Navigating the complexities of China’s business culture and political environment is crucial for a successful market entry.
With over 1.4 billion inhabitants, China has the largest population in the world, offering businesses a vast pool of potential customers and clients. The middle class in the nation is also growing quickly as more and more people move into higher wage tiers. Due to the rise in disposable incomes and consumer spending power brought on by this growth, there is a high demand for a variety of goods and services. Despite economic fluctuations, China has maintained a robust economic growth rate, improving living standards and increasing consumer purchasing power. These factors make China an attractive market for businesses.
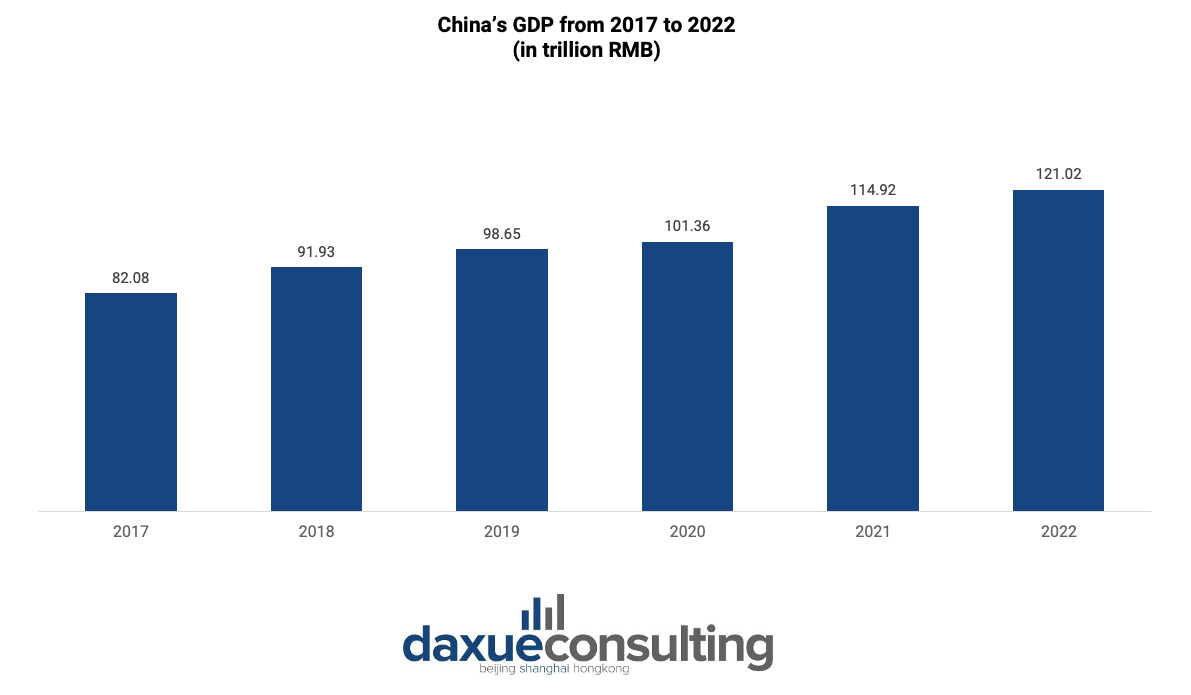
The country is a hub for technology and innovation, with advancements in areas like e-commerce, mobile payments, AI, and electric vehicles. China’s manufacturing capabilities and supply chain infrastructure also makes it an attractive choice for businesses seeking cost-effective manufacturing options.
A glimpse into the Chinese market
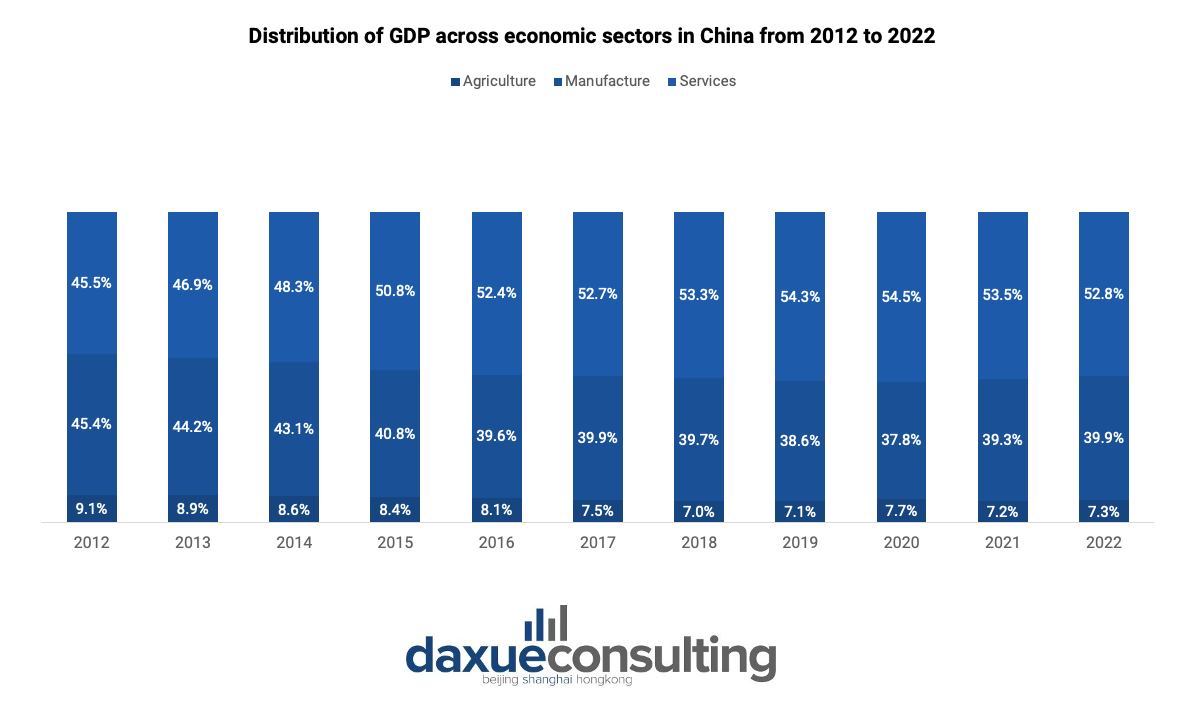
The services sector has witnessed significant growth, accounting for over 52% of the country’s GDP in 2022. This growth is driven by increased consumption of goods, such as jewelry, home appliances, garments, and automobiles. Additionally, in May 2023, retail sales increased by more than 12.7% compared to the same month the previous year.
China’s manufacturing sector, while still substantial, has experienced a decline as a percentage of GDP in recent years. In 2022, it represented nearly 40% of China’s GDP, down from 45.4% in 2012. This shift is attributed to China’s transition towards a domestically-driven consumer spending economy. The country is known for manufacturing a wide range of goods, including iron, steel, textiles, electronics, and automobiles. In fact, China is the world’s largest car manufacturer, producing 32% of global car production in 2021.
Agriculture is the third-largest sector in China, accounting for 7.3% of the country’s GDP last year. Although this percentage may be lower compared to some emerging economies, China boasts a diverse range of agricultural production. The country cultivates various crops including corn, rice, wheat, soy, cotton, peanuts, and apples. It is a significant contributor to global production, leading in the production of nectarines, peaches, peanuts, rice, and wheat.
Designing a strategy to enter the Chinese market
There are several steps that can be taken to devise a successful market entry to China:
1. Market overview and potential assessment
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape in China and effectively assess the challenges, potential risks, and opportunities, it is essential to analyze the business environmental conditions. This analysis allows businesses to evaluate the factors that can impact their brand within the Chinese market and provides insights into the evolving market dynamics. By considering these factors, companies can obtain a clearer perspective on the competitive landscape and make informed strategic decisions.
2. Benchmark analysis of successful market entrants
By examining successful market entrants in China, businesses can gain valuable insights and make meaningful comparisons to understand their strategies. This analysis not only helps identify effective practices that can be adopted but also highlights ineffective ones to be avoided. Understanding and learning from the approaches of successful players in the Chinese market can provide brands with a competitive edge, enabling them to make informed decisions and enhance their chances of success.
3. Consumer insights
By actively gathering first-hand data from end-consumers and local professionals, such as brand managers, retailers, importers, and traders, it becomes possible to validate the value proposition and brand concept. Engaging with end-consumers through methods like focus groups allows for a deeper understanding of their preferred purchase channels, trusted information sources, and acceptance of marketing messages. This valuable insight enables the refinement and optimization of marketing strategies, ensuring a stronger alignment with the target audience and enhancing the overall effectiveness of the brand’s communication efforts.
4. Consumer segmentation
Segmenting the market based on key criteria and analyzing demand breakdowns provides valuable insights for targeting specific consumer groups. By quantifying the potential market share, brands can design effective marketing strategies tailored to their audience. Developing data-driven marketing personas that accurately represent different consumer types enables brands to align their offerings with the specific needs of their target customers.
5. Investment allocation and implementation design
The final step in the market entry plan involves synthesizing the research findings to create a comprehensive and actionable road map for entering the Chinese market. This includes designing investment plans for the initial years and beyond, developing a portfolio of marketing actions, prioritizing consumer targeting and gradually expanding operations, implementing partnership and network-building strategies, and establishing financial statements and revenue generation models. This strategic approach ensures a well-rounded and effective market entry strategy in China.

Challenges in entering the Chinese market
1. Market knowledge
Entering and growing in the China market can be a daunting task for managers of foreign-invested enterprises. Due to the size and diversity of China and the lack of reliable centralized/official information databases, it is difficult to obtain information on certain industries, ripe markets, or companies. Thus, market knowledge must be obtained “on the ground” which could pose a significant obstacle for foreign businesses.
2. Unique culture and consumer preferences
Due to its distinctive culture, consumer consumption patterns, and changing trends, entering the Chinese market presents a number of challenges for foreign enterprises. The challenges lie in effectively localizing and adapting products, services, and marketing strategies to resonate with the local population’s distinct tastes, customs, and cultural sensitivities. Continuous research and the use of agile marketing strategies are necessary to stay current on shifting consumer behavior and market dynamics. Successful localization necessitates a major time and resource commitment as well as a thorough knowledge of the Chinese market.
3. Regulatory environment
China has a complex and constantly evolving regulatory environment. For example, its commitment to reach carbon neutrality by 2060 influenced numerous businesses in various industries to a more sustainable path. Foreign businesses need to navigate through various regulations, licensing requirements, and compliance procedures. To gain a comprehensive understanding of the Chinese regulatory environment, which involves multiple authorities and may have specific requirements or interpretations. Hence, understanding and adhering to Chinese laws and regulations can be a time-consuming and challenging process.
4. Intellectual property protection
Ensuring the protection of intellectual property rights is a matter of concern for businesses venturing into the Chinese market, as there have been instances of intellectual property infringement and the sale of counterfeit goods in the past. It is crucial for companies to implement suitable measures to safeguard their intellectual property.
Therefore, engaging a strategic consultant can provide valuable insights into the competitive landscape and offer guidance on leveraging local advantages. Collaborating with local partners may also be necessary in some cases to navigate the market successfully, build a local network, and adapt your products, services, and marketing strategies to suit Chinese consumers’ preferences and cultural context.
How to make a successful market entry strategy in China
- China’s attractiveness as a market stem from its large population, robust economic growth, and technological progress.
- To successfully enter the Chinese market, businesses need to address challenges such as adapting their offerings to align with the local market’s preferences, acquiring market knowledge, understanding the unique culture, navigating regulatory complexities, and implementing strategies to protect intellectual property.
- Partnering with a strategic consultant and collaborating with local partners can help overcome these challenges and achieve success in the Chinese market.
To have further information, contact us and subscribe to our newsletter.





