The total number of Chinese smartphone users has reached 748 million in 2019. Approximately 53% of the population uses smartphones, leaving much of the smartphone market in China untapped. This number is expected to reach 868 million by 2023. With the sudden prevalence of smartphones in China, smartphone user habits are different in China from rest of the world.
Chinese consumers’ dependence and use of smartphones is much different from laptops. China’s fast technological development skipped over the laptop era, many Chinese consumers’ first ‘computer’ purchase was a smartphone. Chinese mobile users spend most of their time on social networking apps, watching short videos, taking pictures, and playing games, according to a study by Zhongjin.
How WeChat makes Chinese smartphone consumption more malleable
In addition, Chinese APPs like WeChat and Alipay are so powerful and omnipotent that consumers in China do not necessarily have to be loyal to a specific operating system. WeChat has replaced phone calls and SMS texts, so when consumers switch phones, they do not have the need to keep the same operating system. So long as they can download WeChat, all their contacts are saved, and accessible from any phone.
WeChat’s feature “Mini Program” enables its users to access APPs within WeChat without having to download them. So far, WeChat Mini Programs own over 200 million daily active users and provides a wide range of services that cover people’s day-to-day needs. This gives Chinese consumers more freedom when purchasing smartphones or switching smartphone brands from one to another and poses more challenges to smartphone companies.
Leaders of the smartphone market in China
While faced with fierce competition from Apple and local Chinese smartphone companies like Xiaomi, Vivo, and Oppo, Huawei still owns the leadership in the Chinese smartphone market with a market share of 39.80% by the 3rd quarter of 2019. Apple’s sales keep declining, but the company still takes up to 8.2% of the market share. Unfortunately, companies like Samsung and HTC have dropped out of the chart of top companies on smartphone consumptions in China.
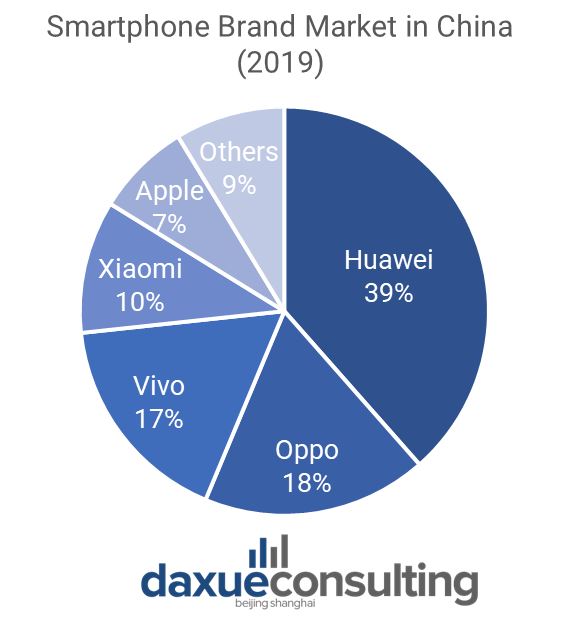
Data Source: Canalys, Only Apple is foreign, the other top five smartphone brands are domestic
By the 3rd quarter of 2019, the smartphone penetration rate in China has reached approximately 53%, which is a huge leap as compared to 40% in 2012. China has already taken the title as the world’s first country to chalk up over 1.1 billion 4G mobile users, with still hundreds of millions expected to upgrade to Smartphones over the coming years. Although the Chinese smartphone market has been gradually approaching saturation in the past few years, the arrival of 5G will bring new opportunities and challenges to smartphone makers like China’s giant tech company Huawei, Apple (苹果) and other local Chinese smartphone companies.
Huawei smartphones in China

[Source: Baidu – Huawei smartphones in China]
Huawei has come a long way since its establishment in 1987. In 2019, the Chinese tech giant’s smartphone business operates across the globe, covering over 170 countries and regions. Huawei launched its first Android smartphone U8220 in 2009 and created its own smartphone series Huawei Honor in 2013. Other Huawei smartphone series include Mate, Nova, P, and Maimang, which were designed and priced to appeal to different market segments. At the Huawei Developer Conference 2019, Huawei officially announced the launch its own operating system, the HarmonyOS, as part of Huawei’s project “Internet of Things,” followed by which, Google stopped its collaboration with Huawei as its response to Huawei’s ambitious move.
Apple’s iPhone in China
The iPhone is a line of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, the CEO of Apple on January 9th, 2007, and was released on June 29th, 2007. Third-party as well as Apple’s applications are available on Apple’s app store, which launched in mid-2008. As of the 3rd quarter of 2019, over 1.8 million apps are available on Apple’s app store, as compared to 500,000 apps in 2012. Traced back to 2012, there were five generations of iPhone models, each accompanied by one of the five major releases of iOS (formerly iPhone OS). The original iPhone was a GSM phone and established design precedents, such as screen size and button placement, that have persisted through all the five models. By 2019, Apple has released 24 different versions of iPhone and will announce the launch of iPhone 12 in September 2020.
Android smartphones in China
Android is a Linux-based operating system for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. It is developed by Open Handset Alliance, led by Google which financially backed the initial developer of the software, Android Inc., and later purchased it in 2005. Android, Inc. was founded in Palo Alto, California in October 2003 by Andy Rubin (co-founder of Danger), Rich Miner (co-founder of Wildfire Communications, Inc.), Nick Sears (once VP at T-Mobile) and Chris White (head of design and interface development at Web TV). Despite its humble start, Android takes up approximately 74% of the smartphone market in China from 2013 to August 2019. In 2019, Google officially announced the launch of Android Q (also called Android 10) for its Pixel smartphones, which was considered as a refreshing and innovative move of Google.
iPhone VS Android smartphones in China
Apple Inc’s declining share of the smartphone market in China suggests that its customers won’t always wait for the next iPhone when rivals, such as Huawei and Xiaomi, have plenty of flashy new models available in the Chinese smartphone market. According to Bloomberg, Apple’s sales from greater China (includes Taiwan and Hong Kong) dropped 27% during the holiday season this year in its second-largest market as compared to last fiscal year. This means that other companies like Huawei, Xiaomi, and Vivo have been eating up Apple’s market share in China with fairly high speed and Apple’s target consumers have fewer needs for upgrading their iPhones every year. Although iPhone 12 will be launched in September 2020, Apple seems to be stuck at its bottleneck with few innovations on its recently released products. Additionally, as mentioned earlier in the article, Apple’s major rival Huawei hasn’t stopped taking innovative steps. Its newly released software platform “HarmonyOS” will replace Android on Huawei smartphones, which made it not only Apple’s biggest rival and all Android smartphones rival as well. Therefore, it is possible that Apple would lose its status as the must-have accessory for China’s hip and rich.
Future Prospects: Will the dawn of 5G reshape the smartphone market in China?
Chinese smartphone companies have been trying to get out of this very awkward position where they are not competitive enough to be in the high-end market but reluctant to stay in the low-end market for long. Unlike Apple who targets high-end consumers in China, Chinese smartphone companies including Huawei, Xiaomi and Vivo, have been taking a different pricing strategy with fairly low profits in order to penetrate lower-end demographics in China. However, as the arrival of 5G, these companies might seize the opportunity to re-position their brands.
Author: Isabella Li
Additional Sources:
- Forbes
- The New York Times
- Bloomberg
- Businessweek
- Statista
- Counterpoint
- Margin Capital
- Pocket-link
- CNBC
- China Internet Watch
Picture Source: China iPhone