Open innovation (OI) is the process of integrating external expertise into the innovation processes of a company or organization. The overall purpose of implementing an open innovation strategy is for companies to take advantage of external ideas, resources, and market channels in order to advance their own technology and products. It essentially enhances a firm’s technological capabilities and industry competitiveness by combining the internal and external ideas available to them. Hence, open innovation offers a great way to enhance a firm’s overall performance in the market. The market for this OI business paradigm in China has seen great success over the past years and offers many future opportunities to come. The open innovation market in China has succeeded due to its emphasis on firm openness, the digestion of external knowledge, and on the value created by combining and advancing these two assets.
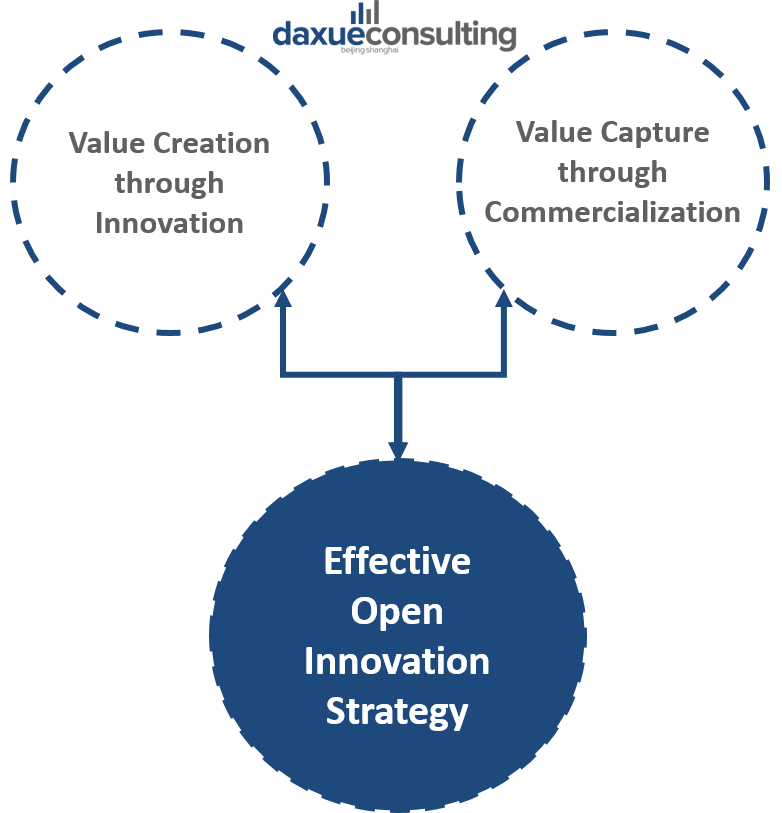
In order to implement an effective open innovation strategy in China, companies must balance value created internally through innovation with the value captured through the commercialization of external sources/assets of knowledge.
Open innovation in China: Initiatives for Chinese economic development
In an effort to open endless frontiers of growth, China has announced many initiatives that display its global aspirations to develop and advance the notion of the innovative economy. In particular, instead of using its massive labor force to replicate goods and manufactured products developed mostly by Western firms like before, the government has implemented a large-scale organic endeavor to bring out the entrepreneurial spirit of China. Specifically, billion-dollar investments from the government and leading tech enterprises, a huge domestic consumption market, and a growing talent base have transformed the Chinese innovation process completely.
In particular, since 2015, the State Council of China has put forward several innovation-centric national strategic initiatives such as the “Internet Plus,” “13th Five-Year Plan,” “Made in China 2025” and the “New Generation of Artificial Intelligence Development Plan.” These initiatives aim to encourage more digital innovations by leveraging the Internet of Things, big data, cloud computing and AI technologies to construct a “Digital China.” Backed by strong government mandates, incentive plans, and billions of dollars in both private and public investment, China has made significant progress in building a solid digital foundation to cement itself as a leader in the global innovation market. It now ranks among the top three worldwide for venture capital investment in key areas such as digital technology, including virtual reality, autonomous vehicles, 3D printing, robotics, and AI. China is also one of the world’s largest e-commerce markets and is already a major global force in mobile payments.
