Founded in the US by Sam Walton in 1962, Walmart has now grown to be the largest retailer in the world with over 10,500 stores across 19 countries. The brand’s story with the Chinese market started in 1996 with Walmart’s first location in Shenzhen. Walmart became one of the earliest foreign companies that set foot in the country. By adapting its business model to cultural differences and sourcing locally, Walmart in China was able to avoid some of the pitfalls that foreign retailers have faced over the past few decades.
Nevertheless, the retail giant encountered some major struggles with relating to Chinese consumers. The results were stagnant sales, food safety scandals, and an eventual dramatic decrease in the retail store number among China since 2018. Over the past 5 years, Walmart closed more than 100 supercenters nationwide. Reasonably, some might put a question mark over why Walmart has failed to understand Chinese consumers while having entered the market for decades.
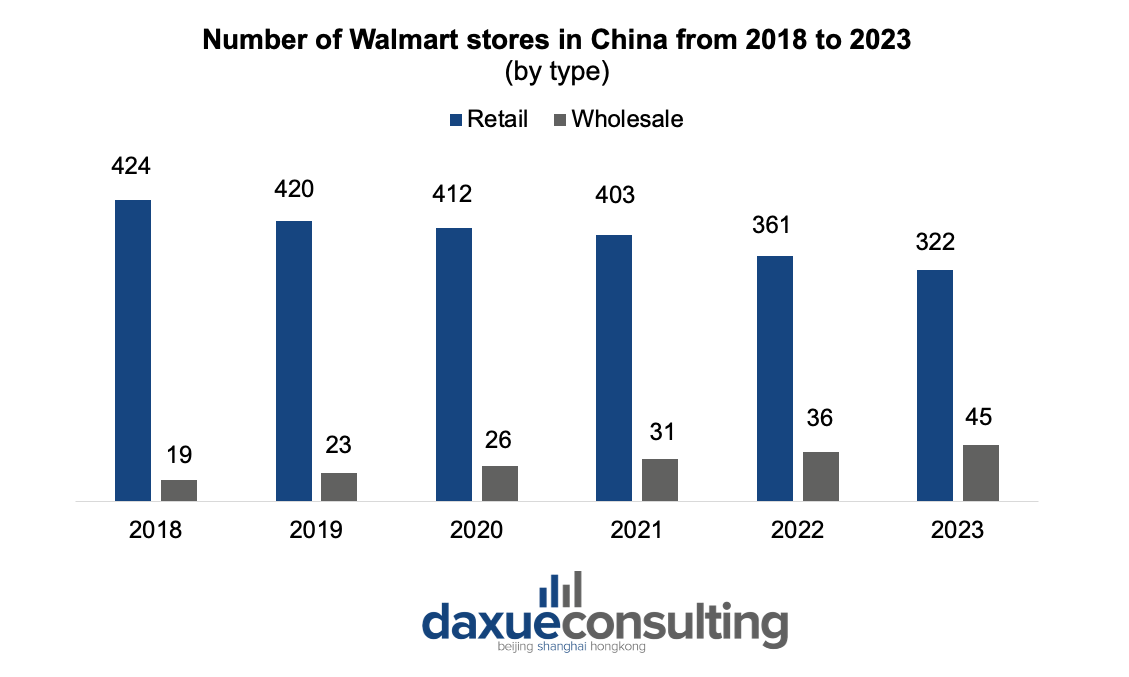
Despite the struggles of Walmart’s retail stores, Walmart-owned membership store Sam’s Club is fairly popular among Chinese consumers, whose members reached over 4 million by the end of 2022. In 2023, Sam’s has 45 stores nationwide, vaunts great familiarity with the local market, and exhibits a swift response to consumers’ ongoing needs.
Download our report on Gen Z consumers

Supermarkets are struggling to make ends meet in the Chinese retail industry
Facing the ever-increasing competition from online retailers, soaring rental costs, and the challenges posed in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, hypermarket retailers have been struggling in the fast-moving Chinese retail market. In 2019, Carrefour sold 80% of its stake to China’s local company Suning. Despite Walmart’s various efforts to stay competitive, such as sourcing locally to maintain low pricing and incorporating sustainability to cut down operation costs, the old business model of hypermarkets can hardly compete with emerging models like group buying and e-grocery.
Current Walmart’s situation: strategic moves to recover
In 2007, Walmart spent USD 1 billion and acquired 35% of the parent company of Trust-Mart, a Taiwan-based hypermarket chain plan. This major investment by Walmart accelerated its expansion across Chinese regions. As of 2012, Trust-Mart had over 100 outlets across China, including many stores in lower-tier cities.
The retail giant operates in various formats, but one of the main remains to be the supercenters. They mainly aim at saving consumers’ time and money. Walmart’s stated corporate mission is “Save people money, so they can live better”. Their business model allows them to sell commodities with low prices harmonized across all their shops nationwide.
Walmart’s upgraded supply chain mechanisms and the largest multi-temperature cold chain distribution center
The survival of supermarkets also hinges not on the visible storefronts and shelves but on the underlying operational concepts, distribution systems, and supply chain mechanisms that sustain them.
In 2021, Walmart in China spent USD 85 million for an extensive upgrade of its automatic sorting system to enhance the quality of logistics services and warehouse management through the integration of big data technology at the distribution center. Currently, the brand boasts one of the largest multi-temperature cold chain distribution center in the domestic retail sector, enabling it to achieve one-hour delivery within the coverage area. Thus, during the third quarter of 2023, Walmart experienced an 8.7% year-on-year increase in revenue, coupled with a 3.9% year-on-year rise in operating profit.
Sam’s Club is the exclusive membership-based extension of the Walmart store line
Sam’s Club in China is a members-only warehouse. The brand has a similar business model as Costco in China, which provides low-cost, bulk products for both business and personal use. In the third quarter of 2023, Walmart-owned membership store achieved remarkable growth, with an 8.0% increase in membership income and a 10% surge in same-store sales.
Although supermarkets are struggling to profit, membership-based wholesale clubs are booming in the Chinese market. Notably, although Sam’s Club first entered the Chinese market as early as the late 90s, not until recent years did warehouse clubs become trendy among consumers. As the income level of Chinese consumers continues to increase and more emphasis has been put on the quality of products, a membership card becomes a worthy investment among Chinese families. Additionally, the increase in the ownership of private vehicles over the past decades allows more consumers to purchase bulk items.

Partnership with JD.com as the key to success in the Chinese market
Apart from traditional retail, Walmart in China has been partnering with JD.com since 2016, which allows customers to enjoy the convenience of e-commerce channels. In 2017, Walmart’s subsidiary Sam’s Club also launched its first official flagship store on JD.com. As of 2022, Walmart is one of the fastest-growing retail supermarkets on JD Daojia, providing a one-hour delivery service through over 400 Walmart online supermarkets across the country.
Generally, China is the largest e-commerce market, accounting for almost 50% of the world’s transactions. Thus, by building a robust online foundation through collaborations with JD.com which holds 15.9% of the total market share, Walmart significantly secured its position and obtained competitive advantages by tapping into the Chinese consumer needs
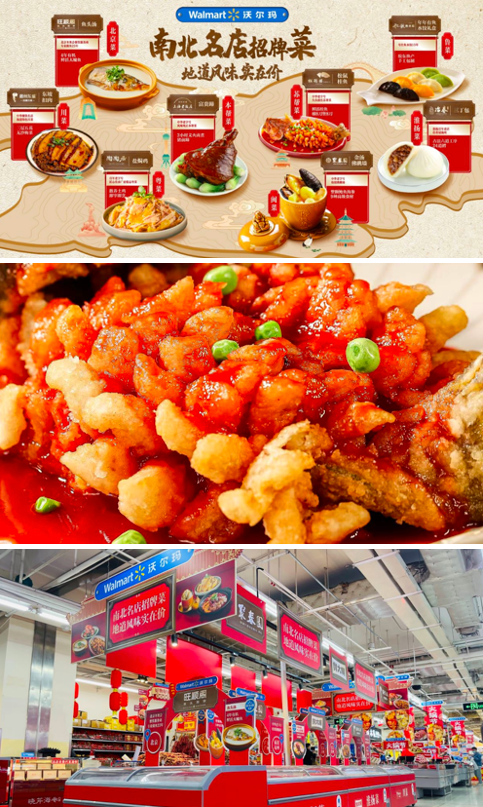
The house specialties of famous restaurants as at-home banquet solutions
Walmart Hypermarkets has introduced an innovative at-home banquet solution in collaboration with renowned restaurants nationwide, aiming to meet the preferences of urban families. Leveraging its extensive retail expertise and efficient supply chain, Walmart facilitated 18 restaurants to enter the broader consumer market. The first food chain was strategically introduced in 2022 right before the New Year and Chinese New Year festivities.
Generally, the whole idea challenges conventional perceptions of ready-to-cook food. The at-home banquet solution encompasses over 70 authentic and affordable dishes from eight major cuisines, ensuring a diverse dining experience for customers. Despite its “frozen dishes nature” Walmart maintains high-quality standards by partnering with reputable brands and meticulously controlling ingredient sourcing and production processes.
The end-to-end performance is supported by temperature-controlled logistics and an efficient online-to-offline fulfillment service. This initiative not only optimizes costs but also empowers restaurants to enter supermarkets, exemplified by brands like Xibei and Wangxiangyuan making their debut in Walmart channels. The brand’s transparent collaboration model and robust supply chain provide crucial support, enabling regional restaurant chains to expand nationally with ease.
In a shifting market, Walmart’s strategic approach not only fosters a win-win partnership with restaurants but also creates enduring value for communities and customers.

Walmart’s renovative approach to the supply chain, product lines and e-commerce to regain positions in China
- Supermarkets, especially foreign retailers, are grappling with challenges in meeting the demands of Chinese consumers.The giant hypermarket retailers like Walmart are cutting off the number of stores in China and cooperating with local tech giant like JD.com for digital transformation.
- Renovations to the supply chain, including an automatic sorting system and a multi-temperature cold chain distribution center, empower the retail giant to outperform competitors in delivering fast and fresh products.
- Walmart continues to expand in China through its subsidiary Sam’s Club, as the business model of membership-based warehouse clubs becomes increasingly popular among Chinese consumers.
- The US retailer incorporates new ways to appeal to local customers such as strategic partnerships with beloved restaurant chains, while maintaining high quality of the ingredients and timely delivery.





