Due to the growing demand for entertainment and the rapid development of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), China’s virtual influencer industry is experiencing exponential growth. According to iiMedia, in 2022, China’s virtual influencer industry was valued at RMB 186.61 billion overall, with a core market size of RMB 12.08 billion. Projections indicate that by 2025, these figures will rise to RMB 640.27 billion and RMB 48.06 billion yuan respectively.
Download our report on Gen Z consumers

According to the China Advertising Association, the volume of virtual human Key Opinion Leaders (KOL) in 2023 increased by 292% compared with that in 2022. Many brands seize the opportunity, now partnering with virtual influencers and enlisting them as brand ambassadors. In keeping with this trend, Chinese tech heavyweights like Baidu and Tencent are actively exploring the development of intelligent, scenario-based virtual humans. Despite the current challenges faced by the virtual human industry, the market potential remains immense.
Phenomenal virtual influencers exert significant influence
The distinctive style captivates the public’s attention
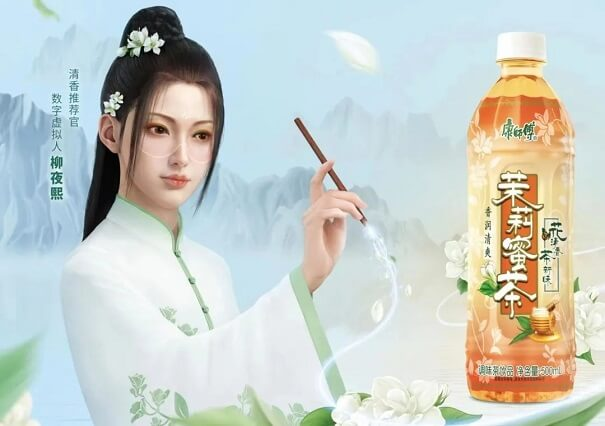
On Halloween night in 2021, a virtual personality named Liu Yixi swiftly amassed over one million followers within a mere six hours of its debut. The released video seamlessly blended elements of Chinese aesthetics, beauty, and suspense, garnering widespread acclaim.
As a virtual beauty influencer nurtured by the Chuangyi (创壹) technology over 8 months, Liu Yixi’s allure and cutting-edge technology left an indelible impression on the public. Subsequent videos mainly take the form of short films, exploring the relationship of “technology, life, and humanity.” The response from viewers has been huge, and various advertising and co-branding activities followed. According to the 2023 KOL Marketing White Paper, Liu Yexi, as a KOL with strong influence and appeal, ranked second on the list.

Embrace the power of virtual influencers to unlock business potential
Numerous brands opt to collaborate with virtual influencers as a strategic approach to address the challenges associated with revitalizing their brand and rejuvenating their brand image. Brands can not only increase their impact on Gen Z consumers but also open up new directions for their brands through virtual technology.
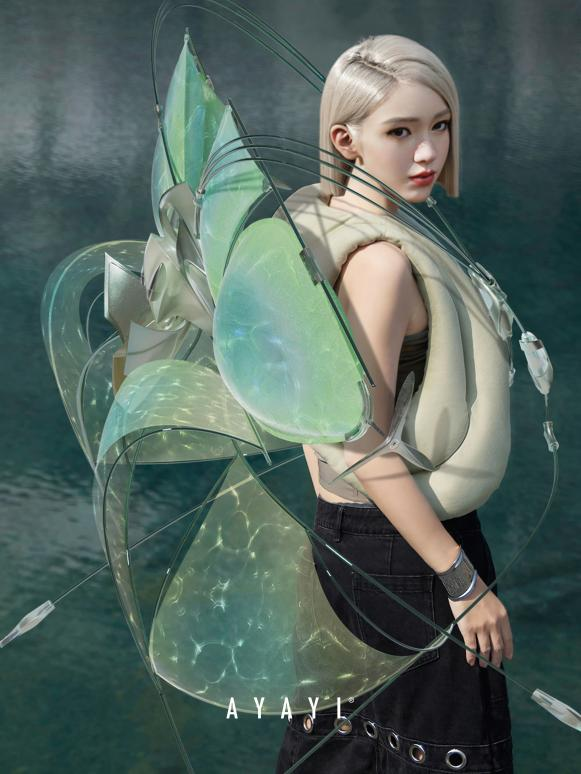
As China’s first meta-human and innovative virtual fashion KOL, AYAYI has ignited profound discussions about the future of the fashion market through her cutting-edge technology and exquisite fashion sense. AYAYI enjoys a substantial fan base on Xiaohongshu(121,000) and Weibo(897,000), and her impact is far-reaching among Generation Z, the majority of whom are female.