From Gartner Research, as of December 2017, the total number of internet users in China reached 772 million, representing a market penetration rate of 55.8%. Furthermore, the shared economy business, which integrates social resources to serve civilians, was booming in 2017. The number of users of shared bicycles, for example, reached 221 million. In addition, the number of people using mobile payments in China increased to 531 million in 2017, and users’ mobile habits are being further consolidated by the day. This large mobile user base and exponential growth in consumer data generated by the digital market are facilitating a future for even better and more advanced digital innovations. Thus, the integration of innovative digital technologies into various industries has led to the emergence of new markets. From this, we are also witnessing the creation of new products and services that will serve as the impetus driving China’s future economic development and new open innovation strategies.
China’s digitalized economy is the ideal environment for Open Innovation
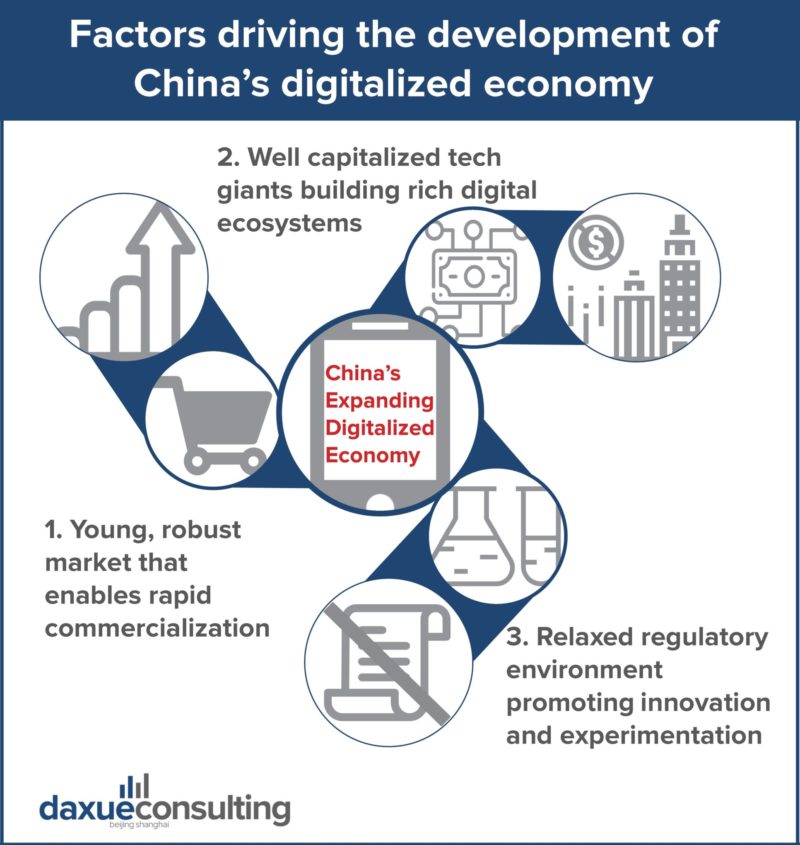
China’s leading factors driving the development of China’s digitalized economy include one, a robust young market that enables rapid commercialization, two, well-capitalized tech giants building rich digital ecosystems, and three, a relaxed regulatory environment promoting innovation and experimentation.
Unlike their U.S. counterparts, Chinese tech infrastructures (software and platform solutions) can be easily tailored to meet a diverse set of client needs. Chinese platforms are also more scalable, open, customizable, and flexible compared to their MNC counterparts. This is where the two sides need to work together, an opportunity for foreign firms to tap into China’s open innovation market. However, it is important to understand that China’s open innovation strategy has largely been successful for Chinese firms due to the advantageous treatment they receive from the government. In addition, they benefit greatly on a policy level simply by being domestic and homegrown. Another factor foreign enterprises must take into consideration regarding their China-based OI initiatives.
Open Innovation Strategy: Riding the wave of China’s Digital Transformation
Digitalization is increasing the interconnectedness of business ecosystems, making it quick and easy to connect everything including organizations, machines, and individuals. This physical and digital interconnectedness is necessary for providing the intelligence needed to manage business complexity. As a result, digital technologies have underpinned and accelerated the importance of business ecosystems for modern and globally adaptive enterprises. A business ecosystem is a dynamic network of entities (people, businesses and things) interacting with one another creating and exchanging value. Business ecosystems offer firms unprecedented access to more business resources and talent on a global scale. This has set the stage for open innovation as enterprises have the ability to improve upon their business models and to provide new services, products, and customer experiences. In order to leverage business ecosystems, organizations will need to shift the entire paradigm of their enterprise model. Replacing the traditional supply-demand economic perspective with a more ecosystem driven perspective that sees the organization as a participant in a wider, more dynamic network of entities.
Therefore, in order to tap into the potential of the innovative Chinese market, or strengthen one’s position, firms must employ these tactics moving forward. The primary OI strategies used by global and Chinese corporates in the Chinese market that have accelerated them to the top of their league are: business ecosystem interactions, academic (knowledge) collaborations, application and platform innovations through 3rd party developers, interacting with users, and collaboration with start-ups.
CONTACT US NOW TO ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ABOUT
1. Open innovation in China through ecosystem interaction – external resource integration
For a growing number of companies, it makes sense to base their entire operations in China in order to commercialize innovations and penetrate the local market. As a result, China becomes the head operational center within the businesses ecosystem, from which companies spread their firm innovations to other emerging markets in Asia and elsewhere in China. This not only benefits the firm geographically in having this proximity to their targeted consumers. But also, is beneficial in terms of having access to specified development zones and technology clusters where they can take advantage of China’s local talent and huge supplier base to accelerate innovation.
In these efforts, organizations are increasingly looking outward on their network and constantly expanding externally within their business ecosystems to drive innovation. To capitalize on these opportunities, CIOs must develop a proactive innovation strategy and select the right mix of business and technology tools to support this strategy. A business ecosystem can drive value as it enables various parties to expose another firm’s capabilities and leverage the capabilities of others to create new services, products, and customer experiences. As organizations can either run power ecosystems or participate in them, these structures and interactions become particularly unique in the digital age. Powerful conglomerates such as Alibaba, Tencent, Baidu, Amazon, Google serve as interesting open innovation examples of this framework.

Here is a diagram of Alibaba’s business ecosystem in China. As seen above, the diagram shows the deeply integrated network of Alibaba’s diverse portfolio containing physical retail, e-commerce, cloud infrastructures, and digital media
An open innovation example of foreign firms taking advantage of China’s vast digital ecosystems can be seen from the recent Starbucks and Alibaba partnership to transform the coffee experience in China. Starbucks indicated that weakness in their China business was due to a change in the delivery environment and that they needed to become more aggressive on delivery by partnering with a third-party vendor. As a result, Starbucks will collaborate across the key businesses within Alibaba’s ecosystem including Ele.me, Hema, Tmall, Taobao, and Alipay to improve their brand. Particularly, they have established “Starbucks Delivery Kitchens” for better delivery order fulfillment. Additionally, they have integrated their presence throughout Alibaba’s multiple platforms in the creation of an unprecedented virtual Starbucks store, providing an unparalleled and even more personalized online Starbucks experience for Chinese customers. This announcement is a great example of implementing open innovation strategies in China as the two iconic, global companies build on their distinct retail and technological strengths to revolutionize the customer experience. Leveraging Alibaba’s ecosystem and ‘New Retail’ infrastructure, Starbucks will be able to provide a unified seamless Starbucks Experience between its store and online presence for customers.


Another company that has implemented a successful open innovation strategy in China vis a vis, external engagement with China’s digital ecosystems is L’Oréal China. L’Oréal China recently announced that it would partner with Tmall’s dedicated research and development arm to create male beauty products specifically for the Chinese market. The partnership aims to catalyze the consumer-to-business (C2B) approach and add a new value chain that better connects consumers, products, and channels. The deal will bring together the China division of L’Oréal and the Tmall Innovation Center (TMIC) to leverage insights from Alibaba’s over 600 million users to help the company tailor its product development and marketing strategies to Chinese consumers. TMIC guides brands through all stages of the production cycle—from discovery to design to development—including market research in China, sales and data analysis and even product testing. Alibaba’s Tmall will assist L’Oreal in providing access to new markets. With Tmall’s unparalleled customer insight, it serves as a great ecosystem partner to help L’Oréal China offer customers its best-in-class personalized product experiences.
As the number-one beauty company in the Chinese market, L’Oréal China will continue to deepen its collaboration with innovative partners locally to unleash the value of data insights and create value for their consumers. In both cases, L’Oréal and Starbucks have successfully engaged with the external ecosystems available to them in order to advance their product and innovate upon their business strategy. By partnering with Alibaba, both companies gained access to a whole new population of digital customers. This ‘New Retail’ strategy of infusing their mortar based operations with an established online presence has allowed them to digitally innovate and outsource a portion of their business while staying focused on their product. They are thus perfect examples of successful open innovation in China using different innovation methods to activate new growth drivers.
2. Open innovation through Inward Ecosystem Interaction
Innovation starts with insight. Typically, companies have formal innovation methods for generating insights such as from market research departments, R&D labs, and product development groups. These departments do market research, survey consumers in China, and run experiments to gather this knowledge. But there are many other insightful sources of innovation, both inside and outside the organization that companies often fail to use. One of those is the use of internal competition and expertise to generate ideas. Specifically, employees can be excellent sources of creativity that can inform future innovation directions due to their intimate understanding of the company and its products and markets.
3. Open innovation through Collaboration – Innovation and research centers in China
Complex problems demand collaborative responses, whether that’s creating an innovative new service or solving a firm-wide issue, no one organization or individual can do it alone. What’s then required is a collaboration among actors with complementary capabilities and assets, along with network proximity to prestigious knowledge hubs. When a business actor reaches out externally, whether to academia or sector-specific research centers to solve an industry problem, this allows the firm to gain exposure to previously closed sources of knowledge, and when utilized in the proper context, bring innovative solutions to the business.
L’Oréal again provides a great example of how product making companies have implemented an open innovation strategy using research centers in China. The company opened a Research and Innovation center in Pudong district, Shanghai to better adapt its global strategy to the specific features of the Chinese market. L’Oréal’s Research Centre is the first facility of its type operated by a cosmetics company equipped with a world-class team of chemists and physicists to advance the understanding of the unique properties of the hair and skin of Chinese consumers. L’Oréal will leverage the valuable knowledge that is obtained from the research that is conducted at the Pudong L’Oréal Research Centre to develop innovative and better performing new hair care, skincare, and cosmetic products for a growing number of Chinese and Asian consumers worldwide.


L’Oréal and Ipsos carried out a study, “Portraits of Chinese Women” to unveil and better understand the beauty rituals of Chinese women. This study portrays L’Oréal’s China customer-centric approach with its research department focusing on the specific aesthetic features of Chinese women.
In addition, with China’s world-class infrastructure, abundant skills and strong support from the government, earlier this summer BMW China announced the opening of its new Research & Development Center in China, Shanghai. The center will be the spearhead of innovation for BMW’s R&D network in China and serve as an incubator for future technologies. The Shanghai R&D Center will focus on autonomous driving, digital services, and futuristic design, and will expand collaboration with leading high-tech companies. With its team of experienced and talented professionals, the Chinese Research and Development Center will bring more and more innovative technologies to Chinese customers.

It comprises four departments focusing on future mobility trends and innovative design: the Technology Office China, Digital Products & Services and Digitalization Customer Interface, a Connected and Automated Driving Lab, and the Designworks Shanghai Studio. It covers over 2,500 m² and features an open and flexible working environment that inspires employees and improves cooperation. The R&D team is made up of over 200 technical specialists and designers. More than 90% are Chinese. They come from diverse scientific backgrounds: big data, robotics, AI, human-machine interface, mechanical engineering, business model development, and economics. All the departments of the Shanghai R&D Centre work with other BMW R&D departments around the world as part of a collaborative effort to transform the BMW Group into a high-tech mobility service company. This endeavor by BMW showcases its superior business strategy in open innovation. By establishing a knowledge network of experts to test and improve their product, they can ensure for a consistent and top quality BMW vehicle customized for the Chinese market to be delivered. Furthermore, by incorporating digital and innovative tech labs for organically driven research, BMW strengthens its overall competitiveness in the market and diversifies its business through the assimilation of external innovations.
Within the automotive industry, in particular, companies operating in China are facing a diverse set of challenges in a complex environment. In order to stay competitive and relevant in their respective markets, companies like BMW have been integrating external innovations with emerging tech into their own business model. A trend is pointing towards the notion that the success of a foreign MNC operating in China depends on its ability to adopt an open innovation strategy.
