China, the most populous nation in the world, has set itself the ambitious goal to reach carbon neutrality by 2060. The path from its current status as the world’s biggest emitter of CO2 toward a leading green superpower within only four decades will undoubtedly be challenging. What are Beijing’s strategies for “greening” the Chinese economy?
Green technology has been applied to practical development in many countries in recent years, as it can reduce pollution and promote ecological balance to achieve sustainable development. China has formulated relevant laws to help the transformation of industrial manufacturing. Compared to western countries, the Chinese government has higher control. China mainly relies on administrative means to call for guiding enterprises to save energy, avoid waste, and promote energy development.
On the other hand, compared with developed countries, Chinese industry still lacks the core technology, which leads to inefficient use of capital resources. The economies of scale are also not significant, which can be an opportunity for Chinese enterprises with the potential for improvement.
Behind the human activities and ecological pollution of China
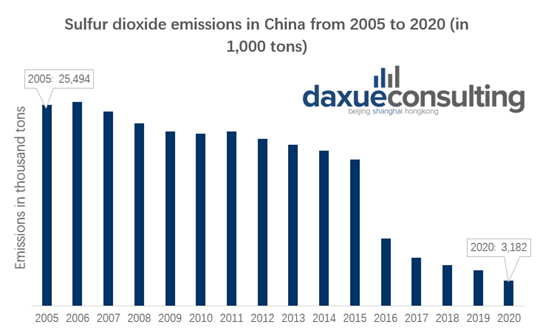
Since the 1980s, China has vigorously developed heavy industry, rapidly promoting China’s economic development, and causing severe harm to the environment. For example, the coal-fired power generation industries, such as mining, have released carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other industrial waste gases, resulting in the greenhouse effect. However, the situation surrounding China’s atmospheric environment has been improving in recent years. Before implementing the sustainable development policy, China’s annual emission of sulfur dioxide in 2005 was as high as 25 million tons, down to around 3.18 million tons in 2020.
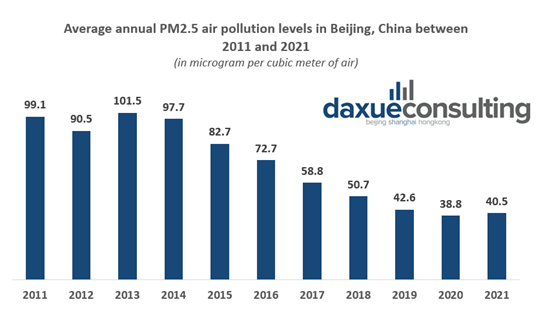
Beijing’s air quality has also considerably improved, going from a concentration of around 100 micrograms of PM2.5 fine particles per cubic meter of air in 2011 to 40 micrograms in 2021. However, the current concentration remains well above what environmental norms dictate in other developed countries (10-15 micrograms being considered “safe”). The resulting pollution has been a source of serious public health concerns in the mainland, leading to an estimated 1.24 million annual death caused by air pollution alone.
Therefore, to solve environmental problems and adhere to sustainable development, the Chinese government calls on enterprises to transform, develop green technology as the core, and reduce or avoid environmental pollution as much as possible while growing the economy.
The importance of Green technology
On the one hand, China has made remarkable achievements in biotechnology. For example, Yuan Longping, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, invented hybrid rice, which has solved China’s deal with the concurrence of the shortage of food for the country’s huge population, agro-technology being one of the country’s top priorities. Moreover, China has created a miracle in agricultural technology in which only 7% of the world’s arable land has fed China’s 1.4 billion people, accounting for 20% of the world’s total population.
Chinese green technology has also stepped forward globally. Green Leading companies in China combined green technology with products and showcased them at the U.S. ecological exhibition in Los Angeles in 2014. For instance, BYD implements the innovation of China’s new energy photovoltaic technology and provides electric vehicle batteries with a service life of up to 40 years, with an annual attenuation of only 0.3%, and the overall technology has reached the leading global level.

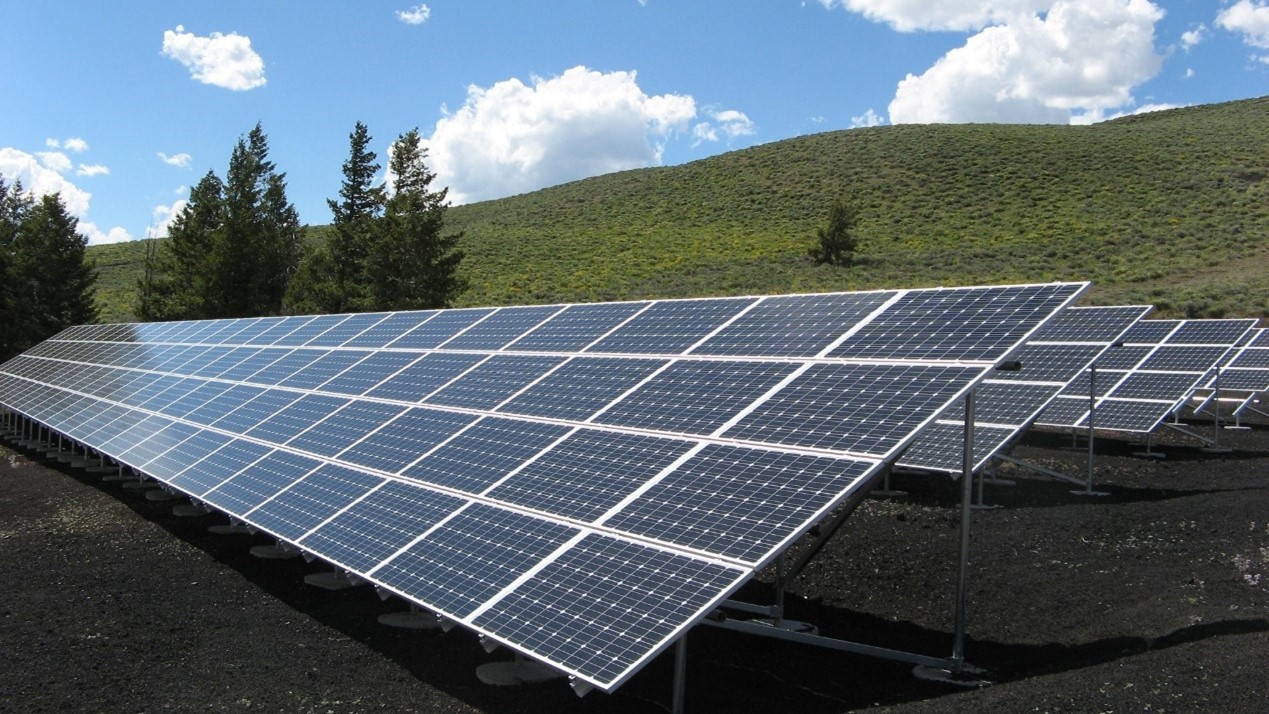
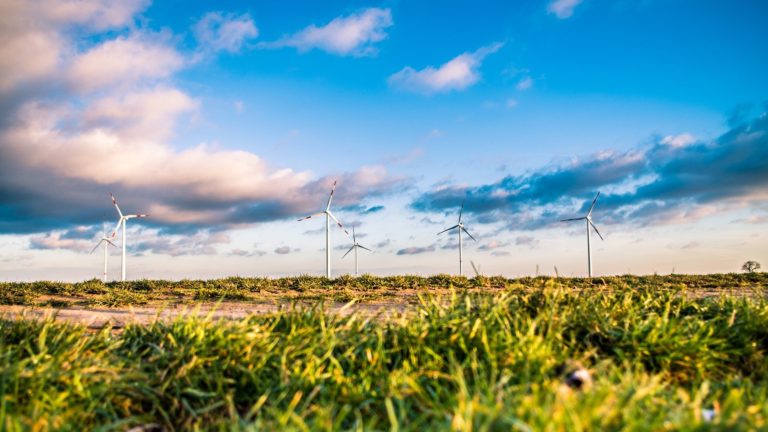
Furthermore, China supports the structural upgrading of the production process, eliminates industries with high pollution and high energy consumption, and accelerates the development of green technology and low-carbon transformation. For example, some policies raise the emission standards for coal-fired power projects; they also suggest reducing the proportion of heavy industry in traditional industries. Moreover, the government accelerates the development of new energy for sustainable development, such as wind energy and solar energy, to form a new low-carbon and efficient energy system. The purpose is to reduce the waste of high energy-consuming industries without lowering the industry’s total output.
The support from the Chinese government has encouraged people to set up companies focusing on green technology or even to develop new products related to it. China will try to apply green technology in new and emerging industries, notably after pledging to reach carbon neutrality by 2060. In September 2020, Xi Jinping outlined China’s transition towards carbon neutrality (net-zero CO2 emissions) by 2060. To do so, the country will have to reach its peak CO2 emission levels by 2030 and drastically cut emissions thereafter.
Key measures supporting China’s energy transition
China’s approach to cutting down on CO2 emissions appears to be focused on incremental steps instead of a sudden disruption. Unlike the many (often unexpected) crackdowns in 2021, the transition towards a greener economy will comprise many small steps across multiple industries. Critical steps towards China’s carbon neutrality goal include:
- Increasing the renewable energy share
- Deploying negative-emission technologies
- Establishing a nationwide green market
Beijing presented short-, medium- and long-term strategies to reach the overarching goal of net-zero emissions by 2060. The country’s response to the Covid-19 pandemic continues to shape investment patterns in the short term. Government raises multiple funds mainly for carbon-heavy infrastructure to ensure economic stability. Overall, the short-term efforts to mitigate climate risk remain limited.
For the long-run development, the Chinese 14th five-year plan envisages targets on energy intensity, carbon intensity, the share of renewable energy sources, and forest coverage. However, many experts argue that the goals outlined in the document remain vague and will not trigger significant action among Chinese industries. In the long term, the country seeks to reduce the role of coal in its energy mix.
Challenges for Beijing to become carbon-neutral
The country faces several challenges in the outlined transition. First and foremost is the industry’s massive dependence on cheap energy coal. There is no doubt that cutting back on coal will be challenging, as China’s energy demand is still growing. Secondly, the ongoing urbanization in China puts pressure on the defined sustainability goals. Cities contribute about 85% to China’s CO2 emissions, and implementing city energy conservation and emission reduction policies can effectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Finally, local governments from provinces that are heavily reliant on industry, such as Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Yangtze River Delta, and Guangdong, have not yet presented an action plan to tackle climate issues and achieve the defined goals defined by president Xi Jinping in 2020.
In addition, large cities face challenges in reducing the carbon footprint of their transportation. The Beijing News in 2021 reported that urban traffic emissions in Beijing have increased by 4% every year over the past five years. To solve this problem, Beijing local government has implemented relevant policies, such as limiting traffic according to the tail number of license plates and restricting vehicles from other provinces. Through industrial relief, Beijing has also moved printing and other industries with high energy consumption and high pollution to the surrounding areas while vigorously promoting the conversion of petrochemical energy into electricity.
Key Takeaway of the development of green technologies in China
- China has made many significant achievements in adhering to green and sustainable development in recent years, such as high-efficient use of renewable power and the innovation of new energy automobiles.
- Developing green science and technology will help China become a world energy exporter, which can export energy-saving and emission reduction policies and effects.
- This new round of technology and energy transformation revolution can effectively reduce the costs and waste of resources.





