Advances in technology and artificial intelligence have made many things possible in China, especially on-demand food ordering. The use of AI in the food and beverage industry in China allows players to save time in the production phase in order to focus on more creative solutions and research. Now robots can be found in restaurants factories using AI in China, with the aim to make the daily life of Chinese consumers easier.
AI in the Chinese catering industry: restaurants are the next target of AI
According to the China Industry Information Network and China Daily, China’s catering industry reached a revenue of 4.27 trillion yuan ($628 billion) in 2018, a new record. In this dynamic sector, the use of artificial intelligence is becoming more and more widespread. The Chinese e-commerce giants have embarked on the race.
Robots in restaurants in China
The most visible application of AI in food and beverage is the use of robots in restaurants in China. Earlier this year, Chinese e-commerce giant JD.com announced plans to open 1,000 restaurants by 2020 where food will be prepared and served by robots.
Chinese robot chefs
The use of robots in restaurants in China raises several questions. Does food prepared by robots taste as good as food prepared by human chefs? What about the job of cook, will this lead to mass layoffs in the restaurant industry? These are questions that several restaurants and cafes have tried to address after installing robots in their kitchens.
A leader in the industry is Xcafé, a restaurant opened by JD.com in Tianjin at the end of 2018. This 400 square meter restaurant can welcome up to 100 people ready to enjoy the dishes prepared by the robot chefs. The process is simple: one person supervises approximately 5 robots who are in charge of all the preparation steps. Receiving orders, choosing products, assembling, cooking and plating up, everything is done by artificial intelligence.
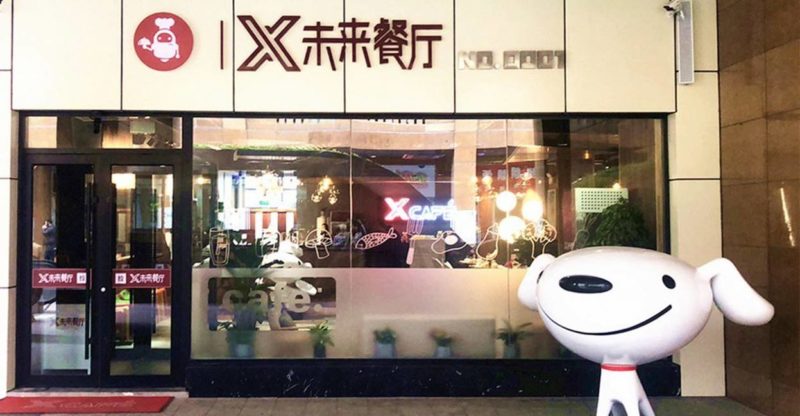

However, the example of Xcafé shows us that robots are not yet independent enough to manage restaurants alone. On the other hand, they can also still represent a big advantage; smart restaurants in China are becoming a real tourist attraction.
Having cooks or robot bartenders is still something new around the world and a lot of chains are promoting it to attract customers who are keen on high tech.
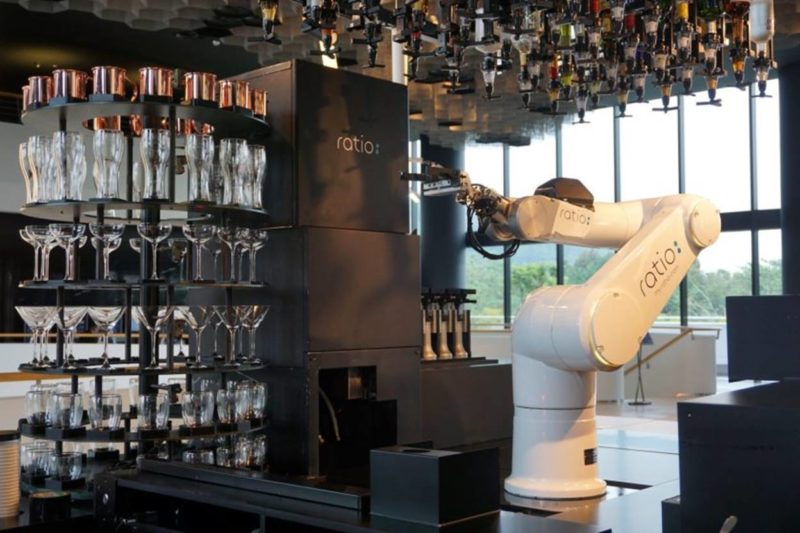
In Shanghai, the Ratio recently opened its doors with an attractive concept: the bartender is a state-of-the-art robot that modeled after the arm and hand of a real bartender. Customers order on a Wechat mini-program and can see the robot prepare their orders in front of them. Of course, as far as human interaction is concerned, human managers are still there to answer customers’ questions.

Chinese robot waiters
The kitchen is not the only place you can find robots in restaurants in China. They are also in the dining room, interacting directly with customers to take orders and serve meals.
Haidilao, one of the largest hotpot chains in China (the only Chinese food company with a revenue of over 10 billion) opened the world’s first artificial intelligence technology restaurant in Beijing in 2018. A fully mechanized service with intelligent robots as waiters and a panoramic screen to order everything to enjoy your private custom-made hotpot experience.
“Our next goal is to be the most intelligent restaurant in Beijing, we are already conducting technical discussions. I believe that in 10 or 20 years, there will be no more people in hotpot restaurants, only two engineers who can take charge of everything”
—Zhang Yong (CEO of Haidilao)
In the dining room, humanoid robots navigate the tables to serve customers their orders, which were taken on ipads. However, the restaurant is so big that there are still human waiters to take care of the 93 tables. In this case, it appears robots are present in restaurants as a novel attraction and not to replace servers.
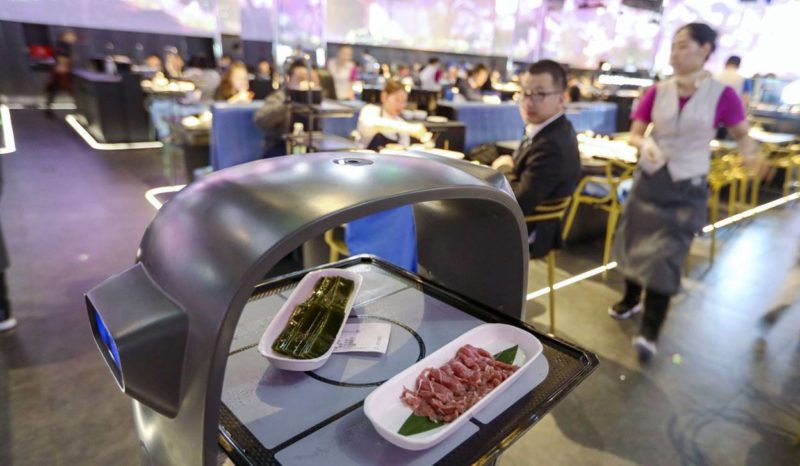

Alibaba has also hopped on board with AI in the Food and Beverage industry in China with Robot.He. Following its New Retail project, the restaurant, located in the Shanghai suburb of Nanxiang is part of a Hema’s store. In alignment with Hema’s Retailtainment strategy, waiters are small robots that bring you dishes prepared by cooks.

Leverage big data to understand customer expectations
AI in the Chinese catering industry also makes it possible to predict customers’ expectations and tastes in order to offer them an ultra-personalized experience. This is what the Chinese pizzeria chain La Cesar has set up.
By analyzing the data collected on Baidu, marketers can see what the current food trends are. The analysis of social networks or other applications such as Dazhong Dianping via web robots can also be very relevant. The idea is to analyze trends to create appropriate recipes and menus. So the restaurant is constantly changing its menu. This reminds us of the business model of major international clothing chains such as Zara, which relies on the continuous renewal of its collections.
Thus, the intelligent software combines searches, comments, and photos to create a list of the most frequently used keywords to produce a monthly report that serves as a basis for managers to create new recipes. This is how the cranberry smoothie became a success after a 2017 analysis showing the trend of sour flavors and cranberries during the summer. Another example is the durian pizza, which is the brand’s best-seller.
In China, KFC also uses data to predict customer choices. Thanks to intelligent software that assembles the customers’ faces and their previous choices, KFC is able to offer a choice adapted to each customer. The facial recognition technology was developed in partnership with Baidu.
Smart restaurants in China: a way to ensure safety and hygiene
Beyond purely marketing applications, AI in China’s F&B has also been used to ensure kitchen hygiene. It has become a very sensitive subject in China since the 2008’s melamine-tainted infant formula scandal. The relatively high frequency of such incidents takes a great toll on consumer trust. Artificial intelligence can be a solution. A camera-based system is currently being piloted in the Zhejiang city of Shaoxing to recognize the bad sanitation habits of cooks. A camera system installed in kitchens is able to recognize 18 different types of health risks such as smoking, using your phone, not washing your hands or touching your hair.
An alert is then sent to managers via a mobile app. The system also recognizes good sanitary habits such as disinfecting surfaces, using gloves, checking the temperature of refrigerators. This system based on motion and facial recognition can encourage employees to maintain good habits that would be financially rewarded.
According to a report, since January 2019, approximately 1,700 cameras have been installed in more than 800 restaurants in Minhang district, Shanghai. The food safety project is led by the Market Supervision and Management Bureau of Minhang, which will also receive alerts.
We can see several advantages to the use of AI in the Chinese catering industry:
- Rapid service, the average robots in restaurants are capable of processing up to 8,000 dishes each day
- More endurance than human cooks and no need to take breaks or change the team.
- Fun, attractive to tourists
- No room for human error, protocols are respected bringing transparency for everyone
- An increasingly important database for marketers and the beginning of the era of extreme personalization
However, it should be noted that the price of a robot remains very high today for the trend of AI in the Chinese catering industry to really grow. For a restaurant to employ a robot worker it must pay about 50,000RMB for each robot and then several hundred RMB each month for its upkeep. To compare, a waiter in Shanghai would cost between 3,000 to 10,000 yuan per month.
While facial and speech recognition systems can be profitable, robot restaurant managers are not yet ready.
AI in food delivery in China
Delivery drones in China
A famous application of AI in the food and beverage industry in China are delivery drones. These are supposed to facilitate the process of meal transport to the country where food delivery apps have an estimated 355 million users.
However, the introduction of drones requires the creation of air routes over cities. A trend that is still being tested today and which causes a real problem of competition between the different brands. Who will have the roads above Beijing, who will have the longest roads to the countryside? The war of automatized food delivery in China has only just begun.
Ele.me, China’s largest delivery application with 260 million users and 53.4% market share, was the first to receive government approval to work on the first air routes for delivery drones.
Thus 17 roads have been approved over Shanghai, in the Shanghai Jinshan Industrial Park. This should benefit more than 100 restaurants in the area. The Ele.me drones used during this test phase are capable of carrying up to 6 kilos and flying at a maximum speed of 65km/hour.
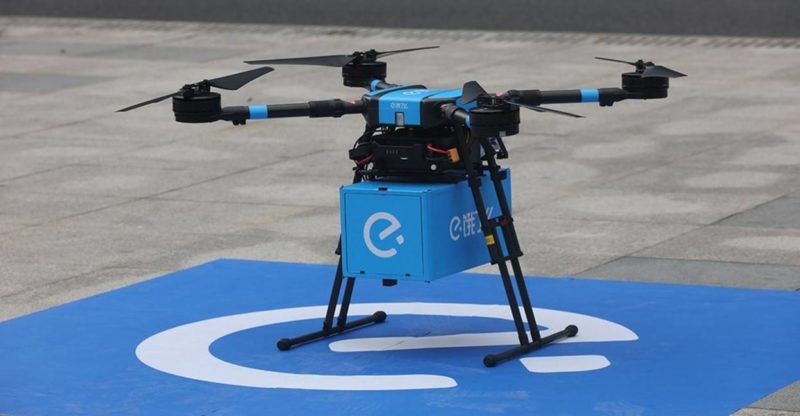

The trend is gaining momentum with China’s e-commerce platform JD.com also entering China’s drone delivery market with a license to experiment with delivery drones in Shaanxi Province last year.
How automated food delivery in China is breaking records
The battle is growing between all the players in food delivery and the stakes remain the same: who will be the fastest?
While drones can become the solution, for the time being, other AI-based software and systems are being used. That’s how Meituan Waimai, commonly known as Meituan, which controls 40% of China’s food delivery market, developed its AI-powered Super Brain, a system to automatize food delivery in China.
The system aims to ensure the best delivery times at any time of the day or night and under any weather conditions. Everything is based on data: artificial intelligence analyzes data before, during and after delivery to always improve. The aim is also to offer customers a very accurate estimate of delivery time in real-time.
This is how Meituan Waimai promised to break all delivery records in China.
AI in China’s F&B: controlling the food supply chain
It all starts in the fields
Artificial intelligence has also made its entry into the world of agriculture in China. Thanks to cloud-based agricultural intelligence, farmers are now able to improve their yield and the quality of their product.
Alibaba recently launched its “ET Agricultural Brain” in Shanghai, a powerful intelligent software based on big data that will change the lives of Chinese farmers.
The AI is able to record all the production details to regulate the full life-cycle of production. Vegetable and pig farmers have already started using the program. This is the case of Tequ Group, a pig breeding company based in Sichuan that has been using Alibaba’s technology for several months to raise its pigs. So each pig has an identifier that allows them to set metrics, to see which pig is sick, which pig is fertile, reducing mortality rates.
AI in factories in China: How robots perform quality assurance
2nd step of the process: the establishment of AI in factories in China. This is primarily used to improve machine performance and ensure quality. For example, the AI modules from EZ Robot Inc. have improved production efficiency, inventory turnover, and equipment utilization across China.
But more recently, a new type of robot has appeared in factories using AI in China: Taste-testing robots.
Powered by artificial intelligence, they aim at guaranteeing the quality of some mass-produced Chinese food such as pork belly, black rice vinegar, fine dried noodles, etc.
The idea sounds crazy but before this job was done by human tasters and the process was slow. Thanks to robotic tasters, the assessment will not vary from one person to another.
According to the report of the China National Light Industry Council, the Chinese food manufacturers that have taken part in the government-funded AI-tasting program have received positive feedback.
The robots can also check that all the food has the same color, smell, and taste.
Finally, AI in factories in China can also sort ingredients. Food sorting is indeed a very time-consuming step in factories because it is carried out by human hands. But with artificial intelligence and especially image and motion recognition systems, factories using AI in China can accelerate this production phase. Products can be sorted by size, color, and freshness.
AI in China’s F&B: ensuring transparency for the customer
If AI in the food and beverage industry in China can directly serve the interests of customers, it is in the tracking of the supply chain.
Mengniu Dairy, China’s second-largest dairy company, is embarking on an effort to bring the centuries-old industry up to date using AI in China’s F&B. In the dairy industry, in particular, the whole process is very delicate and the temperature at each stage of production must remain the same.
Mengniu is now collaborating with Alibaba to use AI to analyze the supply chain, to gain information such as where to manufacture products and where to collect milk, as well as how products can be transferred to customers with maximum efficiency.
Alibaba has indeed big plans to integrate food-tracking blockchain technology into the supply chain in its stores. The company undertook a traceability test conducted last year to track the origins of a package of mangoes thanks to AI. It took only 2.2 seconds compared to 6 days and 18 hours using traditional methods.
How to find the right partner to work with AI in the Food and beverage industry in China
Daxue Consulting offers you a short list of actors developing AI solutions that could be very good AI partners in China. You can find a full list here.
ZhongAn Technology
ZhongAn Technology, the tech subsidiary of Chinese Insurtech giant ZhongAn Online, is a FinTech company focusing on the research and development of technologies in blockchain, AI, big data and cloud computing. They have developed a research center and lab, the Fudan-ZhongAn Blockchain & Information Security Joint Laboratory, to remain at the forefront of research within a large network of AI partners in China.
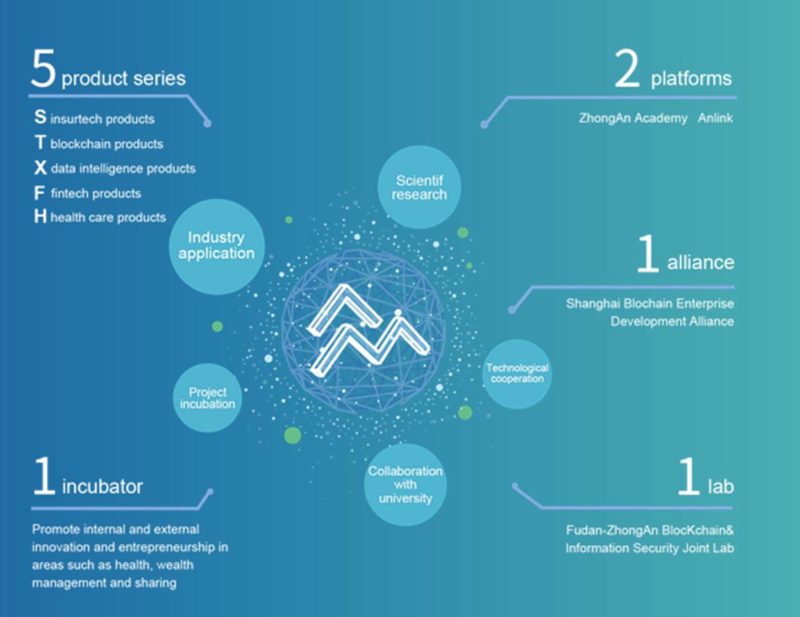
They have already worked on a technology relying on blockchain farming to provide more trustworthy food. They applied blockchain in raising free-range chicken in rural areas. Their project called “Go go Chicken” is already working in more than 200 farms in Anhui, Henan, Guizhou, Shaanxi, Gansu, Hainan, and other provinces. By 2020, it will land in around 2,500 farms in China.
EZ Robot Inc
EZ Robot is not only specialized in AI in China’s F&B but in high-performance robots more generally. They are known for their robots in education and how they are able to interact with children but their robots can also be used in the catering industry. Indeed their robots can be controlled remotely and adjusted by wifi and can have all the useful features: vision tracking, speech recognition, artificial intelligence, 3D printing, etc.

Hongbo Zhicheng Technology
Hongbo Zhicheng Technology is a Chinese start-up based in Shenzen that has been known to have created “stir-frying robots”, i.e. a kind of equipment (non-humanoid) that automatically cooks, such as automatic woks. They are the AI partners in China of some of the biggest names in the F&B industry such as Haidilao or the Japanese fast-food franchise Ajisen Ramen. If you need their robotic solutions for canteens, schools or other facilities, they can also be a good solution. In addition to their machines, Hongbi Zhicheng Technology is developing a research lab in Chinese cuisine to see how robots can improve in Chinese techniques. They have also developed a digital database of recipes for several hundred Chinese dishes.
Infinite Food
Created in 2015, Infinite Food is the right AI partner in China if you want to combine food and robotics.
The company’s core product is a vending machine that prepares and distributes meals on-demand. The strong point is that robots are able to work correctly with fresh products. Today, the company is still looking for ways to improve its product and considers it to be a “restaurant in a box”. It is possible to rent or buy this product.

Despite all these innovations, many people remain doubtful about the use of AI in the food and beverage industry in China. It raises the question of the standardization of Chinese food and the end of creativity in cooking. This calls into question the culinary arts and the profession of chef and waiter. Do robots in restaurants in China mark the end of conviviality? In any case, they undoubtedly help to bring a little transparency into the production process, from the farm and factory to the consumer’s plate.
Author: Steffi Noël
Want to learn more about AI in China?
Check out our AI in China White Paper.