4. Open innovation through Collaboration – Platforms
This node in the open innovation paradigm reflects the trendy rise of the platform business model. Platform business models have sprung up to leverage opportunities within the business ecosystem. A business-driven framework allows a community of partners, providers, and customers to share and enhance digital processes and capabilities. This framework enables for a different combination of business models, leadership, talent, delivery and IT infrastructures that power digital business ecosystems for open innovation. Thus, the platform simply presents organizations with a practical way to innovate and create new forms of value.
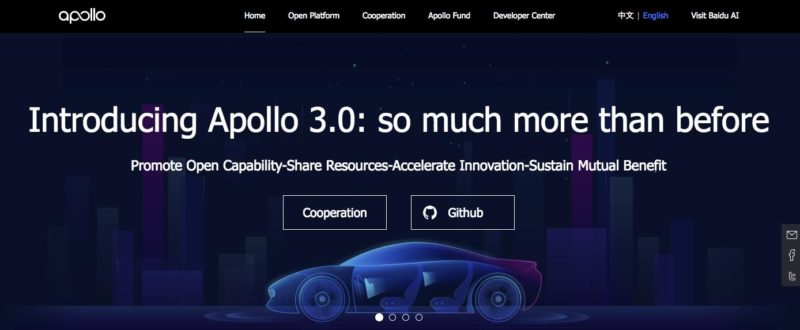
An open innovation example of a Chinese platform that foreign MNCs can take advantage of is Baidu’s Apollo. In April 2017, Baidu announced a one-of-a-kind open platform — Apollo — for autonomous driving solutions, roping in partners from across the globe. As with other open-source platforms, the idea is to accelerate AI and autonomous driving research by opening it up to contributions from other players in the ecosystem. Making the source code available to everyone allows companies to build off of existing research instead of starting from scratch. Apollo delivers an open, complete and reliable software platform for its partners in the automotive and autonomous driving industry. Furthermore, the “Apollo” project offers a complete hardware and software service solution that includes vehicle, hardware and software platforms, as well as cloud data services. Baidu will also open source code and capabilities in obstacle perception, trajectory planning, vehicle control, vehicle operating systems, and other functions which will include a complete set of testing tools. The company will begin by initiating a partnership alliance, working with partners who will provide the best and most compatible vehicles, sensors and other components to achieve broad participation and collaboration. It will also provide references and recommendations to participants of a rapidly expanding ecosystem enabled by Project Apollo. This will be used to lower the entry barriers for research and development of autonomous driving technologies, making it more accessible to the general public and accelerating the overall pace of innovation.
At the CES Asia 2018, BMW China and Baidu announced the signing of an agreement between BMW Connected and Baidu Internet of Vehicles on home-to-vehicle cooperation. The cooperation between BMW Connected and Baidu Internet of Vehicles provides further evidence of BMW’s “In China, for China” Research and Development strategy. BMW has been actively building and integrating China’s digital ecosystem, expanding the implementation of its open innovation cooperation with leading Chinese high-tech companies, and is committed to creating a diversified and smart mobility experience for Chinese consumers. BMW Connected seamlessly integrates vehicles into their users’ digital lives via multiple touchpoints, such as the iPhone and Apple Watch. It is powered by the BMW Open Mobility Cloud, a highly flexible, cloud-based system. With BMW Connected, mobility extends beyond the vehicle. BMW is committed to building a comprehensive mobility ecosystem and providing intelligent, seamless and personalized mobility services for customers.

As a result, foreign companies have the opportunity to partner with Baidu and have access to their open-source platform of higher technologies for vehicles. The Apollo platform ecosystem alliance has reached to over 100 partners, ranging from Original Equipment Manufacturers, Tier1s, core suppliers, travel service providers, emerging companies, hedge funds and investment firms, research institutions, and related governments. Thus, this platform merely serves as a small example of how firms can implement an open innovation strategy in China by engaging with other partners within a general ecosystem of diverse specializations.
5. Open innovation in China through Applications and APIs
Application leaders derive maximum value from new technologies like artificial intelligence, API programs, service-oriented architecture, and the five platforms for digital business: information systems, customer experience, data and analytics, the internet of things, and ecosystems. Therefore, creating APIs that enable ecosystem interactions is important if an enterprise is to benefit from digital business technology platforms and grow into markets that were previously beyond its traditional model of reach.
Applications are important for open innovation enterprises in China because they allow the business to engage in ecosystems that connect them to new partners. For this to be successful, enterprise leaders need to know how to manage APIs as products that their partners and customers wish to use. However, for many Western MNCs delivering business value via applications is dying out as firms struggle to deliver next-generation experiences using innovative application architectures, APIs and machine learning. Hence, application leaders must adopt a product-centric model to maximize the value they deliver on new digital platforms.
APIs are all about empowering users and creating partnerships. APIs have the ability to completely transform your product or an entire business into something much, much better, a platform. By turning your product into a platform (as Apple did to iOS with their app store) you can effectively crowdsource features and innovation from your developer community. There is one main reason why companies build an app ecosystem – to reach a wider audience. Every single app created by your community is another feature that puts you on par with or differentiates you from your competition. Every single feature in your product opens up new and wonderful use cases. Every single use case attracts users that can now use your product to solve their specific problem. Successful companies crowdsource innovation from their community by developing an app ecosystem. It’s an effective way of building a competitive advantage and growing your user base but only if you are ready to commit the resources.


L’Oréal China has begun to promote its huge collection of brands in a high-tech manner through applications with the acquisition of Modiface. Modiface is a beauty tech company that has been teaming up with big cosmetics brands for over a decade to create augmented reality apps for mobile and desktop. Modi faces AR tech powers quite a lengthy list of beauty platforms, including an application where you can digitally try on Estee Lauder’s lipsticks, which you can see in the image below. Furthermore, Modiface also manufactures AR mirrors that superimpose makeup on your face in real time. These technologies are essential because by allowing customers to use AR to try on and test beauty products in the store, it allows for a more immersive and interactive experience that is more customer friendly and preferable to the individual. Thus, it creates value in two ways, firstly, via the commercialization of engaging technologies that enhance customer loyalty and attraction, and secondly, by cutting costs on inventory. For beauty companies, this second facet allows them to now save the products they had previously needed to allocate for testing and sampling.
3rd party Ecosystem: Integrating the App into a platform
For example, a major part of Tencent’s open innovation strategy with WeChat is the development of the app alongside 3rd party internet services and developers. A large portion of WeChat’s success was Tencent’s open innovation strategy in partnering with 3rd party services and developers who were given free reign over Tencent’s platforms and large user base. This helped to develop Tencent’s WeChat into a more user-friendly and service-based app, as opposed to simply being a one-dimensional social media messenger. 3rd party services allowed for external enterprises to use Tencent’s platforms and mini-apps to attract users to their brand and make business transactions for profit. Thus, WeChat’s in-app code allows itself to serve as a hosting platform for other entities. As a result, foreign marketers now have the opportunity to innovate their business by integrating within this open platform and promote their product through social media and advertisement.
6. Open innovation through User interaction
With ever-increasing connectivity, the number and density of connections between people, organizations and things are increasing almost exponentially. All organizations have the ability to connect to a diverse web of customers, partners, and even machines and this can be leveraged for your open innovation strategy in China. Bandwidth and storage are no longer limiting factors. From new insights provided by information and analytics, organizations now have the ability to access, process and analyze vast amounts of information. Analytics gives insights into complexity, revealing new patterns and insights making it possible to create and manage complex business ecosystems. This trend is making information about the organization’s most valuable asset. In accelerating the test, learn, and refine cycle to attain China caliber speeds, companies need to compress the time it takes to turn customer feedback and other data into new features or products.
Furthermore, user interaction allows for a way to engage directly with the Chinese consumer. This relates to the API economy, where business models and channels are based on an exchange of data from the users of the app to an ecosystem of developers. Thus, the internet has provided a way to get instant feedback from consumers everywhere, and Chinese consumers are particularly eager to share their opinions. In online forums and Chinese social media sites, they talk about products they like, share advice, and voice opinions about features, pricing, or policies they dislike. Many Chinese consumer-facing companies have special websites for customers to share their opinions and personalized social media pages where fans can gather and research the product or service. Xiaomi, for example, regularly posts proposed features for smartphone software on an online forum for its fans. Consumers vote for their favorite ideas, and the company adds popular ones to the product development system, sometimes within a week. As a result, Xiaomi has more competitive products and more loyal customers.
7. Open innovation through Startup Collaboration
By working with startups through external digital platforms, Lenovo, for example, has been able to innovate its product line and better meet the needs of its customers. The “Lenovo New Business Development” platform is similar to a startup incubator and allows Lenovo to work with the world’s top start-up teams in exchange for access to Lenovo’s software, hardware development, market, channel, and other services in exchange for startup equity. The NBD has allowed the company to openly innovate its products with the help of startups who are focused on unique and innovative strategies in China. In addition, by adding specialized industry expertise in fields that the company has no previous experience in.
Chinese OI Technologies Forecasted to Disrupt the Industry
Given strong economic growth along with government mandates and incentive plans in digital innovation, enterprises in China now more than ever have the opportunity to digitally disrupt their industries. The exponential growth in recent years in the number of mobile users and online shopping has facilitated innovations in digital marketing that better digest customer behaviors and improve customer service. Also, the next wave of emerging technologies driven by AI has provided businesses with the potential to expand and enhance their products and services. The Chinese government has nominated AI as a major national economic strategy for the next decade. It has become an important driving force in the modern day technological revolution and industrial transformation that will profoundly change the means of human production and ways of life. Thus, businesses looking to capture the Chinese open innovation market must accelerate the adoption of new technologies, including BI and analytics, AI and cloud computing. Furthermore, they must increase their innovative, driven investments in order to be in the best position to capture the digital business opportunities of China’s tomorrow.
The Challenges in Establishing Open Innovation Initiatives in China
Despite the inconveniences due to China’s cybersecurity and data sharing related laws, along with concerns about a market being less welcoming to foreign companies, foreign companies operating in China nevertheless still plan to continue their businesses and increase their investments in China. From the AmCham China 2018 Business Climate Survey, investment in Research and Development in China rose 3%, with 32% of companies increasing investment. Although China has been actively encouraging foreign companies to establish R&D bases in the country, most companies still emphasize ‘development,’ and not the research part of Research and Development. Also noted in the survey, more companies in certain industries are upgrading their digital capabilities in order to overcome increasing market competition and rising operational costs. In particular, technology hardware, software, and services (79%) and automotive (70%) reported the most ambitious plans for Research and Development in China increased investment.
As China embarks on the path of restructuring its economy from manufacturing to knowledge-driven, export to domestic consumption driven, and from low-cost low-quality to higher-cost higher-quality, there will be more and more innovations that will attract greater interest from abroad. Presently, there are boundless opportunities for foreign companies with advanced technologies and products to enter the Chinese market. At the same time, however, the accelerating pace of digitalization has made it increasingly difficult for foreign firms to respond to and take advantage of the disruptive technologies needed such as artificial intelligence, IoT, cloud computing, automated manufacturing, and logistics, and blockchain enabled supply chains.
Furthermore, companies in China are facing challenges in adjusting to rapidly-changing markets, competing with local counterparts, recruiting and retaining high-quality talent, evolving their business models and supply chains, developing effective Research and Development functions locally and partnering with smaller local businesses. Thus, the need for more in-depth market insight and continued reforms regarding partnerships, fair treatment, and collaboration around technology for OI in China is greater than ever before.
Daxue Consulting has robust experience with open innovation in China
Daxue Consulting’s unique expertise in Chinese market research and niche insight into China’s technological revolution has afforded the ability to successfully assist clients in establishing open innovation initiatives. In the endeavor to implement an OI initiative, Daxue Consulting can produce an optimized research structure to understand the innovation within a particular industry in China. Our broad market oversight allows us to scout for specific innovations that can make your business more competitive and technologically up to date. Furthermore, being agile in market analysis, our service provides clients with a bespoke landscape roadmap that helps them navigate the complexity of their initiatives.
In particular, Daxue Consulting’s insightful knowledge of the current market situation combined with the ability to assess an industry’s level of maturity allows us to better advise enterprises on how to position themselves in China. Working on the ground in China gives an intimate understanding of where China’s geographical networks of innovation and alliances of guanxi are located is crucial to the success of your OI endeavor.
Daxue Consulting offers a strategic advisory for businesses at the micro level. Following initial research, we screen the industry for competition and potential startup collaborations. This process allows us to most effectively engage the traditional OI strategy of providing a touch point for business to interact with innovative ecosystems and partner with local startups. Our holistic offering affords us with a proper framework to break down the value chain and provide businesses with the ability to capture innovations they need and integrate them into their model.
Author: Jeffrey Craig
If you want to know more about Open Innovation strategy in China and innovation methods in China, do not hesitate to contact us at dx@daxueconsulting.com




