As early as 2018, The 5G Technology Working Group at the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology started research into 6G in China. This makes China one of the first countries to explore 6G technology.
In November 2019, the Ministry of Science and Technology, together with other key ministries and research institutions organized a 6G technology research and development work kick-off meeting in Beijing. Since then, Guangdong New Generation Communication and Network Innovation Research Institute has launched a 6G channel simulation on 6G hotspot technology.
What can 6G in China bring that 5G can’t?
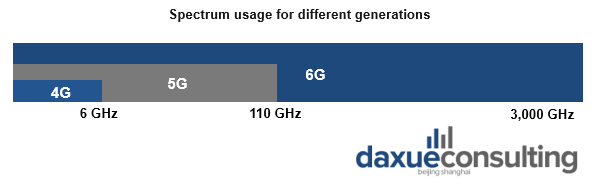
Data Source: Samsung 6G report, Spectrum usage for different generations
6G could make mobile internet speeds of 1 TB per second mainstream. This means users could download around 100 films in less than a second. 6G could also connect our devices more efficiently than 5G, expanding internet coverage to much wider areas. In China, this means making the rural population even more connected to services like e-commerce and online education.
Su Xin, head of a 5G technology working group at the Chinese ministry said: “5G has three application scenarios: large bandwidth, low latency, and wide connection – I think 6G can achieve better application in all three scenarios”. However, there is still no definition for the technology, so the idea behind it remains vague until further development.
As for the next generation of connectivity, “marketing will need 6G as soon as 5G is deployed”. Researchers will need a term to mark the novelty of what they are doing.
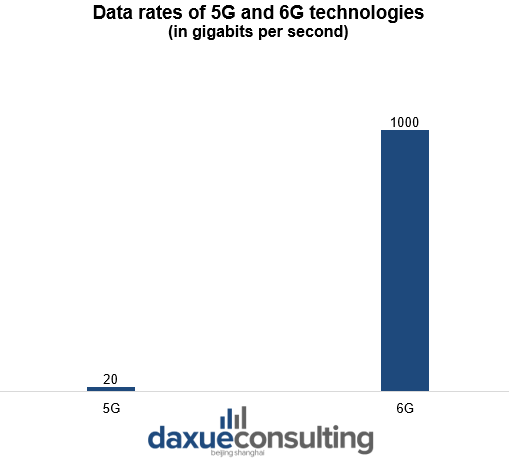
Data Source: ITU, Data rates of 5G and 6G technology
Three drivers of 6G technology in China
The design of 6G networks should consider three driving forces. The first is the demand from new services and new application for faster connection. The second is the demand to solve the existing network problems and challenges. 5G construction brought challenges such as high energy consumption, high cost, and low maintenance efficiency. For the future network design, it is necessary to consider how to solve these issues. Third, the advancement of cloud computing, big data, and AI technology drive 6G development in China.
Existing problems to solve for 6G in China
There are four outstanding problems in the existing networks. One is time delay. The protocol structure has become a bottleneck for achieving lower latency. For 5G wireless networks, the protocol structure is layered. All services are processed layer by layer, and a delay in processing of one layer creates a delay in transmission time. To further shorten the time, it is necessary to break this structure.
Second, there is a need to evolve the support technology of network slicing. 5G supports end-to-end network slicing. 6G network design should consider optimization of slicing in the wireless network and the core network.
The third is to solve the problems of high cost and power consumption caused by a single network structure. At present, 5G network deployment is a unit, full-function base. It makes the entire construction cost high and consumes more power. 6G technologies in China will need to aim to be less power consuming.
Fourth, there is a difficulty in a large-scale base station deployment. It is necessary to think about using of AI to realize the network operation and maintenance.
The companies behind 6G in China
Huawei prepares roadmap for 6G development in China
Yang Tao, vice president of Huawei said the company is now at the explorative stage of 6G development. Whatever measures the US takes to pressure Huawei cannot delay the company’s research and development of the 6G in China.
The company is collecting information such as what are the shortcomings of 5G networks, what consumers can do with 6G, and what 5G technologies to use for the R&D of 6G in China.
Huawei also gave a roadmap of 6G development, which includes deciding the vision for 6G by around 2023, set technological standards by 2026, rolling out relevant technology by 2028 and preliminary commercial use of the network by 2030.
Samsung and Huawei: companies at the front of competition for 6G technology
As Huawei’s 5G technology is out of networks in the USA, Australia and the UK, Samsung Electronics has moved to crank up their global vision for 6G technology, which they claim could be a reality in 8 years. The company is working to develop the sixth-generation telecommunications network technology in an effort to beat Chinese manufacturers.
Samsung’s white paper entitled “The Next Hyper-Connected Experience for All,” outlines Samsung’s vision for 6G. It covers various aspects related to the next-generation network system, including technical and societal megatrends, new services and requirements. In the report, Samsung expects that the completion of the 6G standard and its earliest commercialization date could be as early as 2028.
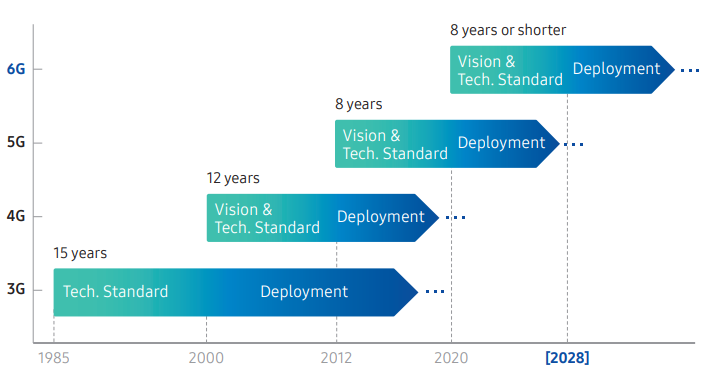
Source: Samsung 6G report, Timeline of different generations
Report notes that both humans and machines will be the main users of 6G. It will provide advanced services such as truly immersive extended reality, high-fidelity mobile hologram and digital replica. Samsung defines three categories of requirements to realize 6G services — performance, architectural and trustworthiness requirements. Examples of 6G performance requirements are a peak data rate of 1,000 gigabits per second and air latency less than 100 microseconds.
The report also introduces candidate technologies that could be essential to satisfy the requirements for 6G, including the terahertz frequency band, novel antennas.
Telecom companies collaborate to promote 6G technology in China
In 2020 ZTE and China Unicom started collaborating on 6G technological innovation and standards. They also have set a series of performance targets including a peak data rate of 1 Tbps, a user experienced data rate of 20 Gbps, and a volume traffic capacity of 100Gbps/m3.
Their research would focus on three-dimensional connectivity, Terahertz communication and integrated communication and sensing.
6G in China still has a long way to go
Vice Minister Wang Xi of the Ministry of Science and Technology said 6G is in the “initial stage, the technical route is still not clear, and the key indicators and application scenarios have not been standardized and defined.” In September 2020, Huawei CEO Ren Zhengfei said that while the company is working on 6G technology, it is still in an “early phase”. Therefore, there’s a long way to go before commercialization.
Mobile networks, particularly 5G, have become a politicized topic between the U.S. and China; it is too early to say for certain whether 6G will encounter the same barriers,
Huawei is on a U.S. blacklist that restricts its access to American technology. Meanwhile, Washington has tried to convince other countries to bar Huawei from their 5G networks. Still, China is pushing on with 6G as it sees the technology being of great importance in the future.
“In this critical period of national development, we must attach great importance to the 6G development, coordinate its planning, promote it with efficiency, and open up for innovation in this area,” Wang said.
Key industries will use 6G technology in China
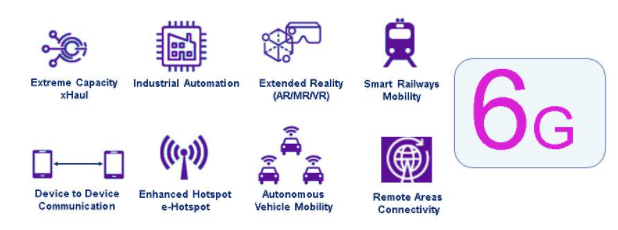
Source: Techplayon, 6G technology applications in industry
6G technologies will be mainly used in sectors including China’s Internet of Things, self-driving automobiles and smart factories. The fast commercialization of 5G networks boosts other domestic players to actively develop 6G technology.
Railway communication
As an infrastructure component, connection between trains, passengers, and cargo requires high data. Railway communications are evolving from supporting only critical signal applications to providing a variety of bandwidth-intensive applications. For example, on-board and roadside high-definition video surveillance, passenger broadband connections, passenger information broadcasting, and remote driving or control.
Extended reality (AR/VR)
This case considers Chinese VR and AR applications to capture multi-sensory input and provide real-time user interaction. In order to provide a completely immersive experience, it requires each user to have a very high data rate and very low latency. Remote connection and interaction powered by holographic communication, as well as all human sensory input information, will further promote data rate and latency goals. The data transmission rate required for multi-view cameras for holographic communication is megabits per second.
Robotics and industrial automation
Digital transformation of manufacturing is the ultimate goal of both 6G and 5G development in China. To achieve high-precision manufacturing, automatic control systems and communication technologies, there should be a high data rate.
The first 6G satellite systems in space
In November 2020 China successfully launched the world’s first 6G satellite into orbit. The satellite has a name after the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. It will serve to test out the performance of the 6G frequency band in space. 6G will be over 100 times faster than 5G which is already ultra-fast. This is because it uses high-frequency terahertz waves to achieve impressive data-transmission speeds. In addition, the novel satellite also features technology for crop disaster monitoring and forest fire prevention.
See our report on AI development in China
Listen to over 100 China entrepreneur stories on China Paradigms, the China business podcast
Listen to China Paradigm on Apple Podcast