and the drivers. This is a stark difference from most other ride hailing platforms in China, where the drivers are contractors who use their own cars. Caocao’s strategy ensures the quality of the cars, which his a problem other Chinese ride-hailing platforms face. Recently, news broke out that several drivers working for Huaxiaozhu operated without a license and some cars failed to meet requirements for ride hailing service.
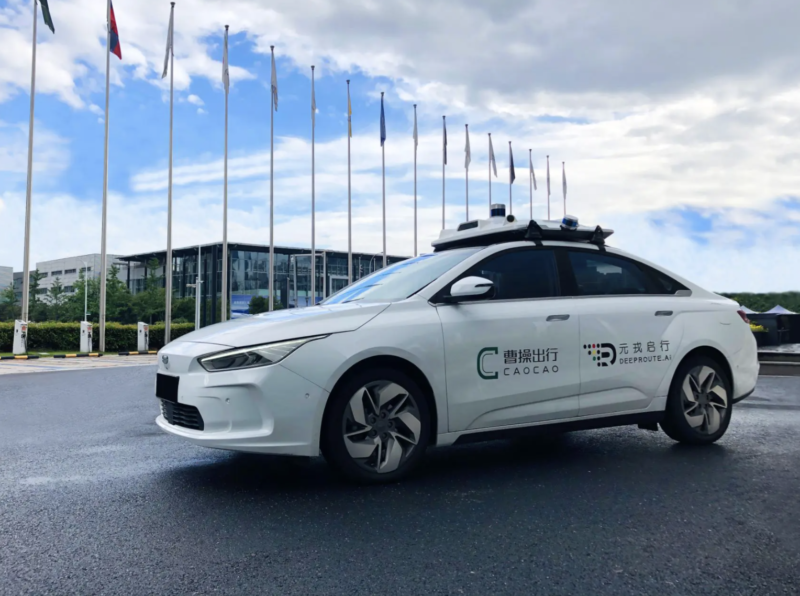

Image Source: Autovision News, Caocao’s robotaxi, powered by DeepRoute’s self-driving system, is also expected to be a booster for Caocao.
Backed by major tech giants, T3 Chuxing’s “Internet of Vehicles” enhances security measures of C2C rideshare model
T3 Chuxing is a new ride hailing company that went online in 2019. The rideshare service is the result of a joint venture from Alibaba, Sunning, Tencent, and three car manufacturers, Chongqing Chang’an Autobomobile, Dongfeng Motors, and FAW (“First Automobile Works”) as well as some smaller investment funds. Thanks to this alliance, T3 Chuxing can differentiate from the other rideshare platforms in China by offering a more integrated marketing approach. In addition to luring users with vouchers and free rides, users may also win tickets to a football games, because Suning, the largest shareholder of T3, is the majority owner of a football team.
Moreover, T3 Chuxing’s “Internet of Vehicles” advances the security measures of C2C rideshare services in China. T3 can remotely interfere with the vehicle if a situation requires. Cameras and software installed in the car ensure that drivers are supervised throughout the orders. The facial recognition system in the car can detect if a driver is dozing off or smoking and report it back to the monitoring center. There is even a button in the car for reporting to the police in the case of an accident.
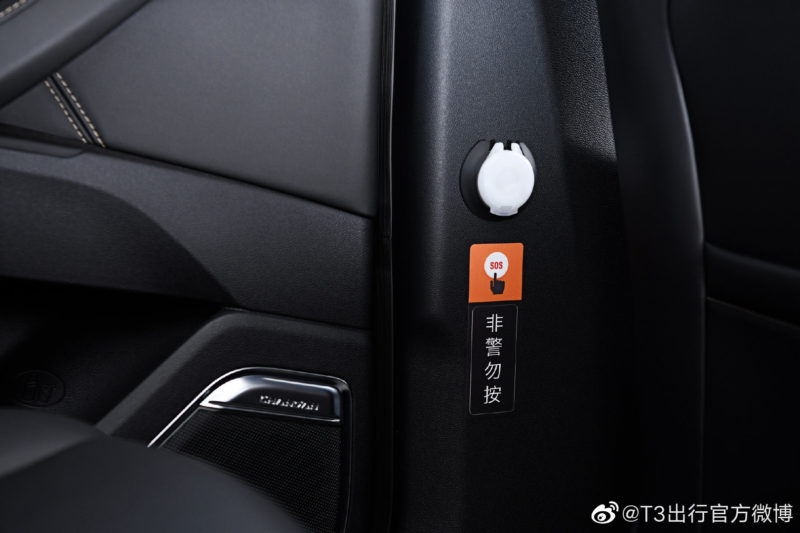

Image Source: T3 Chuxing’s Weibo, The security button in T3’s cars for reporting to the police in the case of an accident.
T3 is not the only ride hailing platform in China resulting from a joint venture
Such a partnership was also found in DiDa Chuxing, a rideshare service backed by online retailer JD.com, New York-listed Trip.com, and the electric vehicle maker NIO. Moreover, FAW launched its ride hailing app in China in September 2019. German automotive company Daimler Mobility AG teamed up with Geely Technology Group to operate a premium ride hailing service in Chengdu, China in December 2019. The German luxury carmaker BMW also launched a premium ride hailing service in Chengdu, China in December 2018.
The prospect of the ride hailing market in China is cheerful yet challenging
Although the revenue of the ride hailing market in China is projected to grow at a double-digit rate, the current business model of rideshare services remains to be examined by the dynamic market. A foreseeable challenge for rideshare suppliers is to retain their domestic customers after achieving the MAU (monthly active users) goals through aggressive subsidies. The precedents of the bike-sharing company OFO and Luckin Coffee have been sounding the alarm. Moreover, although these emerging businesses have offered abundant new jobs in the post-pandemic period, looking ahead, assisted driving and driverless technology are also expected to change the dynamic of the ride hailing market in China.
Learn more about the mobility market in China
Listen to over 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast