China’s diabetes treatment market is about to experience a boom, and this piece explains why. For some background, diabetes is a disorder of metabolism that impairs one’s ability to process blood glucose or blood sugar. The pancreas releases insulin to help body store and use the sugar and fat from the food eaten. Diabetes occurs when pancreas produces little or no insulin or when body does not respond appropriately to insulin. There are two most prevalent types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) and Type 2 diabetes (T2D). As there is currently no cure for diabetes, patients are required to actively manage their conditions to slow down the progression of such disease and stay healthy.
A significant gap still remains in the Chinese diabetes treatment market as only 5.6% of diabetes patients are achieving optimal control of blood glycose, blood pressure and lipid targets concurrently. Optimal diabetes control requires good medical care, patient empowerment, health literacy and self-discipline.
Why diabetes in China should not be overlooked by the medical industry
In 2021, the number of reported diabetes patients in China reached 140.9 million, an increase of 53.7 million compared with 2009, accounting for 26.2% of the total number of reported patients in the world. With the improvement of health awareness among Chinese residents and the popularization of disease treatment and management, the growth of diabetes patients is expected to slow down in the future. However, it is predicted to increase to 164.1 million and 174.4 million in 2030 and 2045 respectively.
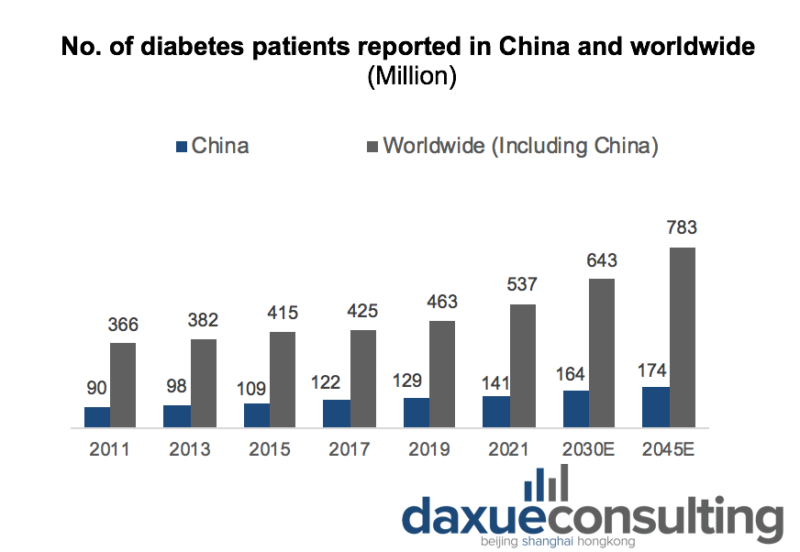
Because of the aging population, the prevalence of diabetes among people aged 20-79 in China is significantly higher than the global average, with an increase in recent years. In 2021, the prevalence of diabetes among people aged 20-79 years in China reached 10.6%, an increase of 1.8% compared with 8.8%] in 2011.
There are an estimated 141 million adults with diabetes in China, which equates to 13% of adults. China has the highest number of deaths from diabetes, with nearly 1.4 million deaths a year.
Type 1 diabetes patients in China
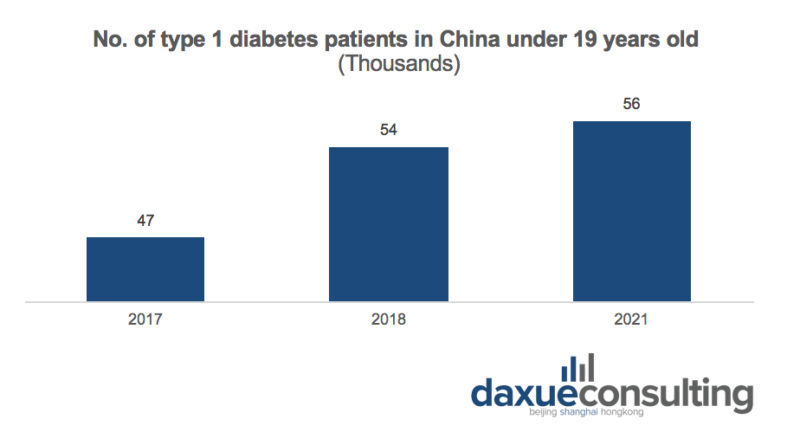
The number of children and adolescents (0-19 years old) with type 1 diabetes in China has been on the rise for many years. In 2021, the number of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in China reached 56,000, an increase of 20,000 patients compared with the same period in 2019.
Prediabetes in China: affecting a third of the population
The standardized prevalence of prediabetes was 35.2% (33.5% to 37.0%) in Chinese adults, diagnosed by the ADA criteria (table 3 and supplementary table 2). No significant differences in the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes were found between urban and rural residents. More than 50.5% of Chinese adults with diabetes have not been diagnosed.
China’s increasing obese and overweight population
The overweight rate of Chinese adults has already exceeded 50%; nearly 20% of children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 were overweight or obese. 10% of children under the age of six are overweight or obese.
In 2021, the Chinese CDC published its latest data on the size of Chinese adults in The Lancet. According to the study, about 85 million Chinese adults aged 18-69 were obese in 2018, 48 million men and 37 million women.
China’s population develops diabetes at a much lower BMI compared to westerners
One big challenge of the Chinese diabetes treatment market is attributable to the finding that Chinese people are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes at a considerably lower BMI compared to Western populations. BMI, or in another word Body Mass Index, is a measure of healthy weight using one’s height and weight.
A healthy BMI for most adults is between 18.5 and 24.9. However, according to a recent national survey, diabetes and prevalence of diabetes for participants with an ideal BMI less than 23 kg/m2 was 6.4% and 30.7%. The mean BMI of T2D diabetes patients in China are around 25 kg/m2. Both suggest that BMI and adiposity relationship differs between different populations. The relatively higher risk of type 2 diabetes at a lower BMI for the Chinese population may be partly explained by Asians having a higher percentage of body fat than those of Europeans at the same BMI and by the tendency toward visceral adiposity in East Asian population which includes Chinese people.
In addition, the East Asian population, when compared to European or African populations, has also been found to have a higher insulin sensitivity with a much lower insulin response. Furthermore, diabetic nephropathy was also more common among Chinese population than Europeans. Therefore, more specific and urgent strategies are required to prevent and diagnose diabetes and associated diabetic complications as Chinese population are exposed to a much higher risk.
The increasing prevalence of early-onset diabetes in China
The increase of early-onset diabetes in China should not be overlooked. Now, approximately 20% of diabetes patients in China are diagnosed before the age of 40. Individuals suffering from diabetes from a young age will have a higher risk of chronic complications, which will lead to mortality and morbidity in diabetes. Young-onset diabetes patients often had worse glycaemic control and higher prevalence of retinopathy. They were also less likely to be effectively treated with HbA1c and LDL, and to receive organ-protective drugs, such as statins and renin–angiotensin system inhibitors than late-onset diabetes. Moreover, Chinese early-onset diabetes patients had a higher risk of nonfatal cardiovascular disease. This tendency of early-onset diabetes in China should be alarming as it is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Causes of early-onset diabetes
The development of type 2 diabetes and daily eating habits have an evident relationship. Many people usually like to eat high oil, high sugar and high fat food, long-term consumption will lead to excess body weight gain. In obesity, the cells store excessive fat, causing the decline of cells sensitivity to insulin, leading to high blood sugar.
There is a certain genetic probability of diabetes. If both parents have diabetes, the chance of a child suffering from diabetes will be much higher. There are also some patients with diabetes caused by intergenerational inheritance. Although there is a part of type 1 diabetes in children’s diabetes, which is due to congenital causes, such as weak or missing pancreatic function. However, statistics in recent years have found that more and more children have type 2 diabetes rather than type 1 diabetes.
Some diabetic cases are due to the deficiency of the immune system. The lack of antibodies affects the body’s insulin beta cells, resulting in reduced insulin secretion.
Many young people are in the habit of staying up late, when the body’s cortisol and adrenaline are very active, which affects the body’s absorption of sugar; staying up late can also cause glucose levels in the blood to rise, which can also lead to diabetes.
China’s diabetes treatment market
Diabetes will be a major growth point for both China’s pharmaceutical industry and the healthcare industry.
Although the prevalence of diabetes in China has been increasing in recent years, with the continuous medical advancements, the case fatality rate of diabetes in public hospitals has declined significantly in recent years. In 2020, the case fatality rate of diabetes in public hospitals in China was 0.15%, down from 0.25% in 2015.
With the gradual increase of diabetes prevalence, the oral diabetic drug market sales from public hospitals in China were up to more than 20 billion yuan in 2021.
Top 10 oral diabetic drugs in public medical institutions in China (2020-2021):
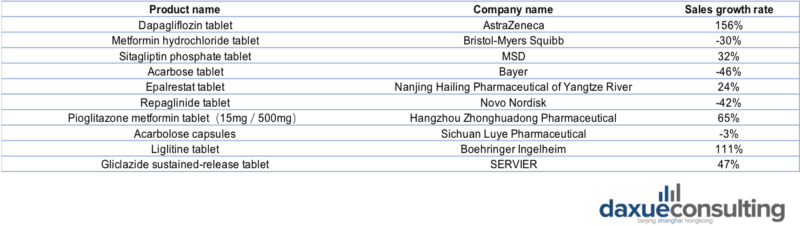
Source: China Commerce Industry Research Institute. Top 10 oral diabetic drugs in public medical institutions in China and their sales growth rate and ranking change from 2020 to 2021
From the perspective of the Top 10 brands, foreign pharmaceutical companies occupied seven positions, with AstraZeneca’s dapagliflozin tablets, Squibb’s metformin hydrochloride tablets, and Merck’s sitagliptin phosphate tablets ranking the top three. Domestic brands only include epalrestat tablets from Nanjing Hailing Pharmaceutical of Yangtze River, Pioglitazone metformin tablets (15mg/500mg) from Hangzhou Zhonghuadong Pharmaceutical and Acarbolose capsules from Sichuan Luye Pharmaceutical.
China ranks second in the world in diabetes-related medical spending, at $165.3 billion. GLP-1 agonists accounted for 18.8% of global diabetic drugs in 2020, with a market share of more than $13.1 billion. In comparison, the GLP-1 receptor agonist market in China is 1.6 billion yuan, accounting for 2.6% of the total diabetes market in China. Therefore, with the excellent clinical efficacy, safety and multiple benefits of GLP-1 products, as well as the promotion of GLP-1 products’ status in the “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in China”, China’s GLP-1 drug market has a large market development space and growth potential.
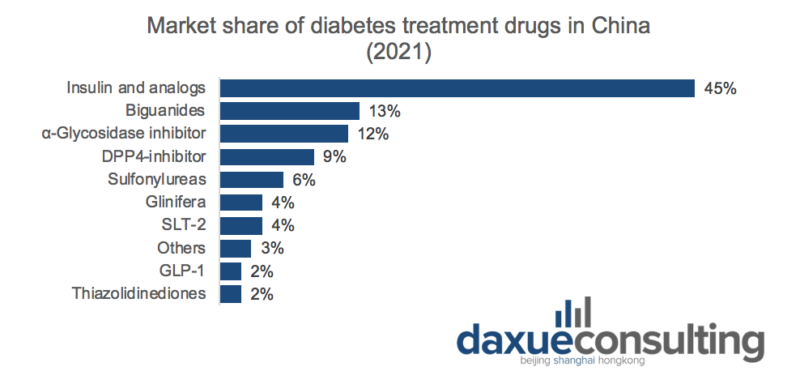
Insulin is one of the most widely used drugs to treat diabetes. The treatment of type I diabetes requires the use of insulin. There are two types of insulin therapy: multiple daily injections and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Insulin infusion therapy is also one of the main therapies for type II diabetes and gestational diabetes. Therefore, insulin syringe is the main product of diabetes treatment equipment. The market size of diabetes treatment devices in China reached 900 million US dollars in 2020, and is expected to reach 1.2 billion US dollars in 2022.
Adverse drug reaction (ADR) of diabetic treatment
In 2021, the National Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring Network received 1.96 million ADR reports of metabolic and endocrine system drugs including 216 thousand serious reports. The main reason behind the increase of ADR events reported in China is the rising prevalence of diabetes patients. Moreover, with the increasing usage of diabetic drugs , the Chinese government is paying more attention to public safety in drug use.
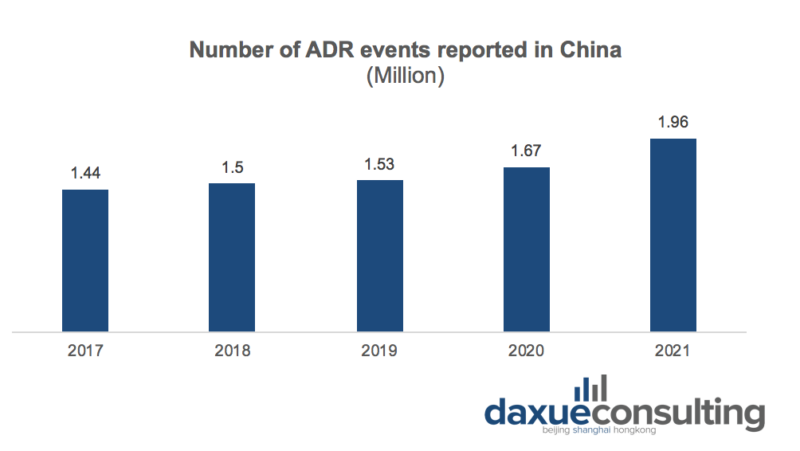
Source: CN-HEALTHCARE. Evolution of adverse drug reaction reports of diabetes treatment drugs in China
Because of the launch of new diabetes treatment drugs (polyethylene glycol losenatide, duratide, dapagliflozin) on the market, there was a sudden surge of ADR events with 0.29 million increase compared to 2020. Among the ADR events reported in 2021, the top three organ systems involved were gastrointestinal system diseases, skin and subcutaneous tissue diseases, systemic diseases, and various reactions at the site of administration.
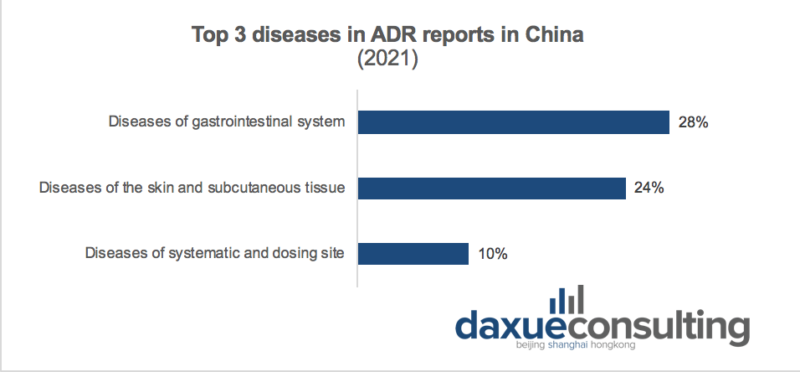
Source: CN-HEALTHCARE. Top 3 diseases in ADR reports in China
According to the ADR reports, the top 3 drug categories were glucocorticoids, biguanides, and other diabetes treatment drugs, and the top 3 drug categories in the number of serious ADR events reported were glucocorticoids, insulin, and antithyroid drugs. In addition , some newer diabetes treatments (e.g., pegylated losenatide, duratide, and dapagliflozin) should be highlighted asthese drugs have risen rapidly in the rankings of both ADR and serious ADR reports.
The medical instrument for diabetes treatment in China
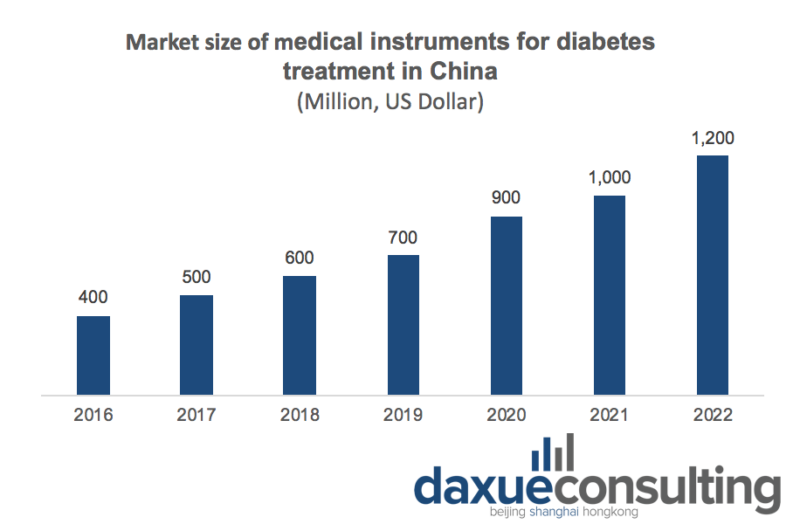
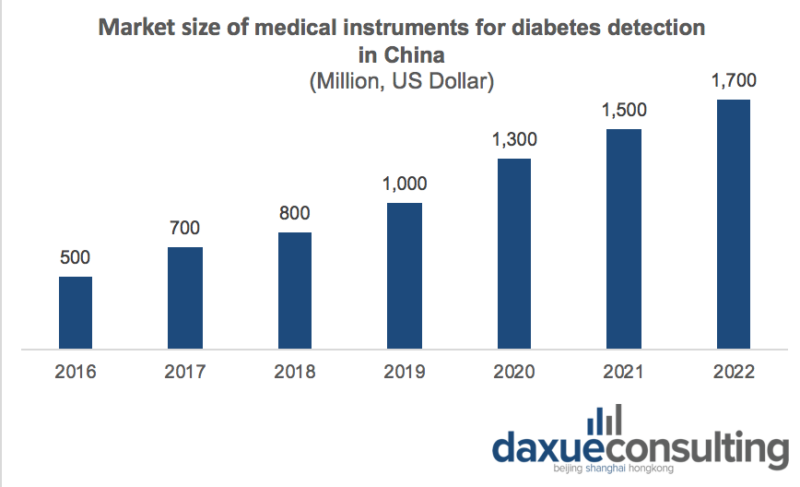
Diabetes monitoring medical devices can be divided into blood glucose monitoring systems, continuous blood glucose monitoring systems and other devices, such as HbA1C and ketone detection. At present, China’s blood glucose monitoring system and continuous blood glucose monitoring system are not included in the national public medical insurance plan. Continuous blood glucose monitoring is not expected to be included in the national public health insurance program for at least another three years. The market size of diabetes monitoring devices in China reached $1.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $1.7 billion in 2022.
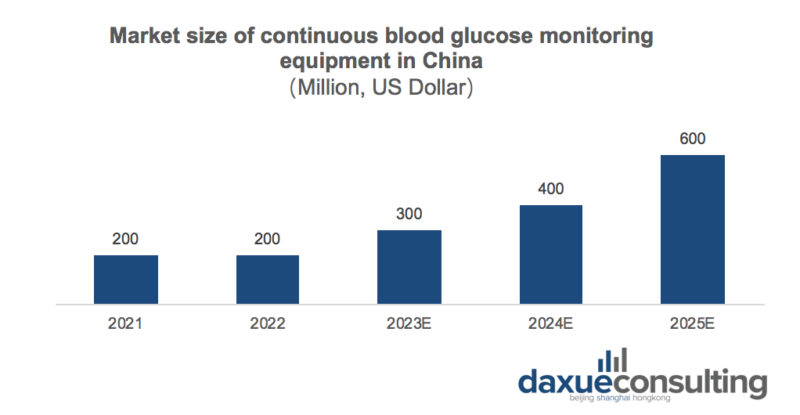
Continuous glucose monitoring systems continuously measure blood glucose levels (usually interstitial glucose) and update the glucose level display every one to five minutes. Benefiting from the advantages of continuous blood glucose monitoring systems over blood glucose monitoring systems and the growing acceptance of patients, the market size of continuous blood glucose monitoring systems in China reached US $200 million in 2021 and is expected to reach US $600 million by 2025. As more continuous glucose monitoring system products come on the market in the future, they will gain wider acceptance and adoption.
Currently, only few companies in worldwide are developing an artificial pancreas, including Medtronic, Microtech and Tandem. China’s first artificial pancreas device is expected to be on the market by 2023. As people gradually realize the advantages of artificial pancreas, the artificial pancreas device market in China is forecast to reach 31 million US Dollar by 2023 and close to 4.88 US Dollar by 2030.
The future of China’s diabetes treatment market
China’s diabetes treatment market is developing rapidly with rising prevalence of diabetes, and the potential demand for medical instruments of diabetes treatment among Chinese patients is enormous. China’s first artificial pancreas device is expected to be on the market by 2023. As we can see from the APR events report, the barriers to enter the market are getting higher. The Chinese government’s drug regulation are becoming more established and the evaluation of drugs safety is more grounded to minimize the risks of new drugs.