Unlike most fashion-oriented virtual influencers, in addition to regular brand activities, she also launched her own namesake clothing brand AYAYI, which blends physical products with digital content and virtual technology. Products are no longer just isolated physical entities, but multi-dimensional experiences closely linked to digital content, constantly pushing the boundaries of traditional fashion aesthetics.

Virtual humans meeting market demand are being mass-generated
China’s virtual influencers mostly demand substantial technical expertise and significant costs to build, but now there are new forms of virtual people. Chinese tech giants have established their own production platforms to launch cost-effective virtual people with a broader market. Tencent Cloud offers its AI Digital Human platform, catering to various industries including banking, government, operators, transportation, and other industries. According to Chen Lei, the product’s general manager, the customized digital human version costs around RMB 1,000 per person. As for the interactive 2D digital person, the daily usage cost is only RMB 9.90.
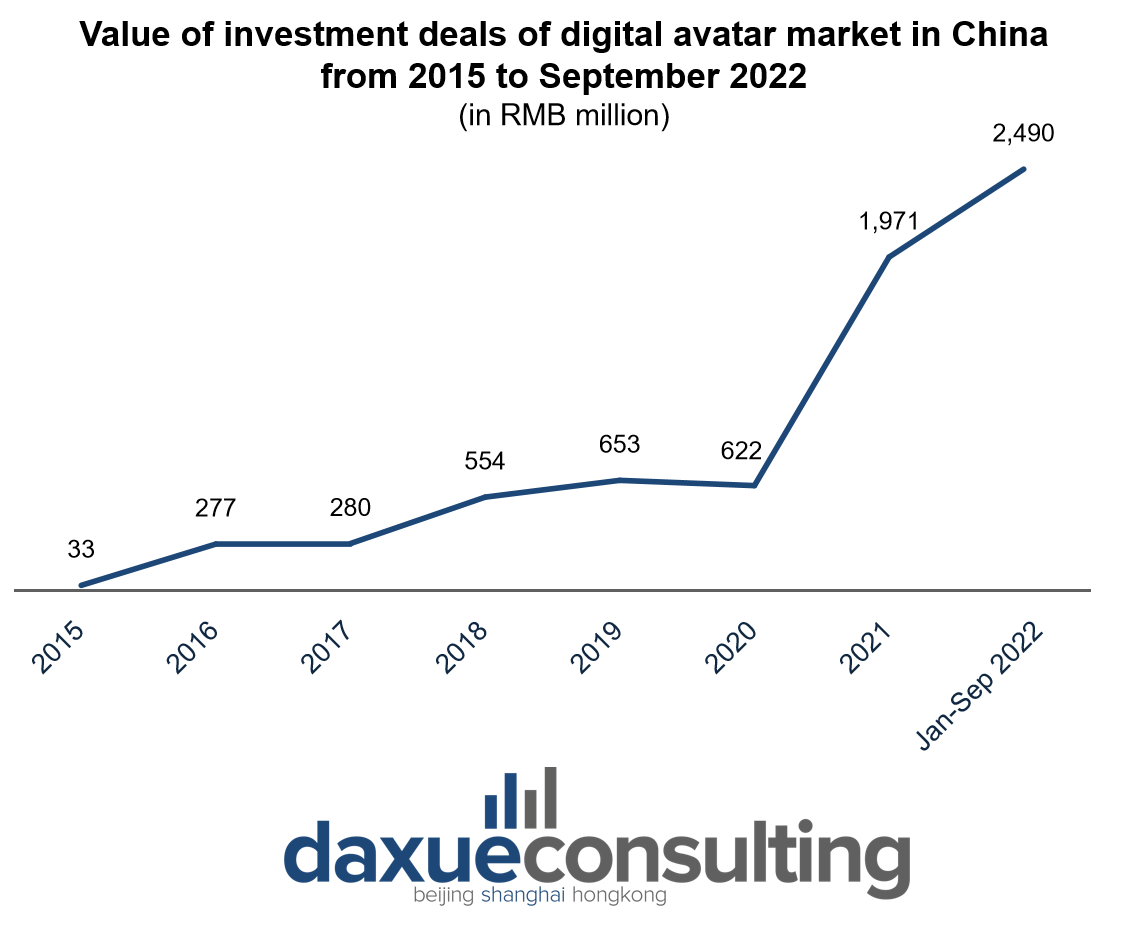
Baidu has also embraced this trend, developing the industry’s first e-commerce marketing model, “Baidu Intelligent Cloud Lingxi“. This model is integrated with the Digital People Live platform, and numerous company owners have actively participated in various broadcasting rooms. By simply uploading a real-person video, a one-to-one replica of the real person with a customized voice can be generated within 30 minutes. These low-cost, ultra-realistic, and training-free virtual humans have reduced labor and training costs, making them the choice for many businesses.

Vtubers: Unleash business potential
The Chinese animation, comic, and game (ACG) market has attracted a large number of young people. The emergence of virtual idol groups has garnered significant attention, with the market continuously increasing.
Different from AI-driven virtual humans, virtual YouTubers (Vtubers) capture the facial and bodily movements of real individuals. The activities of these Vtubers are mainly live broadcasts, and most Chinese Vtubers are active in China’s ACG platform Bilibili. Unlike commercial virtual influencers, they gain popularity with the real talent and charisma behind their virtual appearance, live streaming content is mostly entertainment, such as games, singing, and chatting. Since these virtual idols essentially represent real humans, they bridge the gap between the audience and the virtual human, making it easier for viewers to accept this form of virtual influencer.
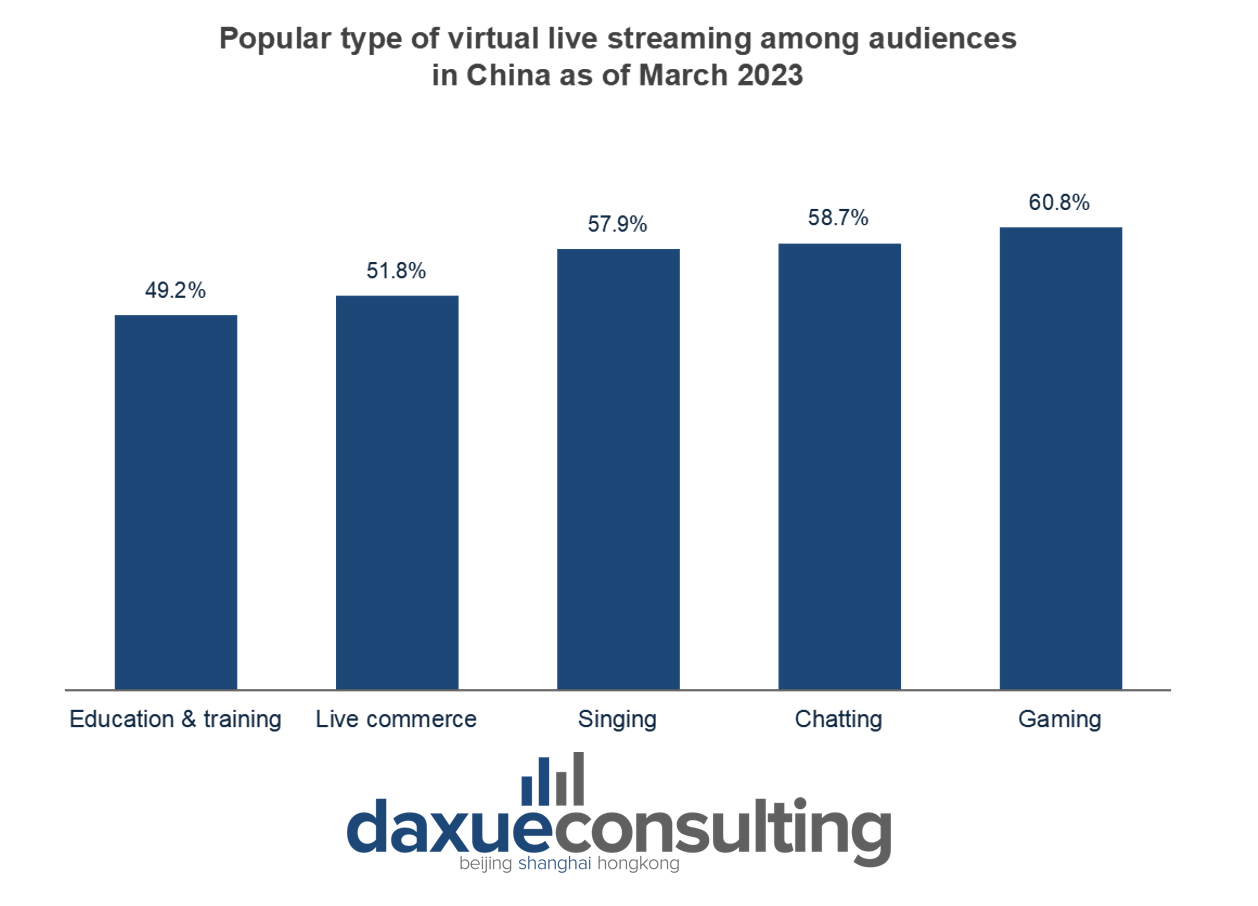
The progress of China’s virtual anchors has been gradual since their introduction in the summer of 2017. Fortunately, this phenomenon has improved after Bilibili opened a virtual zone. After that, the number of virtual anchors in China has surged. However, due to cost and technical constraints, during this period, both individuals and corporations predominantly utilize half-body LIVE2D images, with occasional 3D modeling and limited dynamic capture of the upper body. The majority of practitioners are native ACG enthusiasts, where interest serves as the primary motivation, supplemented by business endeavors. Upon the introduction of the virtual idol project A-SOUL by 乐华(Yuehua) Entertainment and 字节跳动(Byte dance)into this arena, significant changes occurred.
As a new idol group, A-Soul immediately attracted a large number of fans with its full-body motion capture technology, and the details of the characters’ movements can be precise down to the finger movements. A-SOUL also has its own facial expression capture technology. Powerful technology is A-SOUL’s greatest strength. After the launch of A-SOUL at the end of 2020, the entire pan-entertainment business segment increased revenue by RMB 16 million in 2021 and also increased gross margin to 77.7%, and clearly stated that this is due to the lower operating costs associated with virtual artists.
The substantial commercial profits have drawn the interest of major brands, leading to collaborations with KFC and Keep. L’Oreal has also opted to partner with the A-SOUL to launch joint gift boxes and singles. In 2022, A-Soul was featured on the cover of COSMOS magazine, once again proving the huge influence of virtual influencers.

The rise of China’s virtual influencers
Tencent, a leader in virtual human technology, has brought the country’s first fashion virtual idol Xingtong (星瞳) – the only real-time driven realistic virtual human in the industry. Unlike other virtual anchors, Xingtong, as Tencent’s popular IP spokesperson, has tailored a business model to her strengths. Since its inception, it has garnered support from both fans and major enterprises, boasting immense commercial potential. Since 2023, Xingtong has ventured into the realm of live streaming, achieving remarkable success with just two attempts, and quickly emerging as a leader in virtual live streaming. The first live broadcast generated close to RMB 1 million in Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV), while the second sold 4,090 graphics cards, surpassing the million mark in GMV. As a newcomer in product live-streaming sales, these achievements are noteworthy.
While delighting fans with her singing and dancing, Xingtong leverages live commerce to monetize her talent, showcasing impressive commercial acumen. Furthermore, she assumes the role of a spokesperson, engages in collaborative advertising, and amplifies brand appeal to a younger audience. Essentially, Xingtong emerges as a versatile entertainer, underscoring the limitless potential of strategic collaborations in the industry.

Challenges faced by China’s virtual influencers
Although the market is large, the virtual human industry still faces challenges such as a lack of relevant policies, immature key technologies, and an imperfect talent supply system. For mass-produced low-tech virtual people, the facial details are not refined enough to cause the Uncanny Valley effect, which makes people who have a wait-and-see attitude toward virtual people more deterred. Although the virtual idol has strong technical support, the real person still has some defects, which is easy to cause dissatisfaction of fans, making the virtual idol person collapse.
Workable solutions
Deeper research in related fields, such as artificial intelligence and modeling is necessary. At the same time, the development of related technologies such as computer graphics (CG) and extended reality (XR) also should be strengthened. By reducing the limitations of motion capture and face capture through high technology, the public has a more positive attitude toward virtual people and a higher purchase intention for the products and brands they endorse.
Alongside increasing funding, it is also crucial to ensure that the real individuals behind virtual characters do not deviate from the character’s portrayal, thereby maintaining the integrity of the virtual character. This can be achieved through stricter screening processes and higher wages.
China’s virtual influencers: the immense commercial potential coexists with risks
- In 2022, China’s virtual human industry was valued at RMB 186.61 billion overall, it is expected to reach RMB 640.27 billion in 2025
- More virtual humans become KOLs, exerting influence on GenZ.
- Tech companies build their own virtual human creation platforms, offering new options to reduce costs across multiple industries.
- Vtubers transcend traditional entertainment, exploring their commercial potential as leading influencers.
- Despite the high commercial potential, virtual influencer operators face technical, public acceptance, and ethical challenges. Hence, more funding, research, and stringent screening are needed